At its core, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a process that uses the energy of a plasma to deposit high-quality thin films onto a surface at low temperatures. Unlike traditional methods that rely on extreme heat, PECVD introduces precursor gases into a reaction chamber and excites them into a plasma state using an electric field. This plasma contains highly reactive species that then settle and form a solid, uniform film on a substrate, such as a silicon wafer.
The fundamental principle of PECVD is its ability to bypass high thermal energy requirements. It uses a plasma to break down chemical precursors, enabling rapid film deposition on materials that could not withstand the high temperatures of conventional chemical vapor deposition.
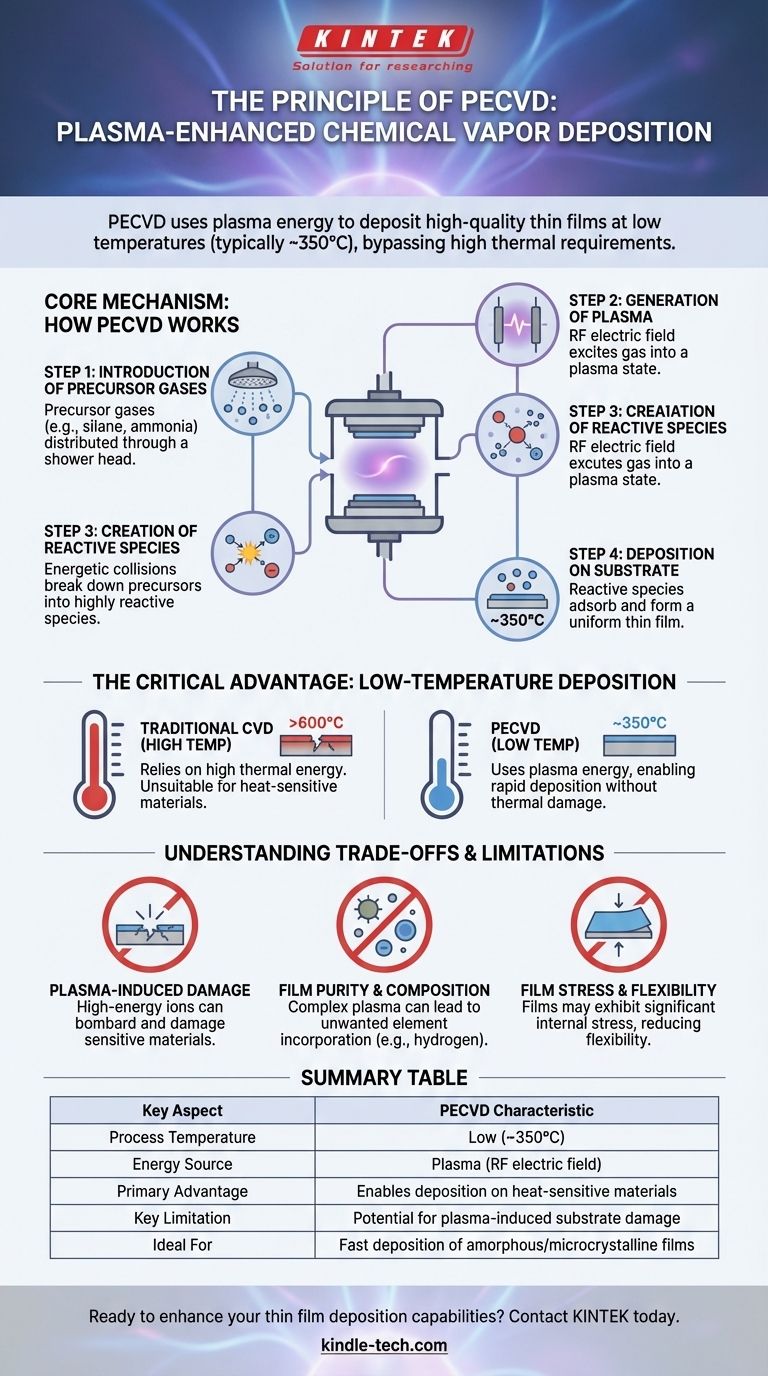
How PECVD Works: The Core Mechanism
The PECVD process can be understood as a sequence of distinct, controlled steps. Each stage is critical for producing a high-quality, uniform thin film.
Step 1: Introduction of Precursor Gases
Precursor gases, which contain the atoms needed for the final film (e.g., silane and ammonia for silicon nitride), are introduced into a vacuum chamber.
To ensure a uniform coating, these gases are often distributed through a perforated plate known as a shower head, which sits directly above the substrate.
Step 2: Generation of Plasma
An electric field, typically a Radio Frequency (RF) voltage, is applied between two electrodes within the chamber.
This electrical energy excites the precursor gas, stripping electrons from the gas molecules and creating a plasma, which is an ionized gas that often emits a characteristic glow.
Step 3: Creation of Reactive Species
Within the plasma, energetic collisions between electrons, ions, and neutral gas molecules break down the stable precursor gases.
This creates a high concentration of chemically reactive species, such as radicals and ions. This step is the "enhancement" in PECVD, as it creates the reactive building blocks for the film without high heat.
Step 4: Deposition on the Substrate
These highly reactive species diffuse toward the substrate, which is typically held at a much lower temperature than in other deposition methods (e.g., around 350°C).
The species adsorb onto the substrate's surface, where they react to form a stable, solid thin film. The byproduct gases are then pumped out of the chamber.
The Critical Advantage: Low-Temperature Deposition
The most significant distinction of PECVD is its ability to operate at low temperatures. Understanding this is key to understanding its value.
Overcoming Thermal Barriers
Traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) relies on high temperatures (often >600°C) to provide the thermal energy needed to break chemical bonds and drive the deposition reaction.
This thermal budget makes it unsuitable for depositing films on materials that are sensitive to heat, such as plastics or fully fabricated electronic devices with delicate components.
Energy Transfer via Plasma
PECVD replaces thermal energy with the energy contained within the plasma. The kinetic energy of the electrons and ions is sufficient to fragment the precursor molecules.
This allows the chemical reaction to proceed at a fraction of the temperature, reducing thermal damage, minimizing stress from mismatched thermal expansion, and preventing unwanted diffusion between the film and the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, PECVD is not without its compromises. A clear-eyed view of its limitations is necessary for making informed decisions.
Potential for Plasma-Induced Damage
The high-energy ions within the plasma can bombard the substrate surface during deposition. For highly sensitive electronic materials, this can cause structural damage that may impair device performance.
This limitation has led to the development of Remote PECVD, where the plasma is generated in a separate chamber to protect the substrate from direct exposure.
Film Purity and Composition
The complex chemical environment of the plasma can sometimes lead to the incorporation of unwanted elements, such as hydrogen from precursor gases, into the deposited film.
This can affect the film's density, optical properties, and electrical characteristics.
Film Stress and Flexibility
PECVD films can exhibit significant internal stress due to the ion bombardment and chemical incorporation during growth.
As noted in some studies, this can result in films that are less flexible than those produced by other methods, like Low-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (LPCVD).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PECVD depends entirely on the requirements of your substrate and the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is depositing on temperature-sensitive substrates: PECVD is an excellent choice due to its fundamentally low-temperature operation.
- If your primary focus is achieving a high deposition rate: PECVD offers a significant speed advantage for producing amorphous or microcrystalline films.
- If your primary focus is minimizing surface damage on delicate materials: You should consider Remote PECVD or an alternative method to avoid the effects of direct plasma bombardment.
Ultimately, PECVD provides a powerful and versatile tool for fabricating advanced thin films precisely where thermal constraints would otherwise make it impossible.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | PECVD Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Low (typically ~350°C) |
| Energy Source | Plasma (RF electric field) |
| Primary Advantage | Enables deposition on heat-sensitive materials |
| Key Limitation | Potential for plasma-induced substrate damage |
| Ideal For | Fast deposition of amorphous/microcrystalline films |
Ready to enhance your thin film deposition capabilities? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including PECVD systems designed for precise, low-temperature processing. Our solutions help researchers and manufacturers deposit high-quality films on sensitive substrates without thermal damage. Contact our experts today to discuss how our PECVD technology can accelerate your materials research and production!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs



















