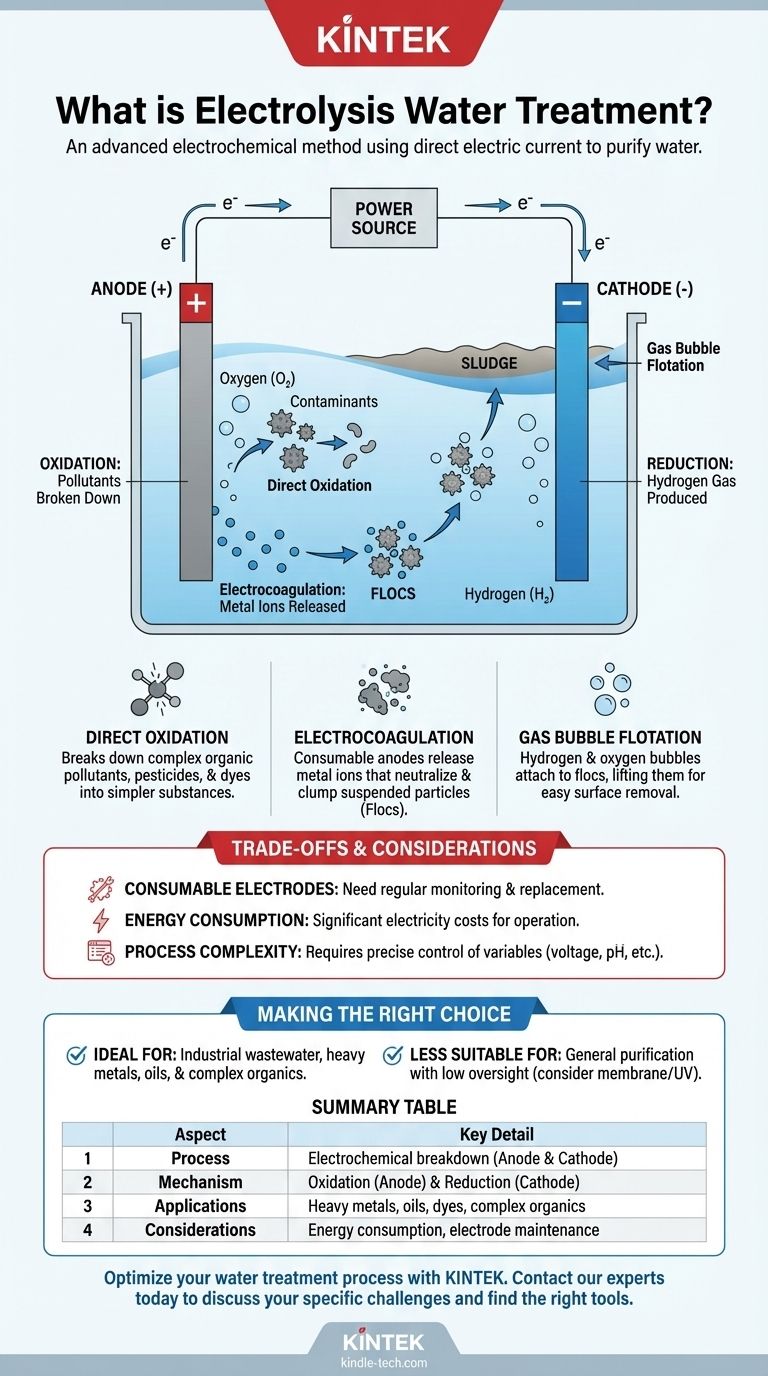
At its core, electrolysis for water treatment is an advanced electrochemical method that uses a direct electric current to initiate chemical reactions and purify water. This process involves passing electricity through electrodes submerged in the water, which forces compounds and contaminants to break down and separate at a molecular level. It is a powerful technique for handling complex wastewater challenges.
The fundamental principle of electrolysis is not about physically filtering water, but about fundamentally altering its chemical composition. By introducing an electrical current, you force non-spontaneous chemical reactions to occur, effectively dismantling pollutants that other methods cannot easily remove.

How the Electrochemical Process Works
To grasp how electrolysis treats water, you must first understand the basic components and reactions involved. The system is driven by an external power source that creates a powerful environment for chemical change.
The Role of Electricity and Electrodes
The process begins when an external voltage is applied to two electrodes—a positively charged anode and a negatively charged cathode—that are placed in the water. These electrodes are often made from "consumable" materials like iron or aluminum, which actively participate in the treatment process by supplying ions into the water.
The Reaction at the Cathode (Reduction)
The negatively charged cathode attracts positively charged ions (cations) from the water, such as hydrogen ions (H+). At the cathode's surface, these ions gain electrons in a process called reduction. This reaction produces pure hydrogen gas (H₂), which bubbles to the surface.
The Reaction at the Anode (Oxidation)
Simultaneously, the positively charged anode attracts negatively charged ions (anions), such as hydroxide ions (OH-). Here, the ions give up their electrons in a process called oxidation. This reaction primarily produces oxygen gas (O₂) and is also where many pollutants are broken down.
The Primary Goal: Contaminant Removal
While the electrolysis of pure water simply produces hydrogen and oxygen, its application in wastewater treatment is far more sophisticated. The reactions are designed to attack and remove a wide range of contaminants.
Direct Oxidation of Pollutants
The powerful oxidizing environment created at the anode can directly break down complex organic pollutants, pesticides, and dyes. This process effectively shatters their molecular structure, converting them into simpler, less harmful substances like carbon dioxide and water.
Electrocoagulation
When consumable electrodes (like iron or aluminum) are used, the anode releases metal ions into the water. These ions act as powerful coagulants, neutralizing the charge of suspended particles and causing them to clump together into larger masses called "flocs," which are much easier to remove.
Gas Bubble Flotation
The hydrogen and oxygen gas bubbles produced at the electrodes attach to the newly formed flocs. This increases their buoyancy, causing them to float to the surface where they can be easily skimmed off as sludge.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Electrolysis is a powerful technology, but it is not a universal solution. Understanding its operational demands is critical for successful implementation.
Consumable Electrodes
As the name implies, consumable electrodes are sacrificed during the process. They corrode and dissolve over time, meaning they must be monitored and replaced periodically. This introduces a recurring maintenance requirement and material cost.
Energy Consumption
The entire process is driven by electricity. The "external voltage" required translates directly into energy costs, which can be significant, especially for large-scale treatment operations. System efficiency is a key factor in its economic viability.
Process Complexity
Effective electrolysis requires precise control over multiple variables. Factors like voltage, current density, the water's pH level, and electrode material must be carefully managed to optimize contaminant removal and prevent unwanted byproducts. It is a technically demanding process, not a simple "plug-and-play" system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing the right water treatment method depends entirely on the specific contaminants and your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is treating industrial wastewater with heavy metals, oils, or complex organic compounds: Electrolysis is a uniquely powerful solution that can break down contaminants other systems can't handle.
- If your primary focus is general water purification with low operational oversight: The energy requirements and need for electrode replacement may make simpler methods like membrane filtration or UV treatment more suitable.
- If your primary focus is a high-purity result with minimal chemical additives: Electrolysis offers an advantage by using electricity and the electrodes themselves as the primary treatment agents, reducing the need for adding bulk chemicals.
Ultimately, understanding the electrochemical principles behind electrolysis empowers you to determine if its powerful, but demanding, nature is the right fit for your specific water treatment challenge.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Electrochemical breakdown using an anode and cathode. |
| Primary Mechanism | Oxidation at the anode and reduction at the cathode. |
| Key Applications | Removing heavy metals, oils, dyes, and complex organics. |
| Main Considerations | Energy consumption and consumable electrode maintenance. |
Optimize your water treatment process with KINTEK.
Electrolysis is a powerful but technically demanding solution. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise control and effective implementation of electrochemical water treatment methods.
Whether you are researching electrode materials or scaling up a treatment system, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for success.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific water purification challenges and discover how KINTEK can support your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double-Layer Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Optical Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Iridium Dioxide IrO2 for Water Electrolysis
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is a three-electrode electrochemical cell system necessary for Ni-Cr alloy corrosion kinetics? Expert Analysis
- Why is a high-precision pressure controller necessary for ODC? Master the Three-Phase Interface for Reliable Data
- What components of an all-PTFE electrolytic cell require regular inspection for maintenance? Ensure Long-Term Reliability
- What role do zirconia porous ceramics play in a supercritical fluid electrochemical cell? Ensure Data Integrity.
- What precautions should be taken when handling and using an all-quartz electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe, Accurate, and Durable Performance
- Why use a three-electrode cell for ionic liquid corrosion testing? Ensure Peak Accuracy in Acidic Media
- What is the functional design of a laboratory three-electrode electrolytic cell? Precision for Titanium Alloys
- What are the guidelines for sterilizing the electrolytic cell? Ensure Sterile, Damage-Free Lab Results



















