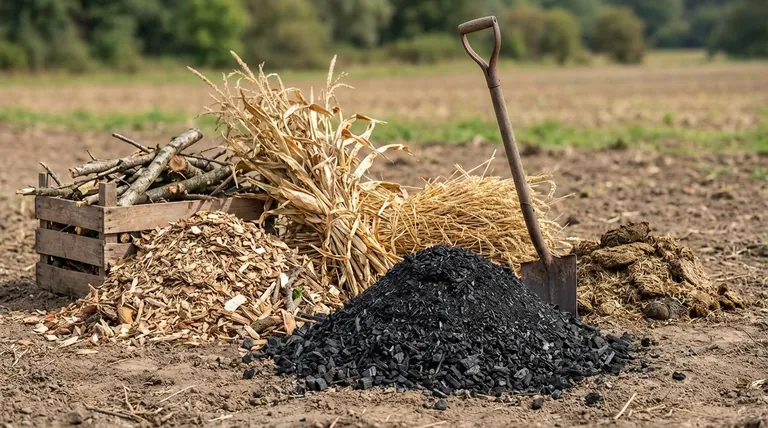
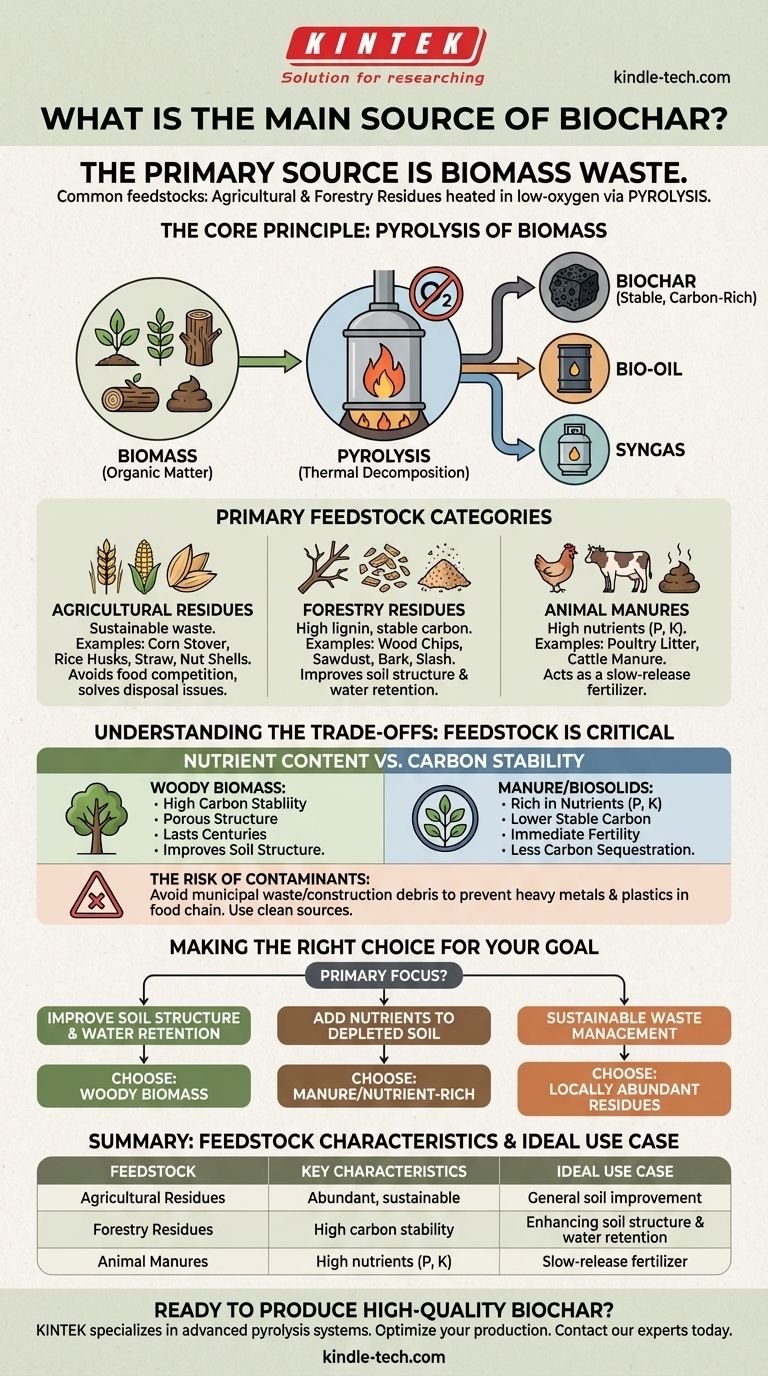
In short, the primary source of biochar is biomass waste, with the most common and sustainable feedstocks being agricultural and forestry residues. This includes materials like wood chips, corn stalks, rice husks, and straw that are heated in a low-oxygen environment through a process called pyrolysis.
The critical takeaway is not simply that biochar comes from biomass, but that the specific type of biomass used as a feedstock fundamentally determines the biochar's properties, cost, and ultimate effectiveness for its intended purpose.

What Qualifies as a Biochar Source?
Biochar can be produced from nearly any organic material. The process, not the specific plant, is what defines it.
The Core Principle: Pyrolysis of Biomass
The creation of biochar relies on pyrolysis, which is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an oxygen-limited environment.
Heating biomass without enough oxygen to cause combustion transforms it into a stable, carbon-rich solid (biochar), along with liquid (bio-oil) and gas (syngas) co-products.
The Definition of Biomass
Biomass is simply organic matter derived from living or recently living organisms. This broad definition means the potential sources for biochar are incredibly diverse, but they are not all created equal.
The Primary Categories of Feedstock
While many materials can be used, a few categories dominate commercial and practical production due to their availability, cost, and resulting biochar quality.
Agricultural Residues
This is one of the largest and most sustainable sources. It consists of the leftover materials after a crop has been harvested.
Examples include corn stover (stalks, leaves), rice husks, wheat straw, and nut shells. Using these "waste" products avoids competition with food production and can solve a disposal problem for farmers.
Forestry Residues
Residues from forestry operations and wood processing are another major source. This feedstock is typically high in lignin, which produces a very stable, high-carbon biochar.
This category includes wood chips, sawdust, bark, and slash (branches and treetops left after logging). Biochar from this source is excellent for improving soil structure and water retention.
Animal Manures
Biochar can be made from various animal manures, such as poultry litter or cattle manure.
The resulting biochar is often lower in stable carbon but significantly higher in essential plant nutrients like phosphorus and potassium. This makes it function more like a slow-release fertilizer.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Feedstock Choice is Critical
The decision of what feedstock to use is the most important variable in biochar production. It creates a series of trade-offs that impact the final product's use case.
Nutrient Content vs. Carbon Stability
Biochar made from woody biomass is highly porous and rich in stable carbon, making it last for centuries in the soil. It excels at improving soil structure and providing a long-term habitat for beneficial microbes.
Biochar from manure or biosolids, conversely, is richer in nutrients but has a lower proportion of stable carbon. It provides more immediate fertility benefits but contributes less to long-term carbon sequestration.
The Risk of Contaminants
Not all biomass is clean. Feedstocks like municipal solid waste, construction debris, or industrial biosolids can contain heavy metals, plastics, or other persistent chemical contaminants.
If these feedstocks are turned into biochar and applied to soil, those contaminants can be introduced into the food chain. For agricultural use, it is crucial to use biochar from clean, known sources.
Cost and Logistics
The most sustainable and cost-effective biochar operations use a feedstock that is locally abundant and low-cost, often a waste product.
Transporting bulky biomass over long distances can make the process prohibitively expensive and negate the carbon benefits. The best source is often the one closest to you.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal biochar source depends entirely on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is improving soil structure and water retention: Choose biochar from woody biomass for its high carbon stability and porous structure.
- If your primary focus is adding nutrients to depleted soil: Opt for biochar made from manure or other nutrient-rich feedstocks to act as a slow-release fertilizer.
- If your primary focus is sustainable waste management: Prioritize locally abundant agricultural or forestry residues to minimize transportation costs and create a circular economy.
By understanding the origin of biochar, you can select a product that aligns perfectly with your environmental and agricultural goals.
Summary Table:
| Feedstock Category | Key Characteristics | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Residues (e.g., straw, husks) | Abundant, sustainable, avoids food competition | General soil improvement, carbon sequestration |
| Forestry Residues (e.g., wood chips, sawdust) | High carbon stability, porous structure | Enhancing soil structure & water retention |
| Animal Manures (e.g., poultry litter) | High in nutrients (P, K), lower carbon stability | Acting as a slow-release fertilizer |
Ready to produce high-quality biochar tailored to your specific goals?
The right feedstock is critical, and so is the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis systems for converting biomass into consistent, high-performance biochar. Whether you're processing agricultural waste, forestry residues, or manure, our lab equipment and consumables are designed for precision, efficiency, and scalability.
Let us help you optimize your biochar production. Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover the perfect solution for your laboratory or production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- What is the function of laboratory autoclaves in SCWR research? Predict Material Compatibility and Corrosion Kinetics
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization



















