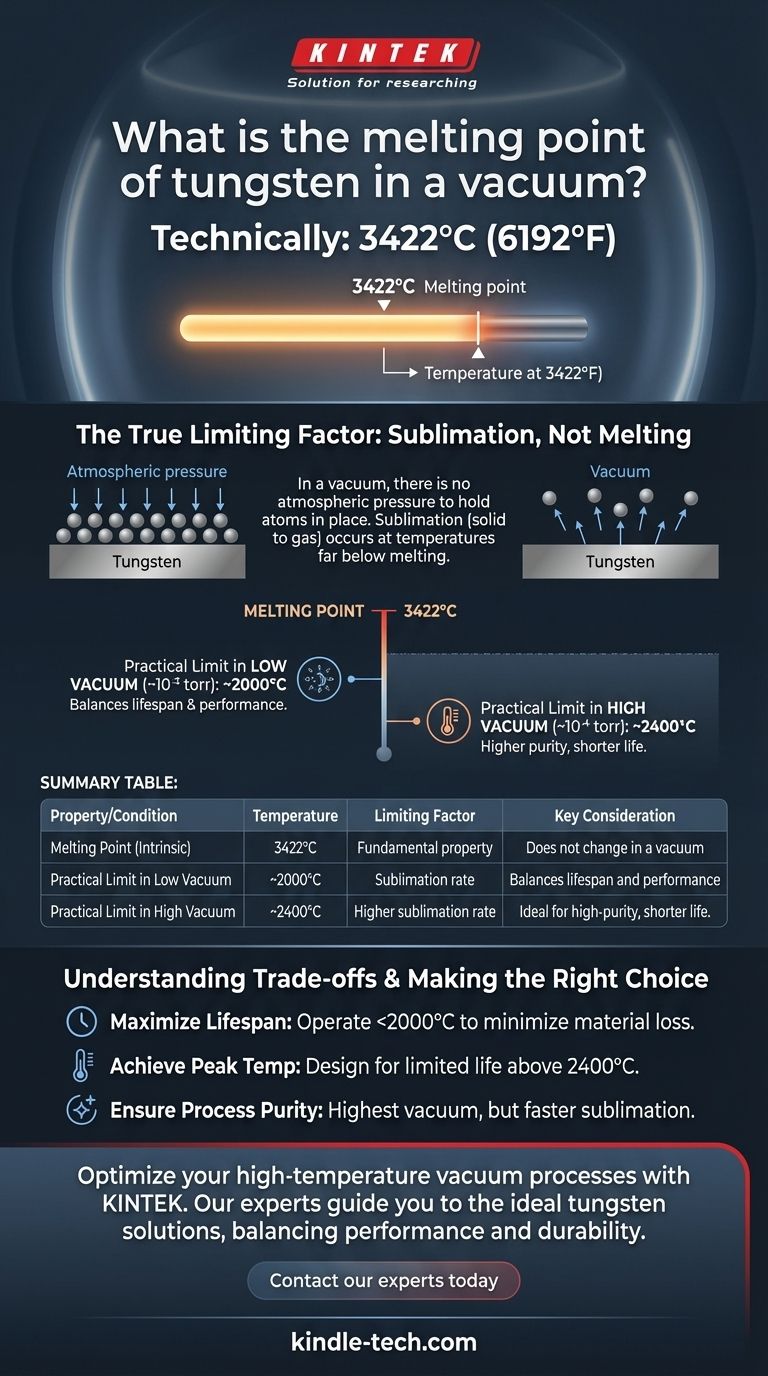
Technically, the melting point of tungsten is 3422°C (6192°F), and this fundamental physical property does not change in a vacuum. However, this value is often misleading in practical applications, as the true limiting factor for tungsten at high temperatures in a vacuum is not melting, but evaporation.
The core issue isn't whether tungsten will melt, but at what temperature it begins to sublimate—turning directly from a solid into a gas. This sublimation process occurs at temperatures far below the actual melting point and dictates tungsten's maximum usable temperature in a vacuum environment.

Melting Point vs. Usable Temperature
Understanding the distinction between a material's melting point and its practical operating temperature is critical for any high-temperature vacuum application.
An Intrinsic Property
The melting point of a pure metal is an intrinsic physical property. It is the specific temperature at which the material transitions from a solid to a liquid state. For tungsten, this is an exceptionally high 3422°C.
The Role of Atmospheric Pressure
Under normal atmospheric pressure, air molecules constantly bombard the surface of the metal. This pressure helps to "hold in" the tungsten atoms, making it more difficult for them to escape the solid structure.
The Critical Factor in a Vacuum: Sublimation
When you remove the atmospheric pressure by creating a vacuum, the behavior of the material at high temperatures changes dramatically.
What is Sublimation?
Sublimation is the process where a substance transitions directly from a solid to a gas, bypassing the liquid phase entirely. Think of it as a form of evaporation for solids.
Why Vacuum Accelerates Sublimation
In a vacuum, there is virtually no external pressure holding the tungsten atoms in place. As the tungsten is heated, its atoms vibrate more energetically until they have enough energy to break free from the surface and enter the vacuum as a gas.
Practical Temperature Limits
This sublimation is why the maximum practical operating temperature of tungsten in a vacuum is significantly lower than its melting point. The rate of material loss due to sublimation increases with both temperature and the quality of the vacuum (lower pressure).
For example, established engineering limits show that tungsten's usable temperature is often capped to control the rate of this material loss. It can be used up to 2000°C in a low vacuum (10⁻² torr) and around 2400°C in a high vacuum (10⁻⁴ torr) before the rate of evaporation becomes problematic for most components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Operating tungsten in a vacuum involves a constant balance between temperature, component lifespan, and process purity.
Temperature vs. Material Longevity
Every increase in temperature exponentially increases the rate of sublimation. Pushing a tungsten heating element closer to its limit means it will degrade faster, requiring more frequent and costly replacement.
Vacuum Level and Performance
A stronger vacuum (lower pressure) is often desired for process purity, as it minimizes contamination from residual air. However, this environment also makes it easier for tungsten atoms to sublimate, which can increase the rate of material loss.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's primary goal determines the ideal operating parameters for tungsten components.
- If your primary focus is maximizing component lifespan: Operate at conservative temperatures, staying well below the 2000°C threshold to minimize material loss from sublimation.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible process temperature: Design for a limited component life, accepting that operating above 2400°C will cause rapid degradation.
- If your primary focus is process purity: Utilize the highest vacuum you can achieve, but be mindful that this will accelerate tungsten sublimation, which could itself become a source of contamination.
Ultimately, managing tungsten in a vacuum is a careful balancing act governed by the physics of sublimation, not melting.
Summary Table:
| Property / Condition | Temperature / Limiting Factor | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point (Intrinsic) | 3422°C (6192°F) | Fundamental property; does not change in a vacuum. |
| Practical Limit in Low Vacuum (~10⁻² torr) | ~2000°C | Sublimation rate becomes significant; balances lifespan and performance. |
| Practical Limit in High Vacuum (~10⁻⁴ torr) | ~2400°C | Higher sublimation rate; ideal for high-purity processes but shorter component life. |
Optimize your high-temperature vacuum processes with KINTEK.
Choosing the right parameters for tungsten components is critical for the success and longevity of your equipment. Whether your priority is maximizing component lifespan, achieving peak temperatures, or ensuring ultimate process purity, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can guide you.
Our specialists can help you select the ideal tungsten-based solutions for your specific vacuum furnace or high-temperature application, ensuring you get the performance and durability you need.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and find the perfect balance for your lab's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the basic of brazing? A Guide to Strong, Low-Heat Metal Joining
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques



















