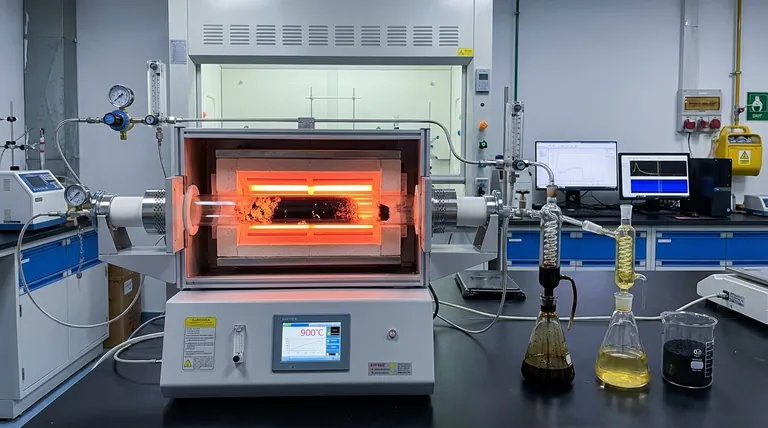
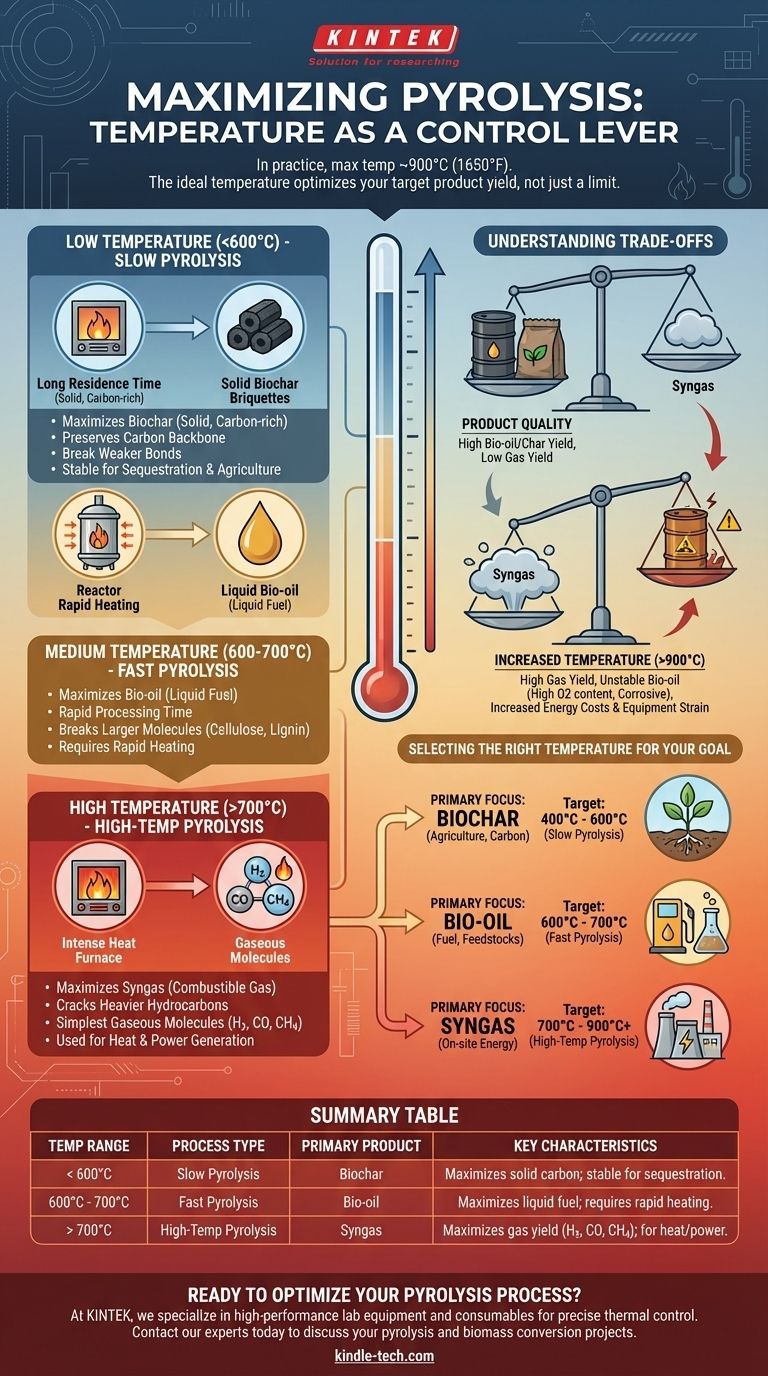
In practice, the maximum temperature for typical industrial pyrolysis processes is around 900°C (1650°F). However, there is no single theoretical maximum, as the ideal temperature is entirely dependent on the specific feedstock being processed and the desired end products.
The core concept to understand is that temperature is not a limit to be reached, but a control lever to be adjusted. The "right" temperature is the one that optimizes the yield of your target product, whether that is solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, or combustible syngas.

Why Temperature Dictates the Outcome
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials in the absence of oxygen. Temperature is the most critical factor in this process because it directly controls the rate and extent of the chemical reactions, determining which molecular bonds break and what new products are formed.
Low Temperature Range (< 600°C)
This process, often called slow pyrolysis, uses longer residence times and lower temperatures.
The primary goal here is to break weaker chemical bonds, driving off volatile compounds while preserving the carbon backbone of the material.
The result is a maximized yield of biochar, a stable, carbon-rich solid.
Medium Temperature Range (600°C - 700°C)
Often referred to as fast pyrolysis, this range is the "sweet spot" for producing liquid fuels.
The higher heat and rapid processing time break down larger organic molecules like cellulose and lignin into smaller, condensable vapors.
When cooled, these vapors form bio-oil, also known as pyrolysis oil.
High Temperature Range (> 700°C)
At these elevated temperatures, the process favors the production of gas over liquids or solids.
The intense heat cracks the heavier hydrocarbon molecules, which would have formed bio-oil at lower temperatures, into the simplest and smallest gaseous molecules like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane.
This mixture is known as syngas (synthesis gas) and can be used as a fuel for generating heat and power.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Higher Temperatures
Pushing the temperature higher is not always better. It introduces significant operational and chemical challenges that must be carefully managed.
Product Quality vs. Yield
Increasing temperature generally increases the yield of gas at the expense of oil and char.
While high temperatures maximize gas production, the resulting bio-oil can have undesirable properties. It often has a high oxygen content, making it unstable, corrosive, and difficult to integrate with conventional fossil fuels.
Energy Costs and Equipment Strain
Achieving and maintaining temperatures above 900°C requires a substantial energy input, which can negatively impact the economic viability of the process.
Furthermore, these extreme conditions demand specialized, expensive materials for the reactor to prevent degradation and ensure operational safety.
Selecting the Right Temperature for Your Goal
Your choice of temperature should be a strategic decision based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar for agriculture or carbon sequestration: Operate at lower temperatures, typically between 400°C and 600°C.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil for fuel or chemical feedstocks: Target the fast pyrolysis range of 600°C to 700°C with rapid heating rates.
- If your primary focus is generating syngas for on-site energy production: Utilize the highest practical temperatures, from 700°C up to 900°C or more.
Ultimately, mastering pyrolysis is about precisely controlling the temperature to dictate the final product.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Process Type | Primary Product | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 600°C | Slow Pyrolysis | Biochar | Maximizes solid carbon yield; stable for sequestration/agriculture. |
| 600°C - 700°C | Fast Pyrolysis | Bio-oil | Maximizes liquid fuel yield; requires rapid heating. |
| > 700°C | High-Temp Pyrolysis | Syngas | Maximizes gas yield (H2, CO, CH4); used for heat/power generation. |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables designed for precise thermal control. Whether you're researching biochar, bio-oil, or syngas production, our reactors and furnaces deliver the accuracy and durability you need to achieve your target yields. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's pyrolysis and biomass conversion projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the function of alumina tubes and alumina wool in a pyrolysis furnace? Optimize Your Biochar Production Quality
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What are the hazards of a tube furnace? Beyond the Obvious Burn Risks
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?



















