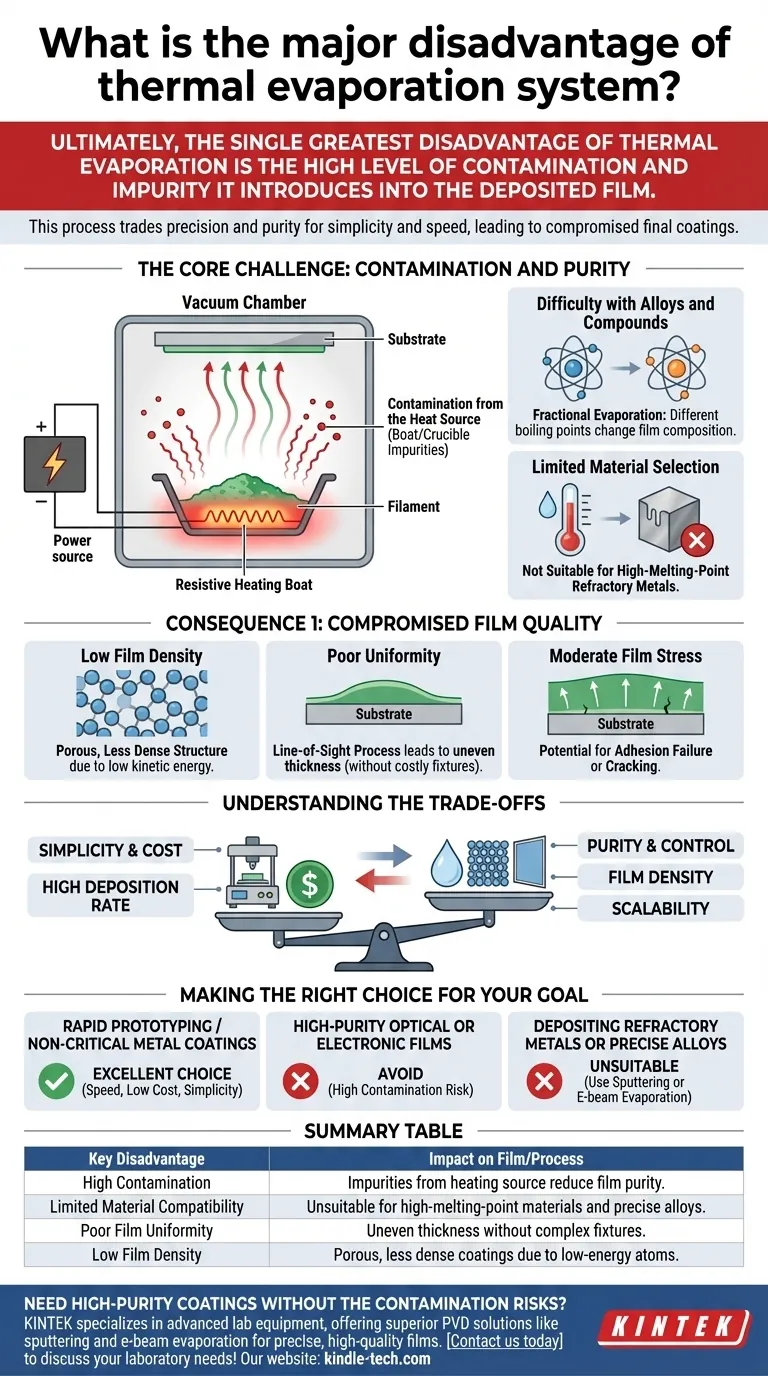
Ultimately, the single greatest disadvantage of thermal evaporation is the high level of contamination and impurity it introduces into the deposited film. While valued for its simplicity and low cost, the process itself creates an environment where elements from the heating source can mix with the desired material, compromising the purity and quality of the final coating.
Thermal evaporation trades precision and purity for simplicity and speed. Its fundamental drawback is the inability to heat a source material without also heating—and potentially evaporating—the crucible or boat holding it, leading to contaminated films and limited material compatibility.
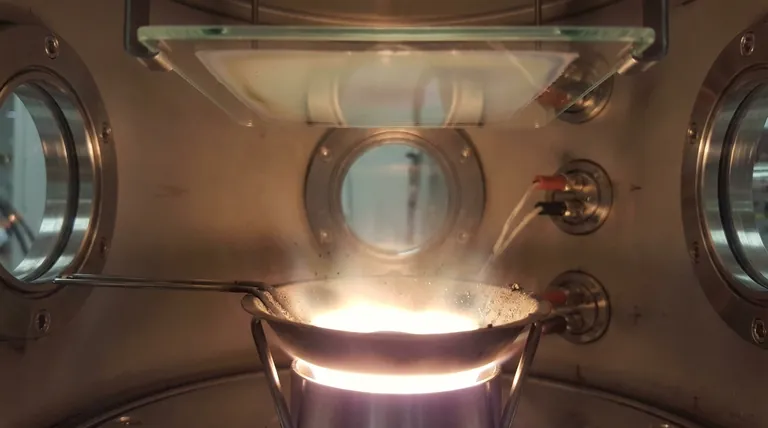

The Core Challenge: Contamination and Purity
Thermal evaporation is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process that uses resistive heating—running a current through a boat or filament—to heat a source material until it evaporates. While simple, this direct heating method is the root cause of its primary disadvantages.
Contamination from the Heat Source
The boat or crucible holding the source material is heated to extreme temperatures. This can cause the boat material itself (often a refractory metal like tungsten or molybdenum) to evaporate or react with the source, releasing impurities that co-deposit onto your substrate. This makes it the least pure of all PVD methods.
Difficulty with Alloys and Compounds
Heating an alloy often results in fractional evaporation, where the element with the lower boiling point evaporates at a much higher rate. The resulting film will have a different stoichiometry (elemental ratio) than the source material, making it difficult to deposit complex materials with precise composition.
Limited Material Selection
The process is not suitable for materials with very high melting points, such as refractory metals like tungsten or tantalum. Achieving the necessary temperatures would require so much power that it would risk destroying the heating element and cause extreme contamination, rendering the process ineffective.
Consequence 1: Compromised Film Quality
The impurities and the low-energy nature of the process directly impact the physical characteristics of the deposited film.
Low Film Density
Atoms leave the source material with relatively low kinetic energy. When they arrive at the substrate, they have little energy to move around and settle into a dense, tightly packed structure. This typically results in a film that is porous and has lower density compared to films made with other PVD techniques.
Poor Uniformity
Thermal evaporation is a "line-of-sight" process, where atoms travel in straight lines from the source. Without sophisticated and costly additions like planetary substrate rotation and uniformity masks, the film will be significantly thicker directly above the source and thinner toward the edges of the substrate.
Moderate Film Stress
The way atoms arrange and cool on the substrate can create internal stress within the film. While often less severe than in some other processes, this stress can still be a concern for sensitive applications, potentially causing adhesion failure or cracking.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition method is about balancing competing priorities. Thermal evaporation's disadvantages are the direct trade-off for its primary advantages.
Simplicity and Cost vs. Purity
Thermal evaporation systems are mechanically simple, relatively inexpensive to build and operate, and do not require complex power supplies. This accessibility is its main selling point, but it comes at the direct cost of film purity and control.
Deposition Rate vs. Control
The process can achieve very high deposition rates, making it fast for applying thick coatings. However, this speed offers less granular control over film growth and properties compared to slower, more energetic methods like sputtering.
Limited Scalability
While simple for a lab-scale coater, achieving uniform coatings over large areas is a significant engineering challenge. It requires complex rotating fixtures that increase the system's cost and complexity, eroding its main advantage of simplicity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your deposition method based on the non-negotiable requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or non-critical metal coatings: Thermal evaporation is an excellent choice for its speed, low cost, and simplicity.
- If your primary focus is high-purity optical or electronic films: Avoid thermal evaporation, as the inherent risk of contamination is too high for performance-critical applications.
- If your primary focus is depositing refractory metals or precise alloys: This method is unsuitable; you must use a technique like e-beam evaporation or sputtering.
Understanding these core limitations allows you to leverage thermal evaporation for its strengths in simplicity and speed, while avoiding it where purity and structural quality are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Key Disadvantage | Impact on Film/Process |
|---|---|
| High Contamination | Impurities from the heating source (crucible/boat) co-deposit, reducing film purity. |
| Limited Material Compatibility | Unsuitable for high-melting-point materials and precise alloy deposition. |
| Poor Film Uniformity | Line-of-sight deposition leads to uneven thickness without complex fixtures. |
| Low Film Density | Low-energy atoms result in porous, less dense coatings. |
Need high-purity coatings without the contamination risks of thermal evaporation? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, offering superior PVD solutions like sputtering and e-beam evaporation for precise, high-quality films. Let our experts help you select the right deposition method for your critical applications. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis



















