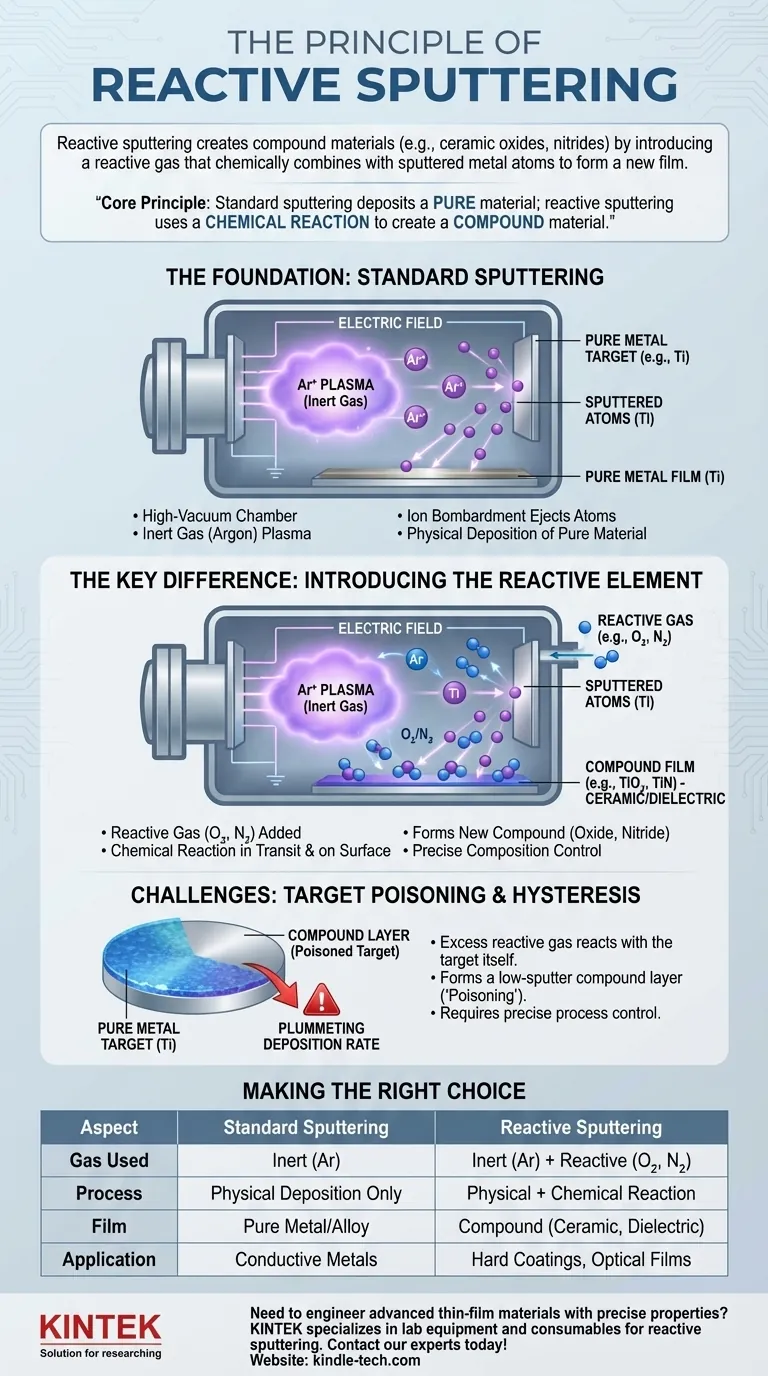
Reactive sputtering is a thin-film deposition process used to create compound materials, such as ceramic oxides or nitrides, on a surface. It modifies the standard sputtering process by intentionally introducing a reactive gas (like oxygen or nitrogen) into the vacuum chamber, which chemically combines with the atoms sputtered from a pure metal target to form a new material on the substrate.
The core principle is simple: standard sputtering deposits a pure material, while reactive sputtering uses a chemical reaction during the process to create a completely different compound material. It transforms a pure metal into a high-performance ceramic coating as the film is being formed.

The Foundation: Understanding Standard Sputtering
To understand reactive sputtering, we must first understand the standard sputtering process. It is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) method that occurs in a high-vacuum chamber.
### The Vacuum Environment
First, a vacuum chamber is pumped down to remove air and other unwanted gases. This ensures the sputtered atoms can travel to the substrate without colliding with contaminants.
### Generating the Plasma
An inert gas, most commonly argon (Ar), is then introduced into the chamber at a low pressure. A strong electric field is applied, which ionizes the argon gas atoms and creates a sustained plasma—a high-energy cloud of ions and electrons.
### The Bombardment Process
The positively charged argon ions from the plasma are accelerated towards and collide with the source material, known as the target (or cathode).
### Deposition on the Substrate
These high-energy collisions physically knock out, or "sputter," atoms from the target. These ejected atoms travel through the vacuum chamber and condense on a substrate, gradually building up a thin film of the pure target material.
The Key Difference: Introducing the Reactive Element
Reactive sputtering builds directly upon this foundation by adding one critical ingredient: a reactive gas.
### The Role of the Reactive Gas
Alongside the inert argon gas, a controlled amount of a reactive gas—typically oxygen (O2) or nitrogen (N2)—is fed into the vacuum chamber.
### The Chemical Reaction
As atoms are ejected from the pure metal target (e.g., Titanium), they travel towards the substrate. During this transit and upon arrival at the substrate surface, they encounter and chemically react with the reactive gas molecules.
### Forming a Compound Film
This chemical reaction forms a new compound. For example, if a Titanium (Ti) target is sputtered in the presence of nitrogen, the deposited film will be Titanium Nitride (TiN), a hard ceramic, instead of pure titanium. Sputtering in oxygen would create Titanium Oxide (TiO2).
### Controlling the Composition
The final chemical composition (stoichiometry) of the film is precisely controlled by managing the flow rates of the inert and reactive gases. This allows for fine-tuning the material's properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, reactive sputtering introduces process complexities that require careful management.
### The "Hysteresis" Effect
The primary challenge is balancing the reaction. If the reactive gas concentration is too high, it won't just react with the sputtered atoms; it will begin to react with the surface of the sputtering target itself.
### Target "Poisoning"
This phenomenon, often called target poisoning, forms a compound layer (e.g., an oxide or nitride) on the target. This compound layer has a much lower sputter rate than the pure metal, causing the deposition rate to suddenly plummet and making the process unstable.
### Process Control Complexity
Effectively running a reactive sputtering process requires sophisticated feedback systems to precisely control the partial pressure of the reactive gas, keeping it in the narrow window between an incomplete reaction and target poisoning.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding between standard and reactive sputtering depends entirely on the material you need to create.
- If your primary focus is depositing pure metals or alloys: Standard sputtering with only an inert gas is the correct and most direct method.
- If your primary focus is creating hard, dielectric, or transparent conductive films: Reactive sputtering is the ideal choice for producing oxides, nitrides, and other ceramic compounds.
- If your primary focus is precise control over a compound's chemical makeup: Reactive sputtering provides the control necessary to fine-tune the stoichiometry and resulting properties of the film.
Ultimately, reactive sputtering is a versatile and powerful technique for engineering advanced materials with specific chemical and physical properties right at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Standard Sputtering | Reactive Sputtering |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Used | Inert gas (e.g., Argon) | Inert gas + Reactive gas (e.g., O₂, N₂) |
| Process | Physical deposition only | Physical + Chemical reaction |
| Resulting Film | Pure metal target material | Compound (e.g., TiN, TiO₂) |
| Key Application | Depositing pure metals/alloys | Creating ceramics, dielectrics, transparent conductors |
Need to engineer advanced thin-film materials with precise properties? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for reactive sputtering and other PVD processes. Our solutions help you create high-performance ceramic coatings like nitrides and oxides with exceptional control and repeatability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's thin-film deposition needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control










