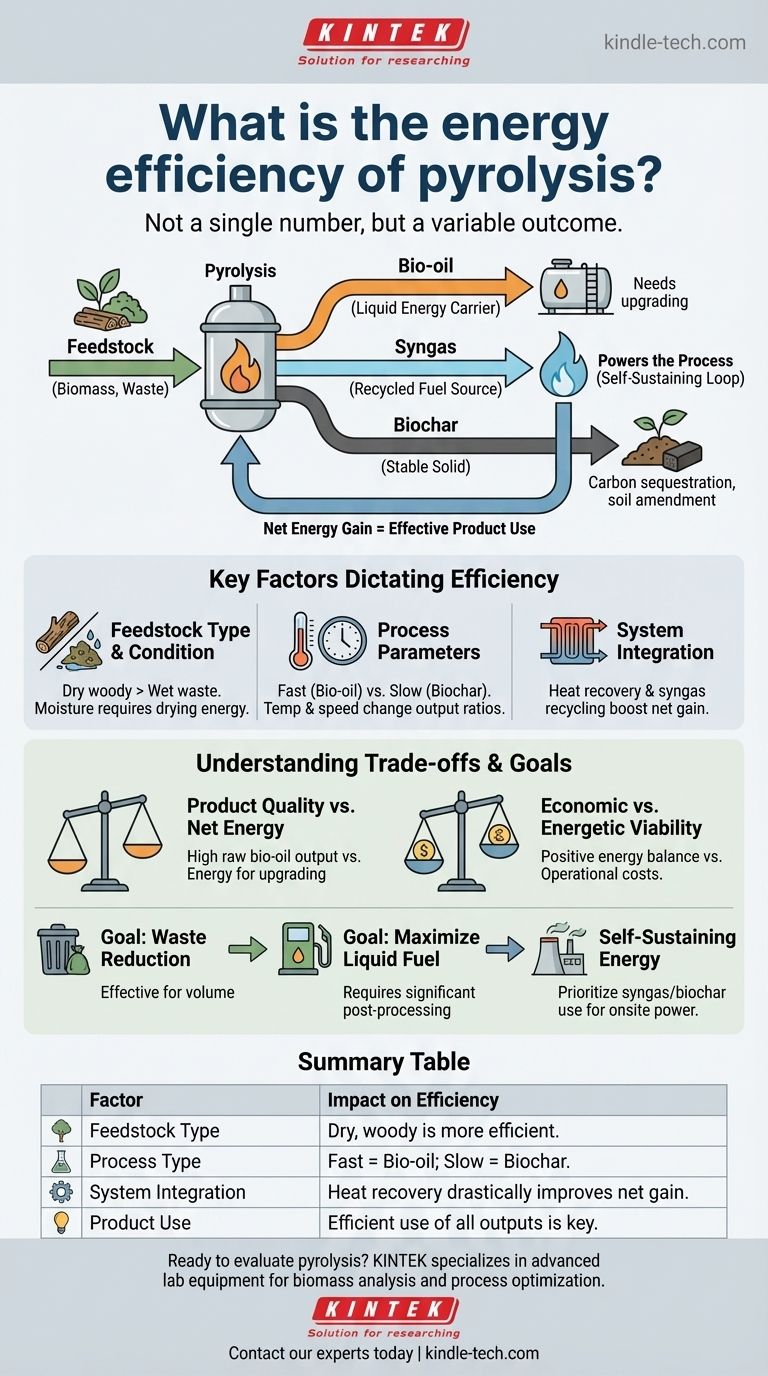
The energy efficiency of pyrolysis is not a single, fixed number. Instead, it is a variable outcome that depends heavily on the feedstock, the specific technology used, and how the energy outputs are measured and utilized. While the process is generally energy-positive—meaning it generates more energy than it consumes—its net efficiency is determined by whether you can effectively use all of its products: bio-oil, syngas, and biochar.
The true measure of pyrolysis efficiency is not found in a single percentage, but in the system's ability to be self-sustaining. A well-designed pyrolysis unit uses the gaseous fuel (syngas) it produces to power the entire process, making its primary outputs of bio-oil and biochar a net energy gain.

Deconstructing the Energy Output
Pyrolysis breaks down organic material in the absence of oxygen, creating multiple energy-containing products. The overall efficiency is the sum of how you use these parts.
Bio-oil: The Liquid Energy Carrier
Bio-oil is a dense liquid often seen as the primary "fuel" output. It can be stored and transported, making it a flexible energy product.
However, its high oxygen content makes it corrosive, unstable, and immiscible with conventional fossil fuels. It cannot be used as a drop-in transportation fuel without significant, energy-intensive upgrading.
Syngas: The Recycled Fuel Source
Pyrolysis also produces a non-condensable synthetic gas, or syngas. This is a mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and methane.
In most modern pyrolysis systems, this syngas is immediately looped back and burned to provide the heat required to sustain the reaction. This internal recycling is the key to making the process self-sufficient and energetically efficient.
Biochar: The Stable Solid
Biochar is the solid carbon-rich material left over after the process. While sometimes viewed as a simple byproduct, it is a stable form of sequestered carbon.
Biochar can be burned as a solid fuel, similar to charcoal, or used as a valuable soil amendment that improves water retention and nutrient availability. Its use directly contributes to the system's overall resource efficiency.
Key Factors That Dictate Overall Efficiency
There is no universal efficiency rating for pyrolysis because it is a dynamic process. Several factors dramatically alter the energy balance.
Feedstock Type and Condition
The material being processed is the single biggest variable. Dry, woody biomass will yield a different energy balance than wet organic waste or scrap plastic.
High moisture content in the feedstock requires a significant upfront energy investment for drying, which can drastically lower the net energy gain of the entire system.
Process Parameters (Temperature & Speed)
The conditions inside the reactor change the output ratios.
- Fast Pyrolysis: High temperatures and short residence times favor the production of bio-oil (up to 75% yield by weight).
- Slow Pyrolysis: Lower temperatures and longer times favor the production of biochar (up to 35% yield by weight).
The choice between these methods depends entirely on which output product you value most.
System Integration and Heat Recovery
Isolated efficiency numbers are misleading. The most efficient systems are those that intelligently manage heat.
This involves using the hot syngas to pre-dry incoming feedstock or capturing waste heat from the reactor to generate electricity or provide heat for other nearby industrial processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
An objective evaluation requires acknowledging the inherent challenges and complexities of the process.
Product Quality vs. Net Energy
Producing a large quantity of raw bio-oil may seem efficient, but this oil requires substantial energy input for hydrotreating and other upgrading processes to become a stable, usable fuel.
Therefore, a system with a high gross output of low-quality oil may have a lower net energy efficiency than a system optimized for a different purpose, such as on-site heat and power generation.
Economic vs. Energetic Viability
A process can be energy-positive but not economically viable. The cost of collecting and preparing feedstock, capital equipment, and product upgrading can outweigh the value of the energy produced.
True viability sits at the intersection of positive energy balance, market value for the outputs, and operational costs.
How to Evaluate Pyrolysis for Your Goal
To determine if pyrolysis is the right solution, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Pyrolysis is extremely effective, converting bulky, low-density waste into dense, more valuable, and more easily managed products.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid fuel: Be prepared to invest in a system that includes the significant post-processing and upgrading steps required to refine raw bio-oil, and factor this energy cost into your net efficiency calculations.
- If your primary focus is self-sustaining energy generation: Prioritize a system designed to burn its own syngas and/or biochar to produce consistent heat and power for a local facility, which is often the most direct path to a high net energy gain.
Ultimately, evaluating pyrolysis requires you to look beyond a single output and analyze the efficiency of the entire, integrated system.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Feedstock Type | Dry, woody biomass is more efficient than wet waste. |
| Process Type | Fast pyrolysis maximizes bio-oil; slow pyrolysis maximizes biochar. |
| System Integration | Heat recovery and syngas recycling drastically improve net gain. |
| Product Use | Efficient use of all outputs (oil, gas, char) is key to high efficiency. |
Ready to evaluate pyrolysis for your specific waste or energy goals? The true efficiency of a pyrolysis system depends on expert design and integration. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory equipment for analyzing biomass and optimizing thermal processes. Our solutions help you accurately characterize your feedstock and model the energy balance for your unique application. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your pyrolysis R&D and help you achieve a truly efficient, self-sustaining system.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products



















