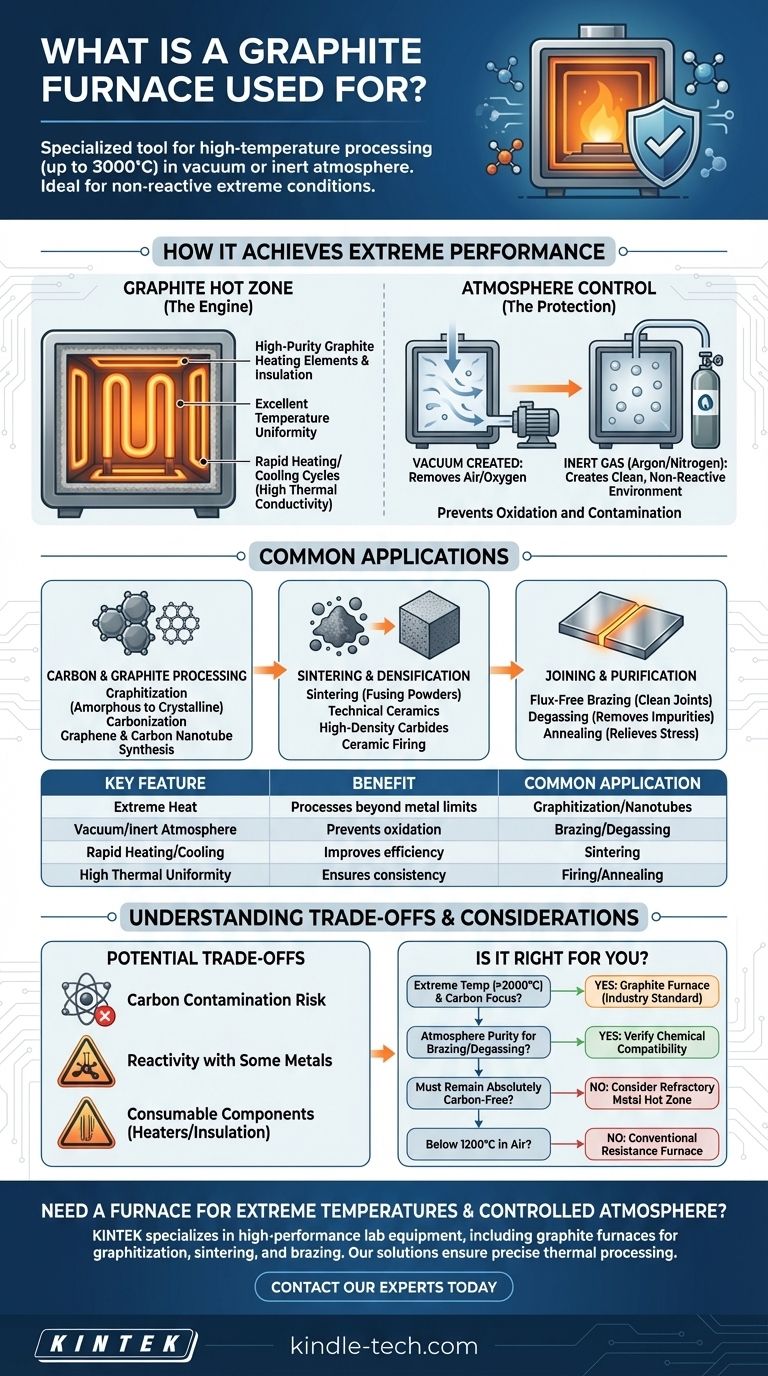
At its core, a graphite furnace is a specialized tool used for the high-temperature processing of materials within a highly controlled environment. It is primarily chosen for applications demanding extreme heat, often up to 3000°C, in a vacuum or a protective, non-reactive atmosphere. Common processes include graphitization, sintering, ceramic firing, carbonization, brazing, and degassing.
The defining capability of a graphite furnace is its ability to achieve temperatures far beyond the limits of conventional metal-based furnaces while simultaneously protecting the material from oxygen and other atmospheric contaminants. It is the solution for thermal processing in extreme, non-reactive conditions.

How a Graphite Furnace Achieves Extreme Performance
A graphite furnace's unique capabilities stem from its core design, which revolves around using graphite as the primary material for the "hot zone"—the area where the heating occurs.
The Graphite Hot Zone: The Engine of High Heat
The heating elements, power connections, and insulation shields inside the furnace are all constructed from high-purity graphite. Unlike metal heating elements (like molybdenum or tungsten) that have lower melting points or become brittle, graphite can withstand temperatures up to 3000°C in a non-oxidizing environment.
This all-graphite construction ensures excellent temperature uniformity and enables rapid heating and cooling cycles, as graphite has high thermal conductivity and low thermal mass.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
Heating materials to thousands of degrees in open air would cause immediate and catastrophic oxidation (burning). A graphite furnace prevents this by first evacuating the air from its chamber to create a vacuum.
Once the air is removed, the chamber can be backfilled with a protective, inert gas like argon or nitrogen. This creates a clean, stable environment, ensuring the material is transformed only by heat, not by reacting with its surroundings.
A Breakdown of Common Applications
The combination of extreme heat and atmosphere control makes the graphite furnace indispensable across several industries, particularly in materials science and advanced manufacturing.
Carbon and Graphite Processing
This is a primary use case. Processes like graphitization (converting amorphous carbon into a crystalline graphite structure) and carbonization (creating carbon by heating organic material) require the exact conditions a graphite furnace provides.
It is also central to the synthesis of advanced carbon materials like graphene and carbon nanotubes.
Sintering and Densification
Sintering is the process of using heat to fuse powders into a solid mass without melting them. A graphite furnace is used for high-temperature sintering of technical ceramics, carbides, and other advanced materials to achieve high density and strength.
Ceramic firing at very high temperatures to achieve specific crystalline structures is another key application.
Joining and Purification
Brazing is a process that joins metals using a filler metal. In a vacuum or inert atmosphere, a graphite furnace allows for exceptionally clean, strong joints on high-performance alloys without the use of flux, which can be a source of contamination.
Degassing uses heat in a vacuum to remove trapped gases (like oxygen and hydrogen) from metals and other materials, dramatically improving their purity and mechanical properties. Annealing is also performed to relieve internal stresses and refine a material's microstructure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a graphite furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper application.
Potential for Carbon Contamination
Because the entire hot zone is made of carbon, there is a risk that the material being processed (the "workload") can become contaminated with carbon, especially at very high temperatures. This is a critical consideration for applications where even trace amounts of carbon are unacceptable.
Reactivity with Certain Materials
Graphite is not completely inert. At high temperatures, it can react with certain metals to form carbides. This can damage both the furnace components and the workload if the materials are not compatible.
Consumable Components
The graphite heating elements and insulation packs are considered consumables. Over time and many high-temperature cycles, they slowly sublimate (turn from a solid to a gas) and must be replaced. This represents an ongoing operational cost.
Is a Graphite Furnace Right for Your Application?
Choosing the right furnace technology depends entirely on your material, temperature, and atmospheric requirements.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature (> 2000°C) for carbon-based materials: A graphite furnace is the industry standard and often the only practical choice.
- If your primary focus is atmosphere purity for brazing or degassing sensitive metals: A graphite furnace provides an exceptionally clean environment, but you must verify its chemical compatibility with your alloy.
- If your primary focus is processing materials that must remain absolutely carbon-free: You should consider an alternative, such as a furnace with a refractory metal hot zone (made of tungsten or molybdenum).
- If your process operates below 1200°C in air: A conventional resistance furnace is a more cost-effective and appropriate tool.
Ultimately, selecting a graphite furnace is a decision to prioritize exceptionally high temperature and atmospheric control above all else.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Heat (up to 3000°C) | Processes materials beyond metal furnace limits | Graphitization, Carbon Nanotube Synthesis |
| Vacuum/Inert Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation and contamination | High-Purity Brazing, Degassing |
| Rapid Heating/Cooling | Improves process efficiency and throughput | Sintering of Ceramics and Carbides |
| High Thermal Uniformity | Ensures consistent material properties | Ceramic Firing, Annealing |
Need a furnace for extreme temperatures and a controlled atmosphere? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including graphite furnaces designed for graphitization, sintering, and brazing. Our solutions ensure precise thermal processing for materials science and advanced manufacturing. Contact our experts today to discuss how a graphite furnace can meet your specific high-temperature application requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- Is a graphite melting point high or low? Discover Its Extreme Thermal Resilience
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures
- What are the properties of graphite at high temperatures? Unlock Its Strength and Stability in Extreme Heat
- What is the thermal coefficient of graphite? Unlock Its Unique Thermal Stability



















