At its core, sputtering is a physical deposition process where atoms are ejected from a solid target material by bombarding it with high-energy ions inside a vacuum. These ejected atoms then travel and condense onto a substrate, forming an extremely thin and uniform coating. Think of it as a microscopic game of billiards, where an energetic ion is the cue ball striking a rack of target atoms, knocking them loose to land precisely where you need them.
Sputtering is not a chemical reaction but a momentum transfer process. It uses ionized gas in a vacuum to physically dislodge atoms from a source material, allowing for the controlled deposition of pure, high-quality thin films that would be difficult or impossible to create with heat-based methods.
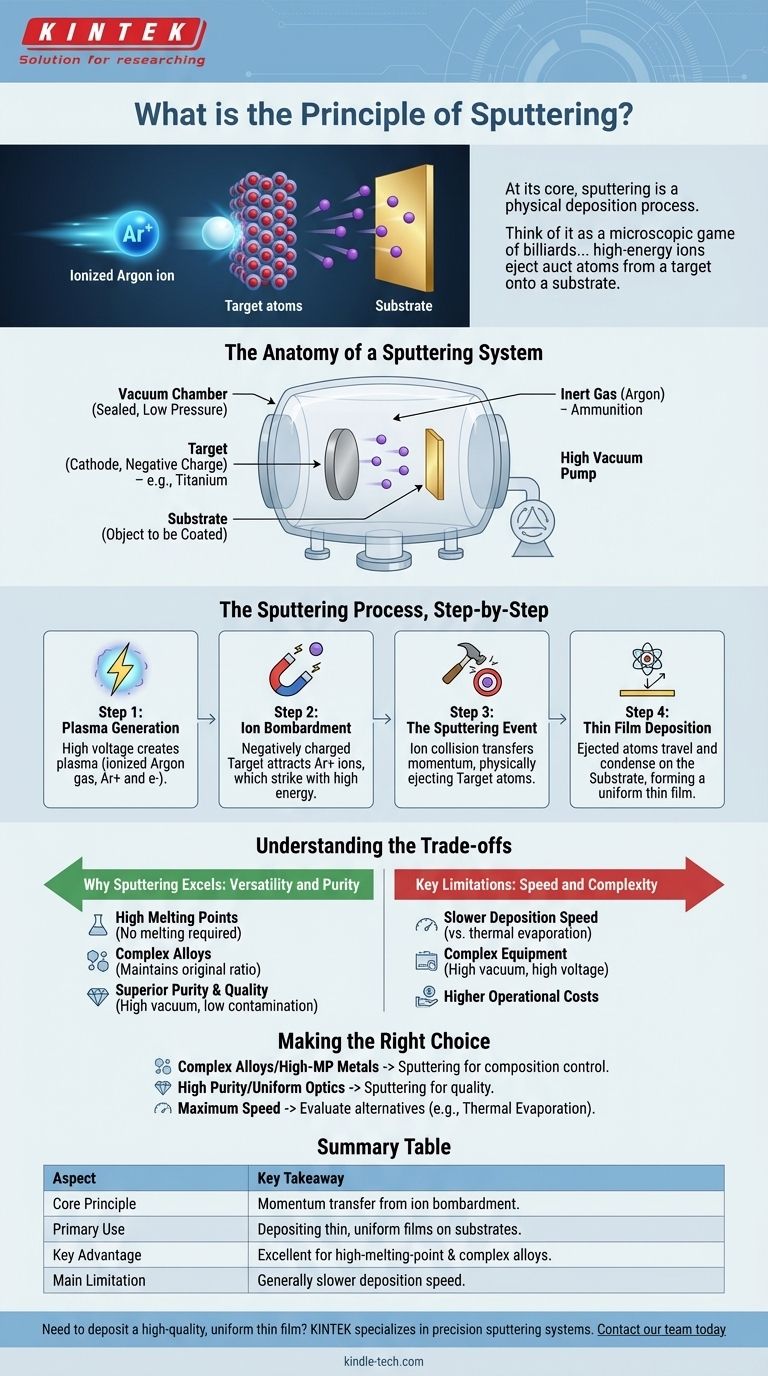
The Anatomy of a Sputtering System
To understand the principle, we must first understand the environment and the key players involved. Every sputtering process occurs within a highly controlled system.
The Vacuum Chamber
The entire process takes place in a sealed chamber. The first step is to pump out almost all the air to create a high vacuum, which removes moisture, dust, and other impurities that could contaminate the final film.
The Target
The target is a solid piece of the material you want to deposit—for example, a block of titanium, gold, or a specific alloy. It acts as the source for the thin film and is given a negative electrical charge, making it the cathode.
The Substrate
The substrate is the object you wish to coat, such as a silicon wafer, a piece of glass, or a medical implant. It is positioned to face the target and collect the ejected atoms.
The Inert Gas
An inert gas, most commonly Argon (Ar), is pumped into the vacuum chamber at a very low pressure. This gas will not react chemically with the target material; its only role is to be the "ammunition" for the bombardment.
The Sputtering Process, Step-by-Step
With the components in place, the process unfolds in a precise sequence to create the atomic-level deposition.
Step 1: Plasma Generation
A high voltage is applied within the chamber. This powerful electric field strips electrons from the Argon gas atoms, creating a plasma—a glowing, ionized gas consisting of positively charged Argon ions (Ar+) and free electrons.
Step 2: Ion Bombardment
Because the target is negatively charged (cathode), it strongly attracts the positively charged Argon ions from the plasma. These ions accelerate toward the target at high speeds, striking its surface with significant kinetic energy.
Step 3: The Sputtering Event
When an energetic ion collides with the target, it transfers its momentum to the target's atoms. If the energy transferred is greater than the forces holding the target's atoms together (their binding energy), one or more atoms are physically knocked loose and ejected from the surface.
Step 4: Thin Film Deposition
These newly freed target atoms travel in a straight line through the low-pressure chamber until they strike the substrate. Upon arrival, they condense and build up on the substrate's surface, forming a dense, uniform thin film, often just a few nanometers thick.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sputtering is a powerful technique, but its value is best understood by recognizing its strengths and limitations compared to other deposition methods like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or thermal evaporation.
Why Sputtering Excels: Versatility and Purity
Sputtering is exceptionally good for depositing materials with very high melting points, as it doesn't rely on melting the source material. It is also a superior method for depositing complex alloys because the atoms are ejected in their original ratio, ensuring the thin film has the same composition as the target.
Key Limitations: Speed and Complexity
The sputtering process is generally slower than thermal evaporation, which can be a factor in high-volume manufacturing. The equipment is also complex, requiring high-vacuum systems and high-voltage power supplies, which can increase operational costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core principle of sputtering allows you to determine when it is the most effective tool for a specific engineering or research challenge.
- If your primary focus is depositing complex alloys or high-melting-point metals: Sputtering provides excellent control over film composition where heat-based methods fail.
- If your primary focus is creating highly pure and uniform coatings for optics or electronics: The high-vacuum nature of sputtering minimizes contamination and ensures superior film quality.
- If your primary focus is maximum deposition speed: You may need to evaluate sputtering against potentially faster methods like thermal evaporation, depending on the material and quality requirements.
Ultimately, sputtering is a foundational tool in modern materials science, offering precise physical control over the creation of thin films, one atom at a time.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Momentum transfer from ion bombardment ejects atoms from a target. |
| Primary Use | Depositing thin, uniform films on substrates like silicon wafers. |
| Key Advantage | Excellent for high-melting-point materials and complex alloys. |
| Main Limitation | Generally slower deposition speed compared to some other methods. |
Need to deposit a high-quality, uniform thin film? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including sputtering systems, to help you achieve superior results for your research or production needs. Our experts can help you select the right configuration for your specific materials and substrates. Contact our team today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods



















