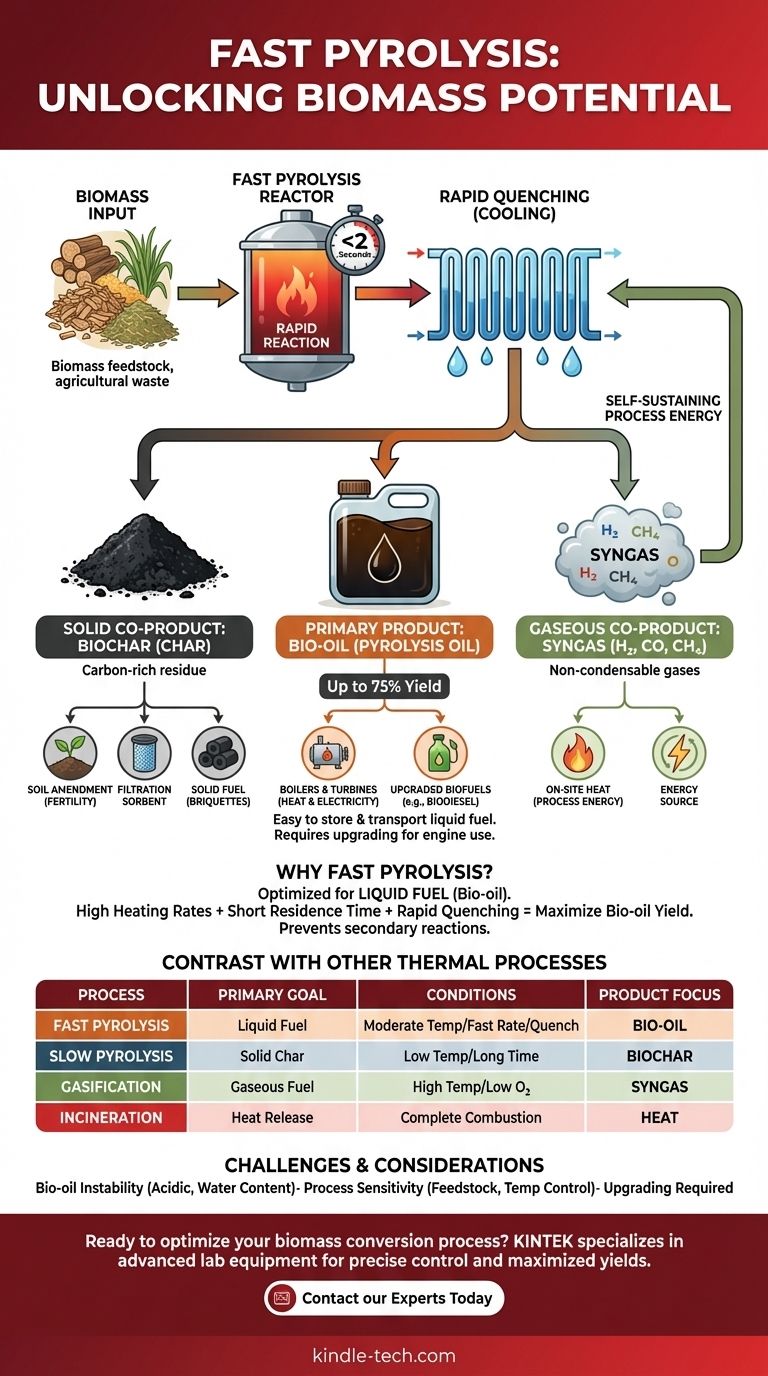
The primary end product of fast pyrolysis is a dark, viscous liquid known as bio-oil (or pyrolysis oil). While the process is specifically optimized to maximize this liquid fuel, it also creates two important co-products: a solid carbon material called biochar and a mixture of non-condensable gases called syngas.
Fast pyrolysis is not about creating a single product, but a specific ratio of products. It is a rapid thermal decomposition process engineered to convert biomass primarily into a liquid fuel (bio-oil) by quickly heating the material and then rapidly cooling the resulting vapors to prevent further reactions.

Deconstructing the Products of Fast Pyrolysis
Fast pyrolysis breaks down biomass in an oxygen-free environment. The specific conditions—high heat and extremely short reaction times—are designed to favor the creation of condensable vapors, which form the liquid product.
The Primary Product: Bio-Oil
Bio-oil is the main goal of fast pyrolysis, often constituting up to 75% of the product yield by weight, depending on the feedstock. It is a complex mixture of oxygenated organic compounds.
This liquid form offers a significant advantage over raw biomass or gaseous products because it is much easier and cheaper to store and transport. Bio-oil can be used as a fuel for boilers and turbines to generate heat and electricity or upgraded into higher-quality fuels like biodiesel.
The Solid Co-Product: Biochar
Biochar (sometimes called coke or charcoal) is the solid, carbon-rich residue left behind after the volatile components of the biomass have vaporized.
While produced in smaller quantities than bio-oil during fast pyrolysis, biochar is a valuable material. It can be used as a soil amendment in agriculture to improve fertility, as a sorbent for filtration, or pressed into briquettes to be used as a solid fuel.
The Gaseous Co-Product: Syngas
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is the stream of non-condensable gases produced during the process. It includes flammable components like hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide.
This gas stream is rarely wasted. In a well-designed system, the syngas is captured and combusted on-site to provide the heat required for the pyrolysis reactor, making the entire process more energy-efficient and potentially self-sustaining.
Why Fast Pyrolysis Prioritizes Liquid Fuel
The distinction between different pyrolysis methods lies in their operating conditions, which are tuned to favor one type of product over another.
The Role of Speed and Temperature
Fast pyrolysis uses moderate temperatures (around 500°C) and extremely high heating rates. This "flashes" the biomass, cracking its complex polymers into smaller, vaporized molecules. The vapor residence time is kept very short—typically less than two seconds.
This brief window is long enough to break down the biomass but too short for the vapors to undergo secondary reactions that would either create more gas or re-polymerize into solid char.
The Critical "Quench" Step
Immediately after leaving the reactor, these hot vapors are rapidly cooled, or "quenched." This sudden temperature drop forces the condensable vapors to liquefy, forming bio-oil before they have a chance to break down further. This quenching step is the key to maximizing the liquid yield.
Contrast with Other Thermal Processes
Understanding what fast pyrolysis is not clarifies its purpose.
- Slow Pyrolysis: Uses lower temperatures and much longer reaction times (hours). This process is designed to maximize the yield of the solid product, biochar.
- Gasification: Uses higher temperatures and a small amount of oxygen. This process is optimized to convert the majority of the biomass into syngas.
- Incineration: Is the complete combustion of material with ample oxygen. Its only goal is to release heat for power generation, not to create fuel products.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, fast pyrolysis is not without its challenges. The process and its products have inherent limitations that must be managed for successful application.
Bio-Oil Quality and Stability
Raw bio-oil is acidic, corrosive, and contains a significant amount of water and oxygen, making it thermally unstable. It is not a "drop-in" replacement for petroleum fuels and often requires further processing (upgrading) to remove oxygen and improve its properties before it can be used in conventional engines or refineries.
Process Sensitivity
The final product yields are highly sensitive to the feedstock and process conditions. Factors like feedstock moisture content, particle size, and precise temperature control can dramatically alter the balance between bio-oil, biochar, and syngas. This requires a high degree of process control to maintain consistent output.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" thermal conversion technology is entirely dependent on the desired end product. You must align the process with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is liquid biofuel production: Fast pyrolysis is the correct choice, as its rapid heating and quenching are engineered to maximize bio-oil yield.
- If your primary focus is a solid carbon product for agriculture or fuel: Slow pyrolysis is a more suitable process for maximizing the output of high-quality biochar.
- If your primary focus is generating a flammable gas for power or chemical synthesis: Gasification is the most direct and efficient method to convert biomass into syngas.
Ultimately, choosing the right technology begins with clearly defining which product stream holds the most value for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Typical Yield | Key Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bio-Oil (Primary) | Dark, viscous liquid; complex mix of oxygenated compounds. | Up to 75% | Fuel for boilers/turbines; can be upgraded to biodiesel. |
| Biochar (Co-Product) | Solid, carbon-rich residue. | Varies | Soil amendment, filtration sorbent, solid fuel. |
| Syngas (Co-Product) | Non-condensable gases (e.g., H₂, CO, CH₄). | Varies | On-site heat for reactor; energy source. |
Ready to optimize your biomass conversion process? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're scaling up bio-oil production or analyzing biochar properties, our solutions help you achieve precise control and maximize yields. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your renewable energy goals with reliable, high-performance laboratory equipment and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















