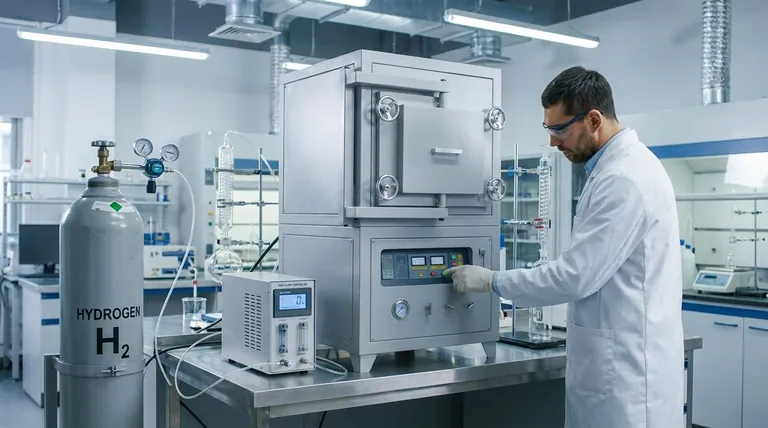
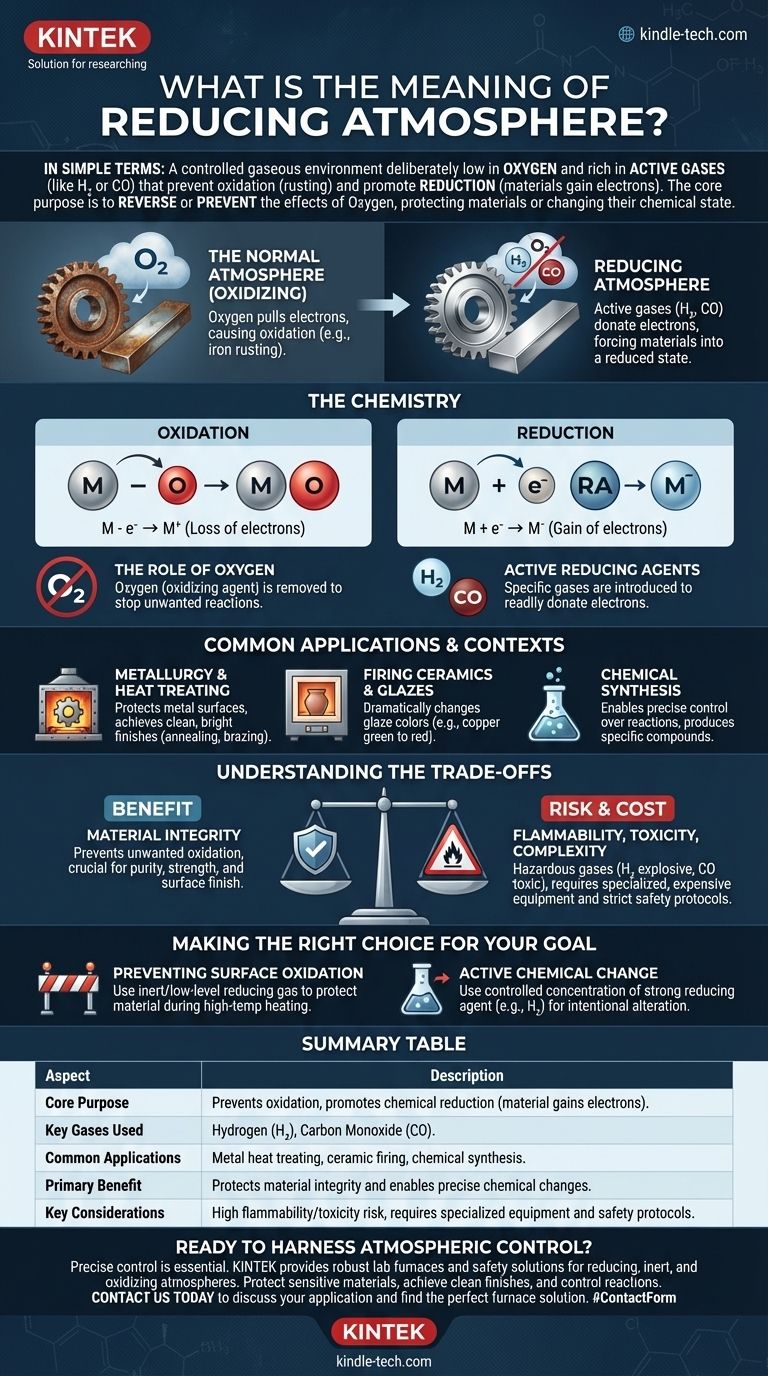
In simple terms, a reducing atmosphere is a controlled gaseous environment that is deliberately low in oxygen and rich in gases that prevent oxidation (like rusting) and promote the chemical process of reduction. This is achieved by removing oxygen and introducing active gases like hydrogen or carbon monoxide, which essentially force materials to gain electrons.
The core purpose of a reducing atmosphere is to reverse or prevent the effects of oxygen. While the air we breathe is naturally oxidizing, a reducing atmosphere is an engineered environment designed to protect materials from oxidation or to actively change their chemical state.

The Chemistry of a Reducing Atmosphere
To understand a reducing atmosphere, you first have to understand its opposite: the normal, oxygen-rich atmosphere we live in.
Oxidation vs. Reduction
Oxidation is a chemical reaction where a substance loses electrons. The most common example is iron rusting. Oxygen in the air pulls electrons from the iron, forming iron oxide.
Reduction is the exact opposite process. It's a chemical reaction where a substance gains electrons. A reducing atmosphere is specifically designed to facilitate this reaction.
The Role of Oxygen
Oxygen is a powerful oxidizing agent. Its natural tendency is to strip electrons from other materials, which is why metals tarnish, fires burn, and apples turn brown.
The first step in creating a reducing atmosphere is to remove or significantly lower the amount of oxygen to stop these unwanted oxidizing reactions from occurring.
Active Reducing Agents
Simply removing oxygen creates a neutral, or inert, atmosphere. To make it actively reducing, specific gases are introduced.
These gases, such as hydrogen (H₂) or carbon monoxide (CO), act as reducing agents. They readily donate their electrons to other materials, forcing those materials into a reduced state.
Common Applications and Contexts
Reducing atmospheres are not a theoretical concept; they are critical tools in advanced manufacturing and science.
Metallurgy and Heat Treating
When heating metals for processes like annealing or brazing, a normal atmosphere would cause heavy scaling and oxidation, ruining the material.
Using a reducing atmosphere with hydrogen or carbon monoxide protects the metal surface and can even clean off existing light oxides, resulting in a clean, bright finish.
Firing Ceramics and Glazes
The color and properties of ceramic glazes are highly dependent on the firing atmosphere.
A reducing atmosphere during firing can pull oxygen atoms out of metal oxides in the glaze, dramatically changing their color. For example, it can turn copper oxide from green (oxidized) to a deep red (reduced).
Chemical Synthesis and Fuel Production
Many chemical manufacturing processes require precise control over reactions. A reducing atmosphere can be used to produce specific compounds by preventing oxidation and promoting desired reduction pathways.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, creating and using a reducing atmosphere involves significant considerations.
Benefit: Material Integrity
The primary advantage is the prevention of unwanted oxidation. This is crucial for maintaining the purity, strength, and surface finish of sensitive materials, especially at high temperatures.
Risk: Flammability and Toxicity
The gases used to create reducing atmospheres are often hazardous. Hydrogen is highly flammable and explosive, while carbon monoxide is extremely toxic.
Handling these atmospheres requires specialized equipment, rigorous safety protocols, and continuous monitoring.
Cost and Complexity
Creating, containing, and controlling a specific gas mixture is far more complex and expensive than simply using ambient air. It requires sealed furnaces, gas flow controllers, and safety interlocks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding why you need a controlled atmosphere is key to its proper application.
- If your primary focus is preventing surface oxidation: Your main goal is to displace oxygen with an inert or low-level reducing gas to protect a material during a process like high-temperature heating.
- If your primary focus is active chemical change: You need to use a carefully controlled concentration of a strong reducing agent like hydrogen to intentionally alter the chemical state of your material, as seen in smelting ores or developing specific ceramic colors.
Ultimately, mastering a reducing atmosphere gives you precise control over chemical reactions, allowing you to protect materials or create new ones.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Purpose | Prevents oxidation and promotes chemical reduction (material gains electrons). |
| Key Gases Used | Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Monoxide (CO). |
| Common Applications | Metal heat treating, ceramic firing, chemical synthesis. |
| Primary Benefit | Protects material integrity and enables precise chemical changes. |
| Key Considerations | High flammability/toxicity risk, requires specialized equipment and safety protocols. |
Ready to harness the power of a controlled atmosphere in your lab?
Precise atmospheric control is essential for successful heat treatment, brazing, and materials synthesis. KINTEK specializes in providing the robust lab furnaces and safety solutions you need to safely and effectively implement reducing, inert, and oxidizing atmospheres.
We provide the equipment and expertise to help you:
- Protect sensitive materials from oxidation.
- Achieve clean, bright metal finishes.
- Control chemical reactions with precision.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of maintaining a continuous argon flow? Optimize PLAP Recovery with High Purity Aluminum
- What is protective atmosphere heat treatment? Prevent Oxidation and Decarburization for Superior Metal Parts
- What are the typical gas compositions for nitrogen-based atmospheres? Expert Guide to Thermal Processing Ratios
- What is the role of high-temperature atmosphere furnaces in CrFe2MnNi alloy prep? Master Microstructural Stability
- What is vacuum inerting? A Safer Method for Preventing Explosions and Oxidation
- What is the use of hydrogen in furnace? A Key to Oxygen-Free High-Temperature Processing
- Why argon is used in annealing? To Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Purity in Heat Treatment
- What is the significance of controlled atmosphere in heat treatment? Prevent Oxidation & Guarantee Part Integrity



















