In essence, thermal evaporation is a coating technique used to deposit a very thin layer of material onto a surface. It is a type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) where a source material is heated in a high vacuum chamber until it transforms into a vapor, which then travels and condenses onto a cooler target surface, forming a uniform film.
The core principle of thermal evaporation is straightforward: use resistive heating to turn a solid material into a gas within a vacuum, allowing its atoms to travel unimpeded and form a pure, thin film on a substrate.

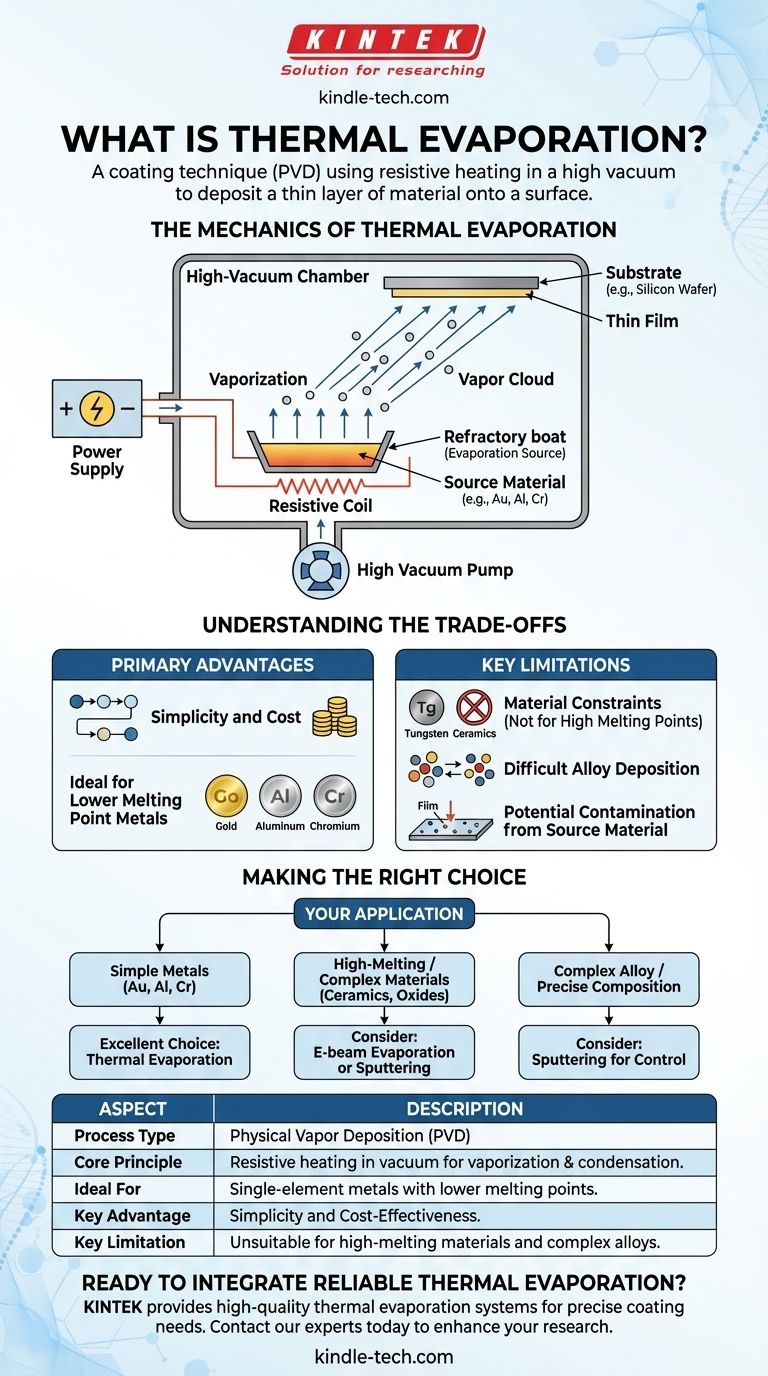
The Mechanics of Thermal Evaporation
To truly understand this process, it's essential to look at the environment it requires, the components involved, and the physics that make it work.
The Core Principle: Phase Transition in a Vacuum
At its heart, evaporation is a phase transition. By heating a material, its atoms or molecules gain enough thermal energy to overcome the forces holding them together in a solid or liquid state.
The process is conducted in a high vacuum for two critical reasons. First, it removes air and other particles that could collide with the vaporized atoms, ensuring they travel in a straight line to the substrate. Second, it eliminates unwanted gases that could react with the vapor and contaminate the final film.
The Key Components
A thermal evaporation system is built from several crucial parts working in concert.
- Vacuum Chamber: Typically made of stainless steel, this chamber houses the entire process and maintains the necessary low-pressure environment.
- Evaporation Source: This is a crucible, boat, or coil made from a refractory material like tungsten or molybdenum, which has a much higher melting point than the material being evaporated. It holds the source material and acts as the heating element.
- Source Material (Evaporant): This is the material you intend to deposit, often in the form of pellets or wire placed in the evaporation source. Common examples include gold (Au), chromium (Cr), and aluminum (Al).
- Substrate: This is the object or surface that you wish to coat with the thin film. It is positioned above the source to intercept the vapor cloud.
- Power Supply: A high-current power supply is connected to the evaporation source, passing electricity through it to generate intense heat via electrical resistance.
The Step-by-Step Process
The deposition follows a clear and repeatable sequence.
- The substrate and source material are loaded into the vacuum chamber.
- The chamber is pumped down to a high vacuum.
- A high electrical current is passed through the resistive boat or coil.
- As the boat heats up, the source material it holds melts and then begins to evaporate, turning directly into a vapor.
- These vaporized atoms travel in a straight line through the vacuum.
- Upon reaching the cooler substrate, the atoms condense back into a solid state, gradually building up a thin, uniform film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, thermal evaporation is not a universal solution. Its simplicity brings both significant advantages and clear limitations that are critical to understand.
The Primary Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
Thermal evaporation is one of the simplest and most cost-effective PVD methods. The equipment is relatively straightforward, and the process is well-suited for depositing a wide range of single-element metals with lower melting points.
The Key Limitation: Material Constraints
The technique's reliance on a heated boat creates a major constraint. It is unsuitable for materials with extremely high melting points, such as ceramics or refractory metals like tungsten, because the boat itself might melt or be damaged before the source material properly evaporates.
The Challenge of Alloy Deposition
Depositing alloys or compound materials consistently is also difficult. Different elements within the alloy will evaporate at different rates based on their unique vapor pressures, leading to a film whose composition does not match the source material.
Potential for Contamination
There is a small but significant risk that the hot crucible material can also evaporate slightly, leading to trace impurities being incorporated into the deposited film. For applications requiring the absolute highest purity, this can be a drawback. This is where a related technique, e-beam evaporation, which uses an electron beam to heat the material directly, often becomes the preferred choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct deposition method depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is depositing simple metals like gold, aluminum, or chromium: Thermal evaporation is an excellent, reliable, and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-melting-point materials, ceramics, or complex oxides: You should consider an alternative like e-beam evaporation or sputtering, which can handle these demanding materials.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex alloy film with precise composition: Thermal evaporation is likely unsuitable, and a technique like sputtering would provide far greater control over the film's final stoichiometry.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental principles allows you to select the most effective and efficient deposition technique for your specific project.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
| Core Principle | Resistive heating of a material in a vacuum causes it to vaporize and condense on a substrate. |
| Ideal For | Single-element metals with lower melting points (e.g., Au, Al, Cr). |
| Key Advantage | Simplicity and cost-effectiveness. |
| Key Limitation | Unsuitable for high-melting-point materials and complex alloys. |
Ready to integrate reliable thermal evaporation into your lab's workflow?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including thermal evaporation systems, to meet your precise coating needs. Whether you are depositing conductive layers for electronics or creating optical coatings, our solutions ensure purity, uniformity, and efficiency.
Let KINTEK empower your research and production. Contact our experts today to discuss how our thermal evaporation equipment can enhance your specific application and deliver the consistent results you require.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is the evaporation process in semiconductors? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications



















