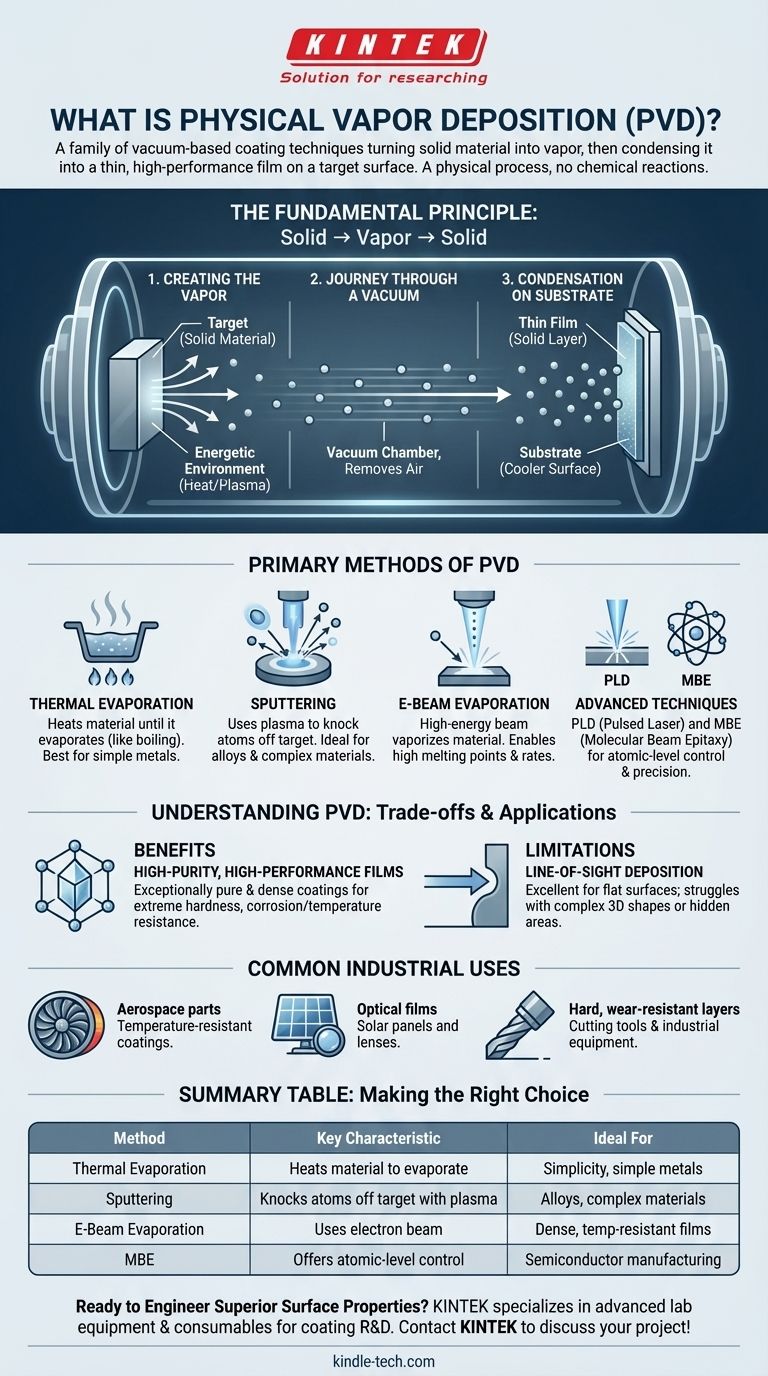
In essence, physical vapor deposition (PVD) is a family of vacuum-based coating techniques where a solid material is vaporized, travels through the vacuum, and condenses onto a target surface to form a very thin, high-performance film. This process uses mechanical or thermodynamic means to transform the material, avoiding any chemical reactions.
The core concept of PVD is not a single process, but a category of methods for turning a solid material into a vapor within a vacuum. This vapor then condenses back into a highly pure and uniform solid layer on a substrate, creating advanced coatings for everything from aerospace components to microchips.
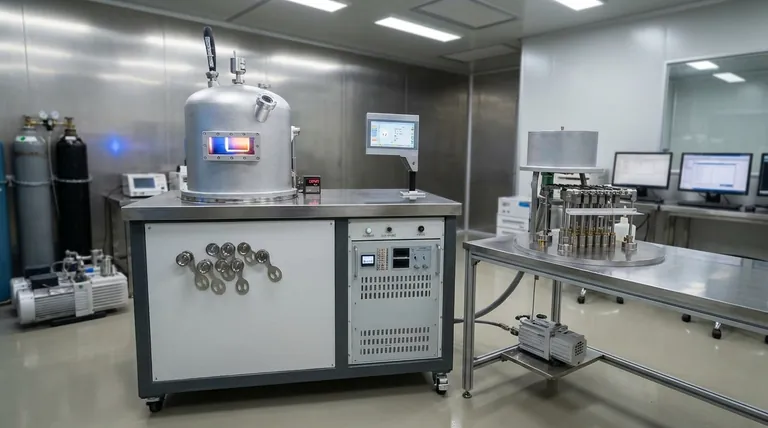

The Fundamental Principle: From Solid to Vapor to Solid
To understand PVD, it's best to think of it as a three-step physical transformation that happens inside a specialized chamber.
Step 1: Creating the Vapor
The process begins with a solid source material, often called the "target." This material is placed into an energetic environment that forces particles to escape from its surface, turning it directly into a gas or vapor.
Step 2: The Journey Through a Vacuum
This entire process occurs within a vacuum chamber. The vacuum is critical because it removes air and other particles, allowing the vaporized material to travel freely in a straight line without colliding with anything.
Step 3: Condensation on the Substrate
Finally, the vaporized particles strike a cooler surface, known as the "substrate." Upon contact, they rapidly cool and condense, forming a thin, solid, and highly adherent film on the substrate's surface.
The Primary Methods of PVD
While the principle is the same, the method used to create the vapor distinguishes the different types of PVD.
Thermal Evaporation
This is a foundational PVD method. The source material is heated in the vacuum until it evaporates, much like boiling water turns to steam. The resulting vapor then coats the substrate.
Sputtering
Sputtering uses electromechanical means rather than just heat. A high-voltage plasma is generated, which accelerates ions to bombard the source material. These collisions physically knock atoms off the target, which then deposit onto the substrate.
Electron-Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
A more precise and powerful version of thermal evaporation, this method uses a high-energy beam of electrons to heat and vaporize the source material. It allows for higher deposition rates and the use of materials with very high melting points.
Advanced Techniques
Other, more specialized methods exist for specific needs. These include Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD), which uses a laser to vaporize the target, and Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE), which offers atomic-level control for creating perfect crystalline films in semiconductor manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
PVD is a powerful technology, but it's important to understand its advantages and limitations to see why it is chosen for specific tasks.
The Benefit: High-Purity, High-Performance Films
Because the process occurs in a vacuum, the resulting coatings are exceptionally pure and dense. This allows for the creation of films with specific desirable properties, such as extreme hardness, corrosion resistance, or temperature resistance.
The Limitation: Line-of-Sight Deposition
A key constraint of PVD is that the vapor travels in straight lines. This means it is excellent for coating flat surfaces but can struggle to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with undercuts or hidden areas.
Common Industrial Uses
PVD's unique capabilities make it essential in many high-tech industries. It is used to apply temperature-resistant coatings on aerospace parts, create optical films for solar panels and lenses, and deposit hard, wear-resistant layers on cutting tools and industrial equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best PVD method depends entirely on the material being deposited and the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and coating a simple metal: Thermal evaporation is often the most direct and cost-effective approach.
- If your primary focus is coating alloys or complex materials without melting them: Sputtering is superior, as it mechanically ejects atoms rather than boiling them.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, temperature-resistant films: E-beam evaporation provides the energy needed for high-performance materials used in aerospace.
- If your primary focus is atomic-level precision for electronics: Advanced methods like MBE are necessary to build the crystalline structures required for semiconductors.
Ultimately, physical vapor deposition is a cornerstone technology for engineering surfaces with properties that the underlying material could never achieve alone.
Summary Table:
| PVD Method | Key Characteristic | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Evaporation | Heats material until it evaporates | Simplicity, coating simple metals |
| Sputtering | Knocks atoms off a target using plasma | Coating alloys or complex materials |
| E-Beam Evaporation | Uses an electron beam for high-energy vaporization | Dense, temperature-resistant films |
| Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE) | Offers atomic-level control | Semiconductor manufacturing, precision electronics |
Ready to Engineer Superior Surface Properties?
PVD technology is essential for creating high-performance coatings that enhance hardness, corrosion resistance, and functionality. Whether you're in aerospace, electronics, or tool manufacturing, selecting the right PVD method is critical.
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for your coating R&D and production needs. Our expertise can help you identify the ideal PVD solution to achieve your specific material goals.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our solutions can advance your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies



















