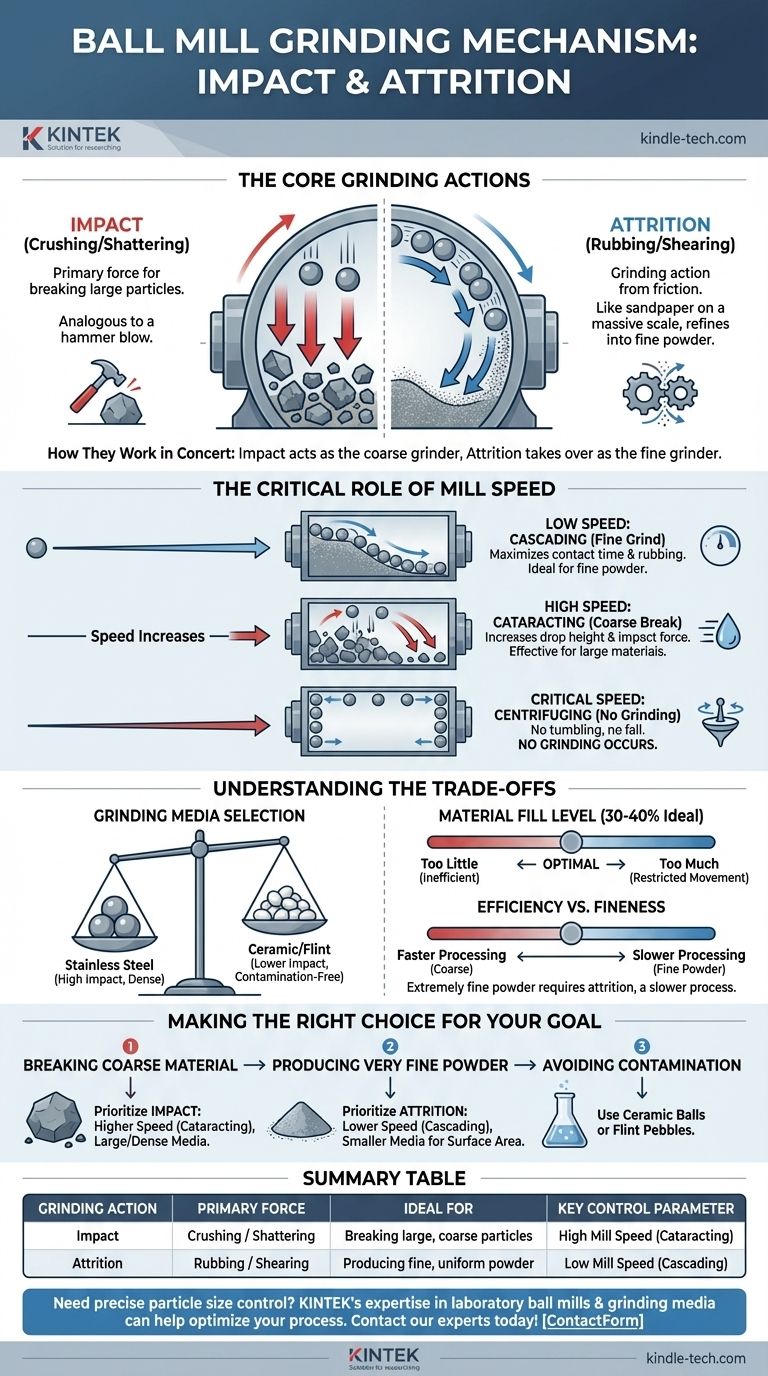
At its core, a ball mill grinds material through two primary actions: impact and attrition. Inside a rotating cylindrical shell, grinding media (typically steel or ceramic balls) are lifted up the side of the shell before cascading and tumbling back down. This motion crushes and grinds the raw material caught between the balls and between the balls and the cylinder wall, progressively reducing it to a fine powder.
The effectiveness of a ball mill is not simply about brute force. It is a controlled process where the rotational speed determines the balance between powerful impacts that break large particles and constant rubbing (attrition) that refines them into a powder.
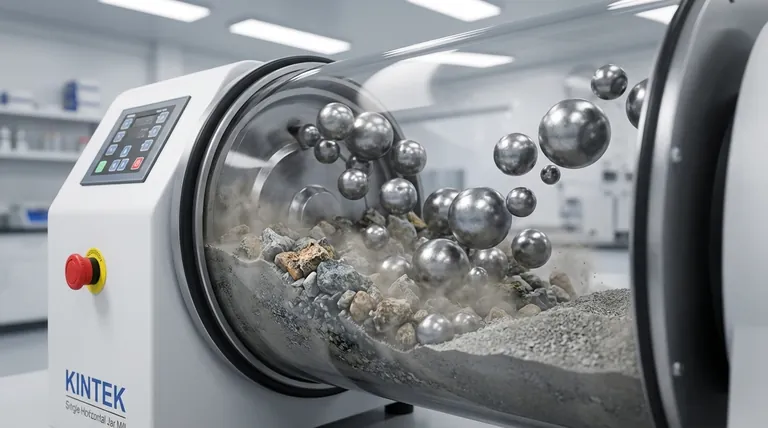

The Core Grinding Actions: Impact and Attrition
A ball mill's ability to reduce material size relies on the interplay of two distinct physical forces. Understanding both is key to controlling the final particle size.
The Principle of Impact
Impact is the primary force responsible for breaking down larger particles. As the mill rotates, it lifts the grinding balls. At a certain height, gravity overcomes the forces holding them to the cylinder wall, and the balls drop.
This free-fall motion causes them to crash down onto the material below with significant force. This action is analogous to a hammer blow, shattering brittle materials and breaking down coarse feed into smaller pieces.
The Principle of Attrition
Attrition is the grinding action that comes from friction. As the balls tumble over one another and slide against the inner surface of the mill, they create immense shearing and rubbing forces.
This constant rubbing wears down the particles, especially those already broken by impact. Think of it as using sandpaper on a massive scale. Attrition is the key action for producing a very fine, uniform powder.
How They Work in Concert
Impact and attrition are not mutually exclusive; they happen simultaneously to different degrees. Impact acts as the coarse grinder, breaking down large chunks. Attrition then takes over as the fine grinder, refining those smaller pieces into the final desired powder.
The combination of these two forces is what makes the ball mill an incredibly versatile and effective tool for a wide range of materials.
The Critical Role of Mill Speed
The balance between impact and attrition is directly controlled by the rotational speed of the mill. This is the most critical operational parameter.
Low Speed: Cascading Motion
At lower speeds, the balls are not lifted very high. They gently tumble over each other in a motion called cascading.
This motion maximizes the contact time and rubbing action between the balls. Therefore, a cascading state prioritizes attrition, which is ideal for achieving a very fine grind when starting with already small particles.
High Speed: Cataracting Motion
As the speed increases, the balls are carried higher up the side of the mill before they fall. This is known as cataracting.
This greater drop height significantly increases the force of impact, making it highly effective for quickly breaking down larger, harder feed materials.
Critical Speed: Centrifuging
There is an upper limit. If the mill spins too fast, it will reach a "critical speed" where centrifugal force pins the balls to the inner wall of the cylinder.
In this state, there is no tumbling and no fall. The balls simply rotate with the shell, and no grinding occurs. This highlights that faster is not always better; control is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a ball mill requires balancing several competing factors to achieve your specific goal efficiently.
Grinding Media Selection
The material, size, and density of the grinding balls are crucial.
- Stainless steel balls are dense and provide high impact force, making them ideal for hard materials and rapid size reduction.
- Ceramic balls are less dense and are used when product contamination from metal is a concern.
- Flint pebbles are a natural, lower-cost option but are less efficient than manufactured media.
Material Fill Level
Ball mills are typically operated with a ball charge filling about 30% to 40% of the mill's volume.
- Too little media results in inefficient grinding, as there are not enough impact and attrition events.
- Too much media restricts the movement of the balls, reducing their drop height and diminishing the force of impact.
Efficiency vs. Fineness
There is a direct trade-off between processing time and the fineness of the final product. Achieving an extremely fine powder requires prioritizing attrition, which is a slower, more energy-intensive process than impact-driven grinding.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your desired outcome dictates how you should operate the mill.
- If your primary focus is breaking down coarse material: Prioritize impact by using a higher rotational speed (cataracting) and larger, high-density media like steel balls.
- If your primary focus is producing a very fine powder: Prioritize attrition by using a lower rotational speed (cascading) and smaller grinding media to increase the total surface area for rubbing.
- If your primary focus is avoiding product contamination: Use ceramic balls or flint pebbles as your grinding media instead of steel.
By mastering the relationship between speed, media, and the forces of impact and attrition, you gain precise control over the final particle characteristics.
Summary Table:
| Grinding Action | Primary Force | Ideal For | Key Control Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact | Crushing / Shattering | Breaking large, coarse particles | High Mill Speed (Cataracting) |
| Attrition | Rubbing / Shearing | Producing fine, uniform powder | Low Mill Speed (Cascading) |
Need precise particle size control for your materials? KINTEK's expertise in laboratory ball mills and grinding media can help you optimize your process for efficiency and fineness. Whether you require high-impact force for coarse materials or fine attrition for powders, we have the equipment and consumables to meet your lab's specific needs. Contact our experts today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What function do high-hardness tool steel grinding jars and balls serve in mechanical alloying? Master Kinetic Transfer
- What is the maximum speed of a ball mill? Find the Optimal Speed for Efficient Grinding
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a colloidal mill? Choose the Right Mill for Your Process
- What are the principles of a ball mill? Master Impact & Attrition for Perfect Particle Size
- How do laboratory pulverizers contribute to finished Ag/Ce-Mn catalysts? Maximize Surface Area and Catalytic Activity
- What is the ball mill method of mixing? Achieve Precise Particle Size Reduction
- Why are different types of grinding systems selected for biomass? Optimize Particle Size for Maximum Reactivity
- What is the principle of colloidal mill in pharmaceutical engineering? Achieve Stable Emulsions & Homogeneous Suspensions



















