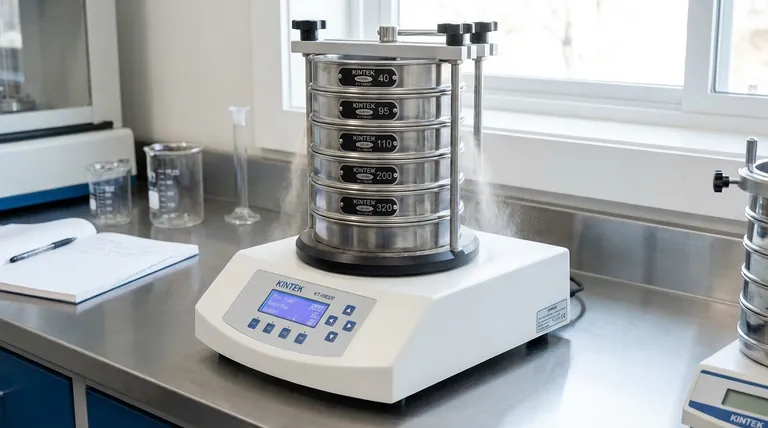
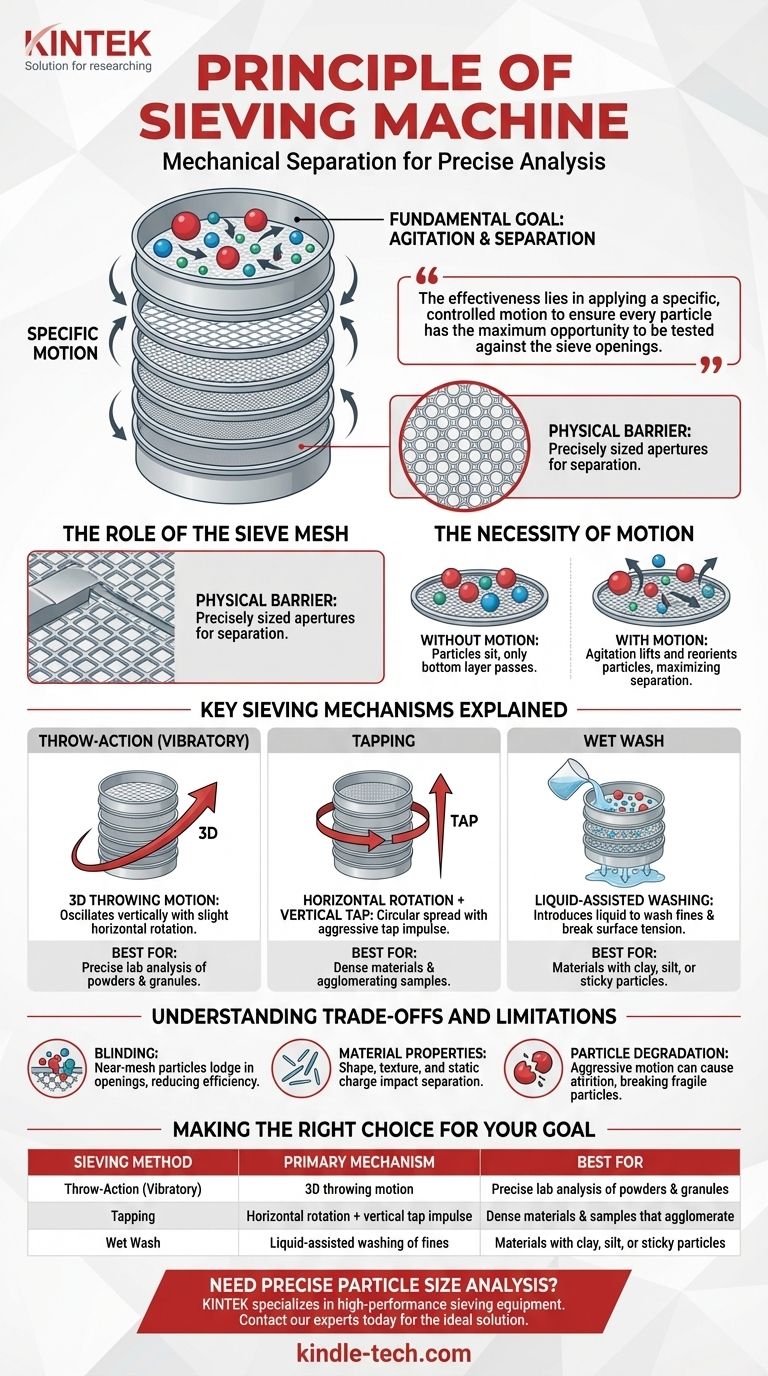
At its core, a sieving machine operates on a simple principle of mechanical separation. It applies a specific motion to a sample, causing relative movement between the particles and a screen, or sieve mesh. Particles smaller than the mesh openings pass through, while larger particles are retained on the surface, achieving effective size-based separation.
The effectiveness of a sieving machine lies not just in shaking a sample, but in applying a specific, controlled motion—be it vibratory, tapping, or wet—to ensure every particle has the maximum opportunity to be tested against the sieve openings.

The Fundamental Goal: Agitation and Separation
The entire process is designed to overcome inertia and inter-particle forces, allowing gravity and geometry to do the work of sorting. Two components are essential: the sieve itself and the motion applied to it.
The Role of the Sieve Mesh
The sieve mesh is the physical barrier that performs the separation. It is a screen with precisely sized and spaced apertures.
A stack of sieves can be used, with the largest mesh openings at the top and progressively smaller ones below, to sort a material into multiple size fractions in a single operation.
The Necessity of Motion
Without motion, a sample would simply sit on the sieve surface, with only the bottom layer having any chance to pass through. Agitation is required to lift and reorient the particles.
This constant movement ensures that each particle repeatedly encounters the mesh surface at different angles, maximizing the probability that it will find an opening if it is small enough to pass.
Key Sieving Mechanisms Explained
Different materials require different types of agitation. The primary distinction between sieving machines is the nature of the motion they impart to the sieve stack.
Throw-Action (Vibratory) Sieving
This is the most common method for laboratory analysis. An electromagnetic drive creates a 3D throwing motion, oscillating the sieve stack vertically while also causing a slight horizontal rotation.
This motion distributes the material evenly across the entire surface of the sieve. The particles are thrown upwards and spin, so when they land, they present a different orientation to the mesh. This is highly effective for most granular and powdered materials.
Modern vibratory shakers allow for digital control of the oscillation amplitude (the height of the "throw"), ensuring the process is precisely repeatable for consistent, reliable analysis.
Tapping Sieving
This method combines a horizontal, circular motion with a sharp vertical "tap" from below. The circular motion spreads the material, while the aggressive tap provides the energy needed to separate particles.
This tapping impulse is particularly effective for breaking up agglomerates (clumps of particles) and for separating dense or heavy materials that are difficult to fluidize with vibration alone.
Wet Wash Sieving
For materials with a high concentration of very fine particles, like clay or silt, dry sieving is often ineffective. These fine particles can adhere to larger particles or clog the sieve mesh.
Wet wash sieving introduces water or another liquid to the process. The liquid helps to wash away the fines, break surface tension, and carry the smaller particles through the mesh, ensuring an accurate separation of the coarser material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sieving is not a perfect process. Understanding its limitations is crucial for accurate interpretation of the results.
The Challenge of Near-Mesh Particles
Particles that are very close in size to the sieve openings can become lodged in the mesh, a phenomenon known as blinding or pegging.
This effectively reduces the open area of the sieve, decreasing its efficiency and potentially skewing the final results. The tapping action in some machines is specifically designed to help dislodge these particles.
Material Properties Matter
The shape and texture of particles significantly impact sieving. Long, needle-like or flat, flaky particles may not pass through a mesh opening even if their volume or mass is small enough.
Furthermore, materials that carry a static charge or are naturally sticky can be extremely difficult to sieve, as they tend to clump together and resist separation.
The Risk of Particle Degradation
The aggressive motion of sieving, especially with tapping shakers, can cause fragile particles to break down. This process, known as attrition, creates more fine particles and will lead to an inaccurate measurement of the original particle size distribution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal sieving method is dictated entirely by your material's characteristics and your analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is highly reproducible lab analysis of powders or granules: Choose a throw-action (vibratory) sieve shaker for its precise digital control and uniform particle distribution.
- If your primary focus is separating dense materials or samples that tend to agglomerate: A tapping sieve shaker provides the aggressive energy needed to break up clumps and fluidize the material.
- If your primary focus is accurately sizing aggregates mixed with clay, silt, or other fines: Wet wash sieving is the only reliable method to clean the particles and prevent mesh blinding.
By matching the machine's principle of motion to your material's properties, you ensure an accurate and efficient particle separation.
Summary Table:
| Sieving Method | Primary Mechanism | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Throw-Action (Vibratory) | 3D throwing motion for even distribution | Precise lab analysis of powders & granules |
| Tapping | Horizontal rotation + vertical tap impulse | Dense materials & samples that agglomerate |
| Wet Wash | Liquid-assisted washing of fines | Materials with clay, silt, or sticky particles |
Need precise particle size analysis for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance sieving equipment and consumables for accurate material separation. Whether you're working with fine powders, dense aggregates, or challenging samples, our range of vibratory, tapping, and wet wash sieve shakers ensures reliable, repeatable results. Contact our experts today to find the ideal sieving solution for your specific application and enhance your laboratory's efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance



















