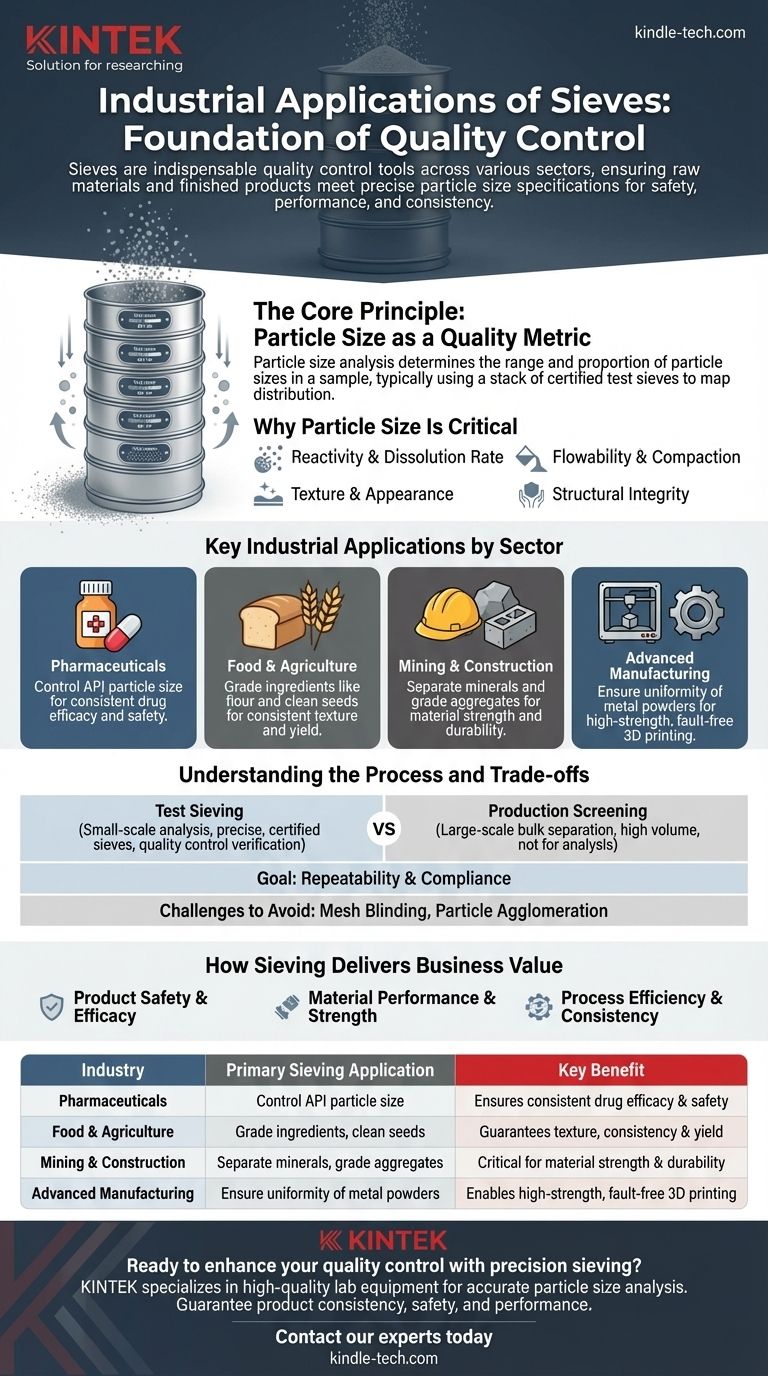
In industrial settings, sieves are indispensable tools for quality control. They are used across a vast range of sectors—from pharmaceuticals and food to mining and aerospace—to perform particle analysis. This process ensures that both raw materials and finished products meet precise size specifications, which is critical for safety, performance, and consistency.
The true industrial application of sieving goes beyond simple sorting. It is a foundational quality assurance process that directly impacts product efficacy, material strength, and manufacturing reliability by guaranteeing that particle size distribution adheres to strict standards.

The Core Principle: Particle Size as a Quality Metric
To understand the role of sieves, you must first understand why particle size is one of the most critical physical characteristics of any granular material.
What Is Particle Size Analysis?
Particle size analysis is the process of determining the range and proportion of different particle sizes within a given sample.
In its most common form, this involves using a stacked column of test sieves, each with a screen of a specific mesh size. A measured sample is placed in the top sieve (the one with the largest openings) and the stack is agitated, causing particles to fall through the screens until they are retained by a mesh they cannot pass.
By weighing the material left on each sieve, an operator can precisely map the particle size distribution of the sample.
Why Particle Size Is a Critical Specification
The size of a particle directly influences its physical and chemical properties. In an industrial context, this means particle size can dictate:
- Reactivity and Dissolution Rate: Smaller particles have a higher surface-area-to-volume ratio, allowing them to dissolve or react much faster.
- Flowability and Compaction: Uniformly sized particles behave differently than mixed-size particles when being poured, mixed, or compressed.
- Texture and Appearance: In consumer products, particle size is a key driver of mouthfeel, smoothness, and visual consistency.
- Structural Integrity: In materials like powdered metals or concrete aggregates, particle size distribution is essential for achieving maximum density and strength.
Key Industrial Applications by Sector
Controlling for these properties is the primary goal of sieving in various industries.
In Pharmaceuticals
The bioavailability of a drug—how much of it enters the bloodstream to have an active effect—is heavily dependent on its dissolution rate. Sieving is used to control the particle size of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and excipients to ensure each dose dissolves correctly and delivers a consistent, safe, and effective therapeutic outcome.
In Food and Agriculture
Sieving is fundamental to food processing. It is used to grade flour for consistent baking performance, remove lumps from spices, separate cocoa solids, and ensure the uniform texture of powdered drinks. In agriculture, sieves are used to clean and grade seeds, removing debris and sorting them by size to improve planting efficiency and crop yield.
In Mining and Construction
In the mining industry, large-scale vibratory sieves (or screens) are used to separate valuable minerals from waste rock. In construction, sieving is used to grade aggregates like sand and gravel. The particle size distribution of aggregate is a critical specification for creating strong, durable concrete and asphalt.
In Advanced Manufacturing (Aerospace & Automotive)
Modern manufacturing techniques like additive manufacturing (3D printing) rely on powdered metals. The uniformity and size of these metal particles are paramount. Sieving ensures the powder layer is dense and consistent, which is essential for printing high-strength, fault-free components like jet engine turbine blades or lightweight automotive parts, directly contributing to fewer internal failures.
Understanding the Process and Trade-offs
It's important to distinguish between the two primary modes of industrial sieving, as they serve different purposes.
Test Sieving vs. Production Screening
Test sieving is a small-scale laboratory process used for quality control. It uses highly precise, certified sieves to analyze a sample and verify that a batch meets specifications.
Production screening, on the other hand, involves large, industrial-scale vibratory screens. Their goal is not analysis but bulk separation—for example, removing oversized particles from thousands of pounds of sugar per hour.
The Goal: Repeatability and Compliance
For both applications, the ultimate goal is repeatability. The sieving process, whether for analysis or separation, must be standardized. This ensures that every batch of product is evaluated and produced under the exact same conditions, guaranteeing compliance with internal standards and industry regulations.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Effective sieving requires overcoming two main challenges. Mesh blinding occurs when particles get stuck in the sieve openings, reducing its efficiency. Particle agglomeration, where small particles clump together, can prevent them from passing through the appropriate mesh, leading to inaccurate analysis. Proper sieve maintenance and sample preparation are critical to mitigate these issues.
How Sieving Delivers Business Value
The decision to implement a rigorous sieving protocol is driven by clear business objectives.
- If your primary focus is product safety and efficacy: Sieving is non-negotiable for controlling active ingredients in pharmaceuticals or removing contaminants from food products.
- If your primary focus is material performance and strength: Precise particle sizing is critical for advanced applications like powdered metals in additive manufacturing or aggregates in high-strength concrete.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and consistency: Sieving ensures uniform raw materials, which leads to predictable manufacturing outcomes, consistent product quality, and reduced waste.
Ultimately, mastering particle control through sieving is a fundamental pillar of modern industrial quality assurance.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Sieving Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Control API particle size | Ensures consistent drug efficacy & safety |
| Food & Agriculture | Grade ingredients, clean seeds | Guarantees texture, consistency & yield |
| Mining & Construction | Separate minerals, grade aggregates | Critical for material strength & durability |
| Advanced Manufacturing | Ensure uniformity of metal powders | Enables high-strength, fault-free 3D printing |
Ready to enhance your quality control with precision sieving?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for accurate particle size analysis. Whether you're in pharmaceuticals, food production, or advanced manufacturing, our reliable sieves and expert support help you guarantee product consistency, safety, and performance.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your laboratory's specific needs and ensure your materials meet the strictest standards.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity



















