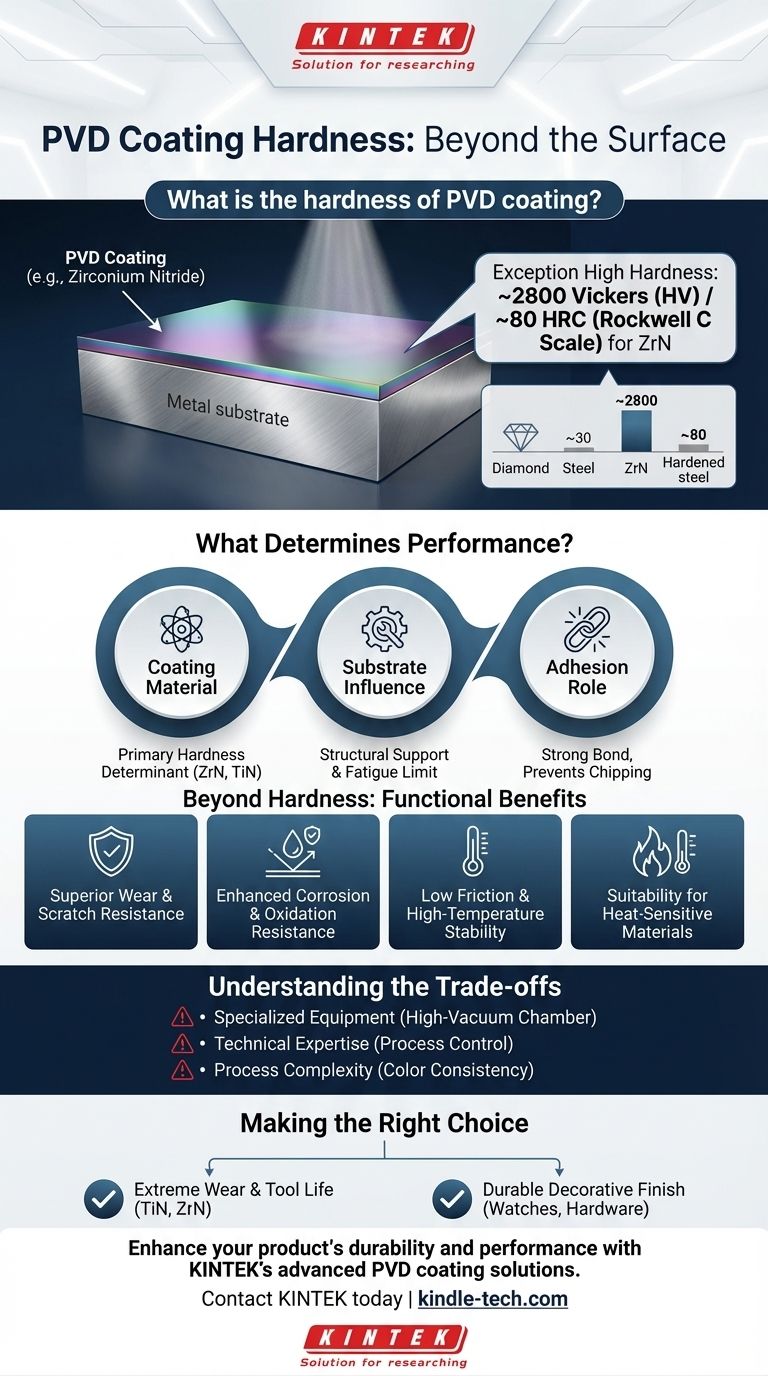
The hardness of a PVD coating depends entirely on the material being deposited, but it is exceptionally high. For example, a Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) PVD coating, often used for "Lifetime Brass" finishes, has a hardness of approximately 2800 Vickers (HV), which is equivalent to about 80 on the Rockwell C scale (HRC).
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is not a single material but a sophisticated process that applies an extremely hard, thin ceramic coating to a substrate. While its hardness is a key feature, its true value lies in how this hardness combines with other properties like wear resistance, adhesion, and low friction to dramatically enhance the performance of the underlying material.

What Determines the Performance of a PVD Coating?
The final properties of a PVD-coated part are a result of the interplay between the coating material, the substrate it is applied to, and the process parameters.
The Coating Material Itself
The specific ceramic compound used for the coating is the primary determinant of its hardness and other characteristics. Materials like Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) and Titanium Nitride (TiN) are common choices, each offering a unique profile of hardness, color, and temperature resistance.
The Influence of the Substrate
PVD coatings are incredibly thin, typically ranging from 0.5 to 5 microns. This means they rely on the underlying material (the substrate) for structural support.
A hard coating on a soft substrate can crack under impact. Therefore, the properties of the final product, including its fatigue limit and endurance, are a combination of both the coating and the base material.
The Role of Adhesion
A key advantage of the PVD process is the exceptionally strong bond it creates between the coating and the substrate. Advanced techniques create strong coating adhesion, ensuring the hard layer doesn't chip or flake off during use, which is critical for performance.
Beyond Hardness: The Functional Benefits of PVD
While hardness is the most cited metric, the practical benefits of PVD extend to several other areas of performance.
Superior Wear and Scratch Resistance
The high hardness directly translates into outstanding resistance to abrasion, scratching, and general wear. This is why PVD is a preferred choice for cutting tools, industrial components, and high-end decorative finishes that must withstand daily contact.
Enhanced Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
The PVD process creates a dense, non-porous ceramic layer that acts as a powerful barrier against environmental factors. This coating is highly resistant to corrosion, tarnish, and oxidation, protecting the substrate material.
Low Friction and High-Temperature Stability
PVD coatings significantly reduce the coefficient of friction on a component's surface. This quality, combined with their ability to withstand high temperatures, makes them ideal for high-performance applications like cutting tools, where reducing heat and friction is critical.
Suitability for Heat-Sensitive Materials
The PVD process occurs at relatively low temperatures (around 500°C). This makes it possible to coat materials that might be damaged or warped by higher-temperature coating processes, expanding its range of applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its significant advantages, the PVD process is not without its challenges and is not the right solution for every problem.
Requirement for Specialized Equipment
Applying a PVD coating requires a high-vacuum chamber and sophisticated equipment to vaporize and deposit the coating material. This machinery represents a significant capital investment.
The Need for Technical Expertise
Achieving a consistent, high-quality PVD finish demands a high level of process control and expertise. Factors like chamber cleanliness, temperature, pressure, and bias voltage must be precisely managed to ensure proper adhesion and uniform color.
Process Complexity for Decorative Finishes
While PVD can produce a wide range of colors, achieving a specific, uniform color can be complex. Improper process control can lead to variations and material wastage, especially when creating unique finishes like jet black or blue.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a PVD coating should be based on your primary performance goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance and tool life: A PVD coating like TiN or ZrN is an industry-standard choice for increasing hardness, reducing friction, and extending the life of cutting tools and industrial parts.
- If your primary focus is a durable decorative finish: PVD provides a far more resilient and long-lasting finish than traditional plating for items like watches, architectural hardware, and jewelry.
- If your primary focus is protecting a heat-sensitive component: PVD's low processing temperature makes it a superior choice over high-temperature alternatives like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Ultimately, PVD is a strategic engineering choice used to impart superior surface properties onto a component, dramatically improving its durability and performance.
Summary Table:
| Coating Material | Hardness (Vickers HV) | Equivalent Rockwell C (HRC) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) | ~2800 HV | ~80 HRC | Decorative finishes, cutting tools |
| Titanium Nitride (TiN) | ~2300-2400 HV | ~80-81 HRC | Industrial tools, wear parts |
Enhance your product's durability and performance with KINTEK's advanced PVD coating solutions.
As a specialist in lab equipment and consumables, KINTEK provides high-performance PVD coatings that deliver exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection—ideal for extending the life of cutting tools, industrial components, and decorative finishes.
Let our expertise help you select the right coating material and process parameters to meet your specific application needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PVD coatings can add value to your products!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition



















