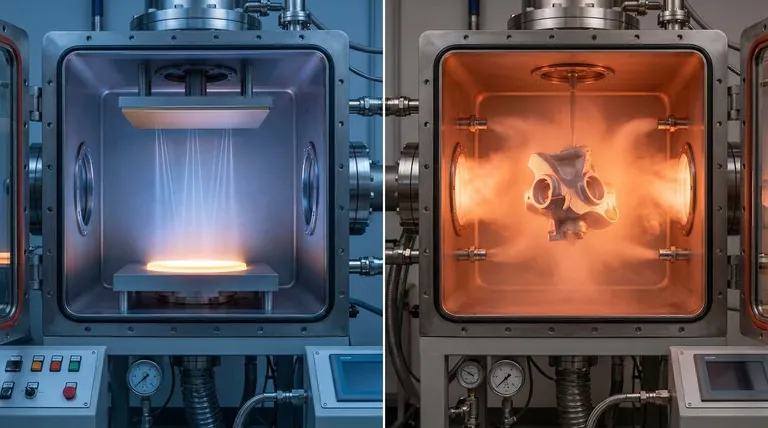
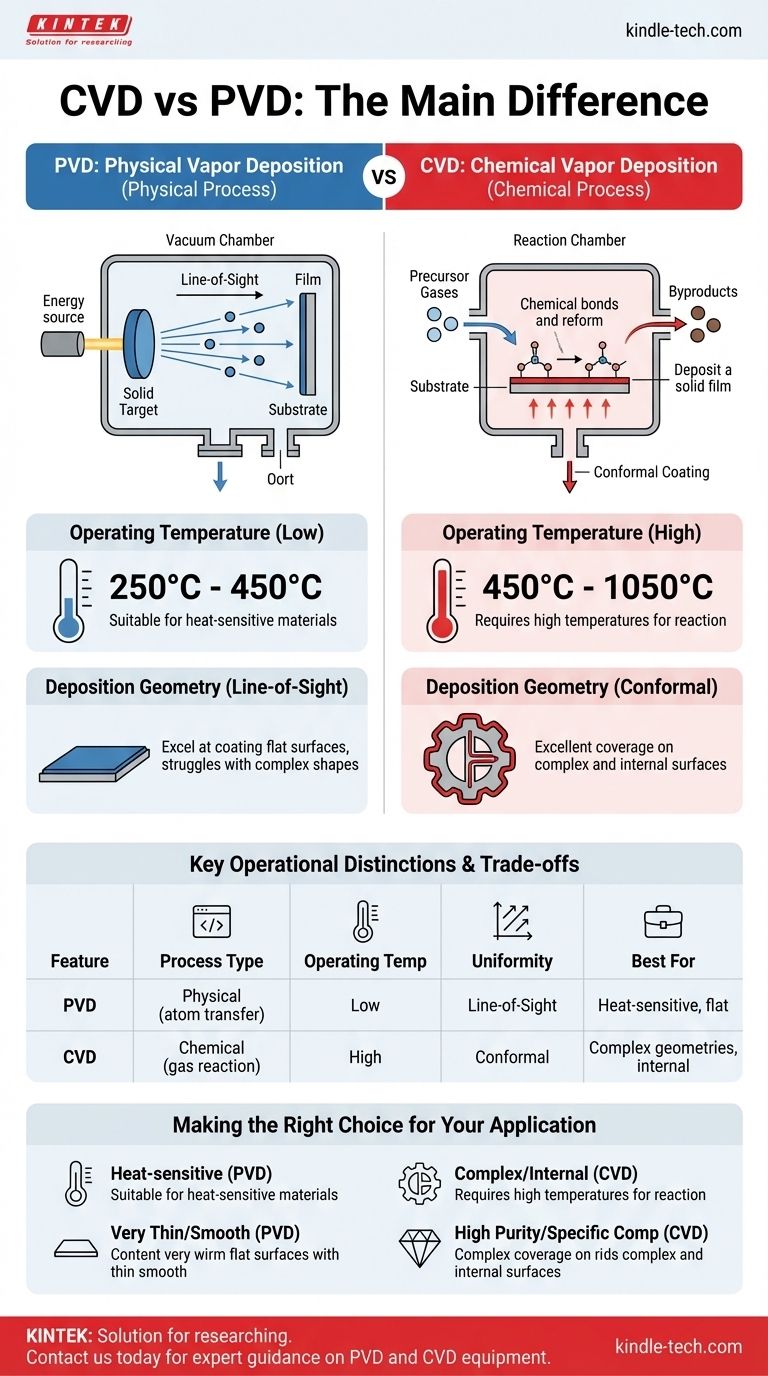
The primary difference between CVD and PVD lies in the state of the source material and the nature of the deposition process. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a physical process that vaporizes a solid material, which then travels in a straight line to condense onto a substrate. In contrast, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a chemical process that uses precursor gases that undergo a reaction directly on the substrate's surface to form the desired solid film.
PVD is a "line-of-sight" physical process, much like spray-painting with atoms, making it ideal for coating surfaces at lower temperatures. CVD is a chemical reaction process, where gas envelops a component, allowing it to uniformly coat complex shapes, but this requires much higher temperatures.
Understanding the Core Mechanisms
Both PVD and CVD are advanced vacuum deposition techniques used to create thin, functional films on a surface. However, how they create that film is fundamentally different.
PVD: A Physical, Line-of-Sight Process
In PVD, the coating material starts as a solid target in a vacuum chamber. This solid is bombarded with energy (like an ion beam) to physically dislodge atoms and vaporize them.
These vaporized atoms travel in a straight line—a "line-of-sight"—until they strike the substrate and condense, forming a thin, solid film. There is no chemical change in the material itself.
CVD: A Chemical Reaction Process
In CVD, the process begins with volatile precursor gases. These gases are introduced into a reaction chamber containing the substrate.
The chamber is heated to a high temperature, which provides the energy for the gases to react with each other and with the substrate's surface. This chemical reaction results in the deposition of a solid film, with other chemical byproducts being exhausted from the chamber.
Key Operational Distinctions
The mechanical differences between PVD and CVD lead to critical distinctions in their operation and application.
Operating Temperature
PVD operates at relatively low temperatures, typically between 250°C and 450°C. This makes it suitable for a wider range of substrate materials, including some that are heat-sensitive.
CVD requires significantly higher temperatures to drive the necessary chemical reactions, usually from 450°C up to 1050°C. This high heat limits its use to substrates that can withstand such extreme conditions without deforming or melting.
Deposition Geometry
Because PVD is a line-of-sight process, it excels at coating flat surfaces or the exposed faces of an object. However, it struggles to uniformly coat complex shapes, internal channels, or the undersides of components due to "shadowing" effects.
CVD's gaseous nature means the precursor molecules envelop the entire part. This allows it to create a highly uniform, or conformal, coating over intricate geometries and even inside complex structures. It also allows for coating many parts simultaneously in a single batch.
Film Properties
PVD generally produces very thin, smooth, and dense coatings. The process offers fine control over the film's structure and durability.
CVD can produce a wider range of film thicknesses, from very thin to quite thick. The coatings are exceptionally pure due to the chemical reaction process but can sometimes be rougher than those produced by PVD.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally superior; the choice involves a clear set of trade-offs based on the application's requirements.
PVD: The Low-Temperature Advantage
The key strength of PVD is its lower processing temperature. This opens up its use for materials like certain steel alloys, aluminum, and even some polymers that would be destroyed by the heat of CVD.
The primary limitation is its line-of-sight nature. Achieving a uniform coating on a part with complex geometry, like a screw thread or a detailed mold, is extremely difficult.
CVD: Superior Coverage at a Cost
CVD's ability to deposit a uniform film on any exposed surface is its greatest advantage, making it the only choice for coating the interior of pipes or complex machine parts.
Its major drawback is the extreme heat required. This high thermal budget severely restricts the list of compatible substrate materials and can sometimes alter the properties of the substrate itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice between PVD and CVD hinges entirely on your substrate material, the geometry of your part, and the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive material: PVD is the correct choice due to its much lower operating temperatures.
- If your primary focus is achieving a uniform coating on complex, 3D shapes or internal surfaces: CVD is superior because its gaseous precursors can reach all exposed areas.
- If your primary focus is a very thin, smooth, and durable surface on a relatively flat object: PVD often provides better control and a smoother finish for these applications.
- If your primary focus is high film purity or a specific chemical composition not easily sourced as a solid target: CVD offers more flexibility through the chemistry of its precursor gases.
Ultimately, understanding these core mechanical and operational differences empowers you to select the deposition technology that aligns perfectly with your engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical (atom transfer) | Chemical (gas reaction) |
| Operating Temperature | 250°C - 450°C (Low) | 450°C - 1050°C (High) |
| Coating Uniformity | Line-of-sight (shadows possible) | Conformal (uniform on complex shapes) |
| Best For | Heat-sensitive materials, flat surfaces | Complex geometries, internal surfaces |
Still unsure which deposition method is right for your application? The experts at KINTEK are here to help!
We specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for all your coating needs. Whether you're working with heat-sensitive materials requiring PVD's low-temperature advantage or complex geometries that need CVD's superior coverage, our team can guide you to the perfect solution.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our expertise can enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Get in touch with our specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do CVD diamonds grow? A Step-by-Step Guide to Lab-Grown Diamond Creation
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- Is sputtering a PVD? Discover the Key Coating Technology for Your Lab



















