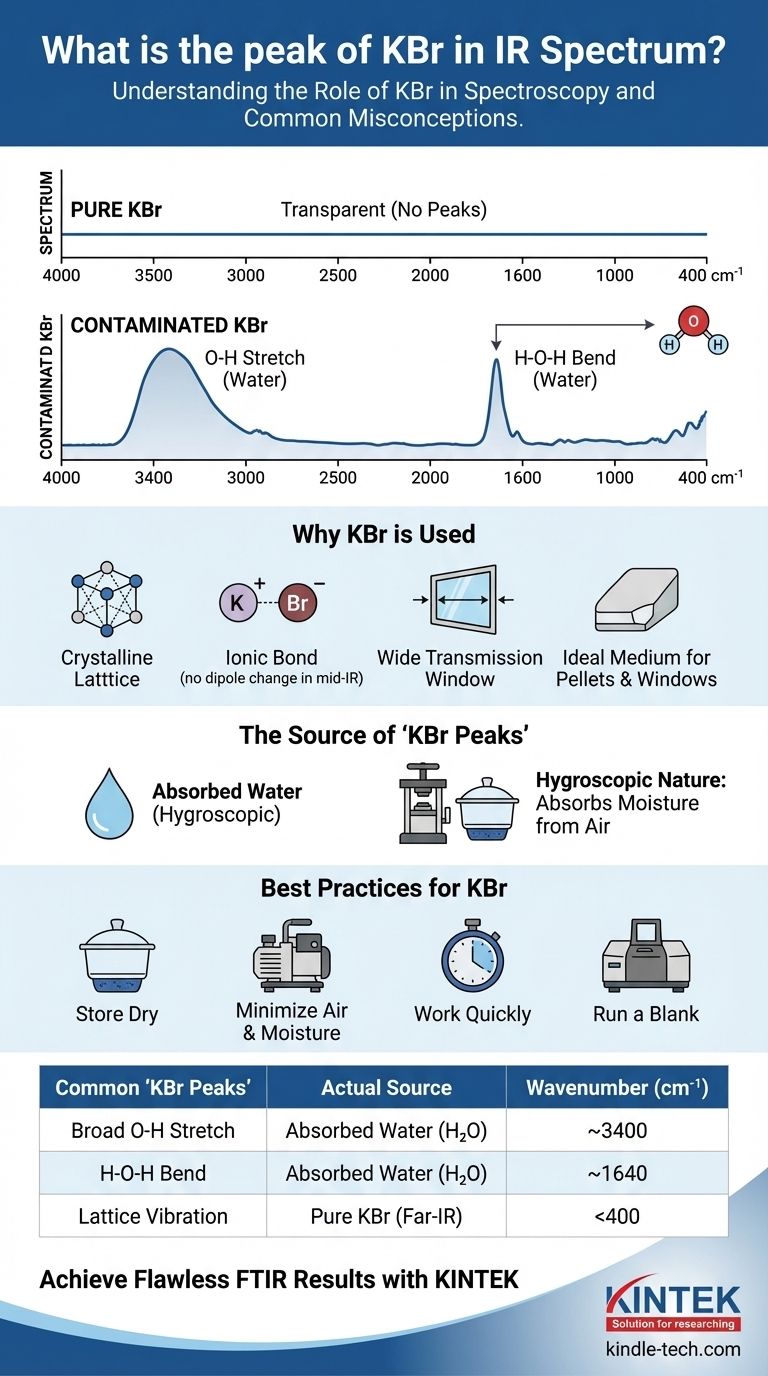
In principle, pure Potassium Bromide (KBr) has no absorption peaks in the standard mid-infrared (IR) range of 4000 cm⁻¹ to 400 cm⁻¹. It is chosen specifically for its transparency in this region. The "peaks" almost universally associated with KBr in a spectrum are not from the KBr itself, but from water (H₂O) that it has absorbed from the atmosphere.
The core issue is a misunderstanding of KBr's role. KBr is not the sample; it is the medium. Its value lies in its IR inactivity, but its tendency to absorb moisture makes it a common source of spectral contamination from water peaks.

Why KBr Is a Standard in IR Spectroscopy
To understand why KBr shouldn't have a peak, we must first understand why it's used so frequently in FTIR analysis, particularly for solid samples.
The Advantage of Ionic Bonds
An IR absorption peak occurs when IR radiation causes a molecule's covalent bonds to vibrate in a way that changes its dipole moment.
The bond between potassium (K⁺) and bromine (Br⁻) is ionic. Pure KBr forms a crystalline lattice structure. The vibrations of this lattice (called phonon modes) occur at very low frequencies, well below the typical 400 cm⁻¹ cutoff of a mid-IR spectrometer.
Therefore, in the analytical region where organic and most inorganic compounds absorb, pure KBr is effectively invisible.
A Wide and Clear Transmission Window
This IR inactivity gives KBr an exceptionally wide and useful transmission window. It allows the radiation from the spectrometer's source to pass through the sample to the detector without introducing interfering signals.
This makes it the ideal material for two main applications:
- KBr Pellets: Mixing a solid sample with KBr powder and pressing it into a transparent disc.
- Optical Windows: Using polished KBr discs as windows in sample cells.
The Source of "KBr Peaks": Contamination, Not KBr
If KBr is transparent, why do analysts so often see peaks in their KBr spectra? The answer is contamination.
The Primary Culprit: Absorbed Water (H₂O)
KBr is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air. This water is the source of the most common "KBr peaks."
- A very broad, strong peak around 3400 cm⁻¹: This is the O-H stretching vibration of the water molecules. It is broad due to hydrogen bonding.
- A sharper, medium-intensity peak around 1640 cm⁻¹: This is the H-O-H bending (scissoring) vibration.
Seeing these two peaks in your spectrum is a classic sign of a "wet" KBr pellet or background.
Other Potential Contaminants
While water is the main issue, other contaminants can appear. For example, a small peak around 1385 cm⁻¹ can sometimes indicate the presence of nitrate (NO₃⁻) impurities. Oils from a grinder or press can also introduce C-H stretching peaks around 2800-3000 cm⁻¹.
The Far-IR Cutoff
As mentioned, KBr does have a true absorption. Its lattice vibration creates a hard cutoff where it is no longer transparent. This occurs at approximately 400 cm⁻¹, marking the lower limit of its useful range.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Best Practices
Using KBr requires careful technique to leverage its benefits without falling victim to its hygroscopic nature.
Store KBr in a Desiccator
Always store spectroscopic-grade KBr powder in a sealed container inside a desiccator. Many labs also use a drying oven (e.g., at 110 °C for several hours) to dry the powder before use.
Minimize Exposure to Air
When preparing a KBr pellet, work quickly. Minimize the time the ground powder is exposed to the humid laboratory air before pressing. Do not breathe on the sample, as your breath is saturated with water vapor.
Use a Vacuum Die
Using a vacuum die to press the pellet helps pull trapped air and moisture out of the KBr matrix, resulting in a clearer, more transparent pellet and a flatter baseline in your spectrum.
Always Run a Blank
Before running your sample, press a pellet of pure KBr from the same batch and run its spectrum. This "blank" or "background" spectrum will show you what contamination (if any) is present in your KBr, allowing you to distinguish these artifacts from your actual sample's peaks.
How to Interpret Your Spectrum
By understanding KBr's properties, you can confidently interpret your results.
- If you see a broad peak near 3400 cm⁻¹ and another near 1640 cm⁻¹: Your KBr has absorbed water, and you should take steps to dry your materials and improve your sample preparation technique.
- If your blank KBr spectrum is a flat line (from 4000 to 400 cm⁻¹): This indicates your KBr is dry and pure, providing a high-quality background for analyzing your sample.
- If you see unexpected peaks not related to water: Run a blank KBr pellet to confirm whether the peaks are from a contaminant in the KBr or are genuine features of your sample.
Understanding your tools is the first step toward generating reliable and accurate data.
Summary Table:
| Common "KBr Peaks" | Actual Source | Wavenumber (cm⁻¹) |
|---|---|---|
| Broad O-H Stretch | Absorbed Water (H₂O) | ~3400 |
| H-O-H Bend | Absorbed Water (H₂O) | ~1640 |
| Lattice Vibration | Pure KBr (Far-IR) | <400 |
Achieve Flawless FTIR Results with KINTEK
Struggling with water peaks and inconsistent baselines in your KBr pellet analysis? KINTEK provides the solutions you need for reliable spectroscopy.
We supply high-purity, spectroscopic-grade KBr powders and pellets, along with vacuum dies and drying ovens, to help you minimize hygroscopic contamination and produce clear, interpretable spectra. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures your laboratory operates with precision and efficiency.
Ready to improve your sample preparation and data quality? Contact our spectroscopy experts today to discuss your specific application needs and discover how KINTEK's consumables and equipment can enhance your FTIR workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- kbr pellet press 2t
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy



















