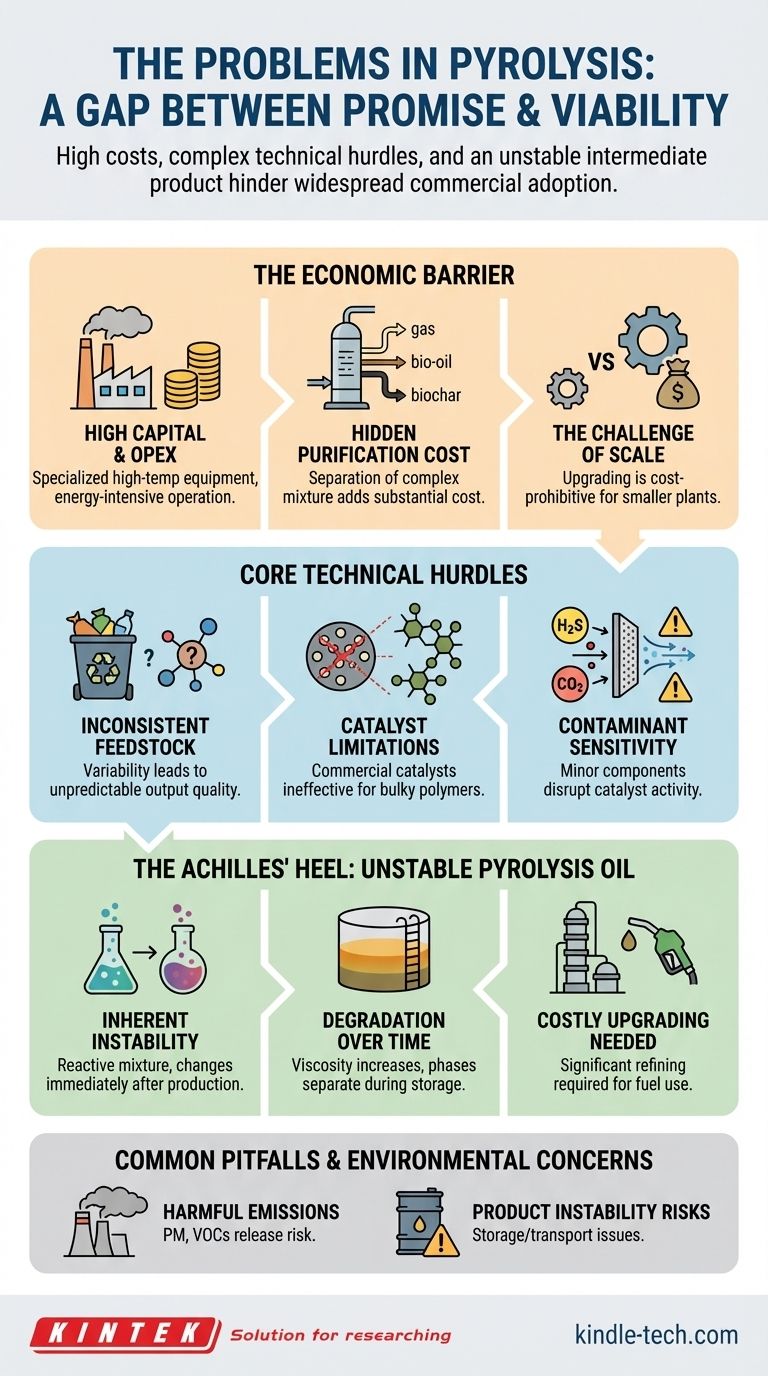
The fundamental problem with pyrolysis is the significant gap between its theoretical promise and its practical, commercial viability. The process is challenged by a combination of high costs, complex technical hurdles in scaling and operation, and the production of an unstable, low-quality intermediate product that requires expensive upgrading.
While pyrolysis is an effective thermochemical process for converting waste into energy, its widespread adoption is hindered by a trio of interconnected challenges: unfavorable economics, process control difficulties, and the inherent instability of its primary liquid product, bio-oil.

The Economic Barrier: Why Pyrolysis Struggles to Compete
The financial case for pyrolysis is often difficult to justify. The high costs are not a single issue but a series of compounding expenses that accumulate throughout the process.
High Capital & Operating Costs
Pyrolysis requires specialized equipment capable of handling high temperatures, which leads to significant initial investment. Furthermore, the process is energy-intensive, demanding sustained heat and long residence times, which results in high ongoing operational costs.
The Hidden Cost of Purification
The output of pyrolysis is not a clean, ready-to-use product. It's a mixture of gas, liquid (bio-oil), and solid (biochar) that requires efficient separation and purification. This downstream processing adds substantial cost and complexity to the overall operation.
The Challenge of Scale
The economics become even more difficult for smaller plants. The complexity and operational challenges of upgrading pyrolysis products to higher-value chemicals are often too expensive to justify at a small scale, making cost-effectiveness a major obstacle.
Core Technical Hurdles in the Process
Beyond the costs, fundamental engineering and chemical challenges must be overcome to run a reliable and efficient pyrolysis operation.
Inconsistent Feedstock
The composition of biomass and other waste streams can vary significantly. This feedstock variability directly affects the quality and composition of the final products, making it difficult to achieve consistent, predictable output.
Catalyst Limitations
Commercial catalysts, such as those based on silicon and zeolites, are optimized for smaller petrochemical molecules. The bulky, complex polymers found in biomass are often too large for the narrow pores of these catalysts, limiting their effectiveness and efficiency in biomass pyrolysis.
Contaminant Sensitivity
The process can be sensitive to minor components within the feedstock. Elements like ethane, propane, H2S, or CO2 can negatively impact a catalyst's activity and stability, disrupting the entire system.
The Achilles' Heel: Unstable Pyrolysis Oil
Perhaps the most significant challenge is the nature of the primary liquid product itself. Bio-oil is not a direct substitute for crude oil and has several critical flaws.
Inherent Chemical Instability
Pyrolysis oil is a complex mixture of reactive, intermediate decomposition products. It is not a stable substance and begins to change almost immediately after it is produced.
Degradation Over Time
During storage, bio-oil slowly degrades through condensation reactions. This causes a gradual increase in viscosity and can even lead to phase separation, where the oil separates into unusable layers.
The Need for Costly Upgrading
The instability, high oxygen content, and acidity of bio-oil mean it almost always requires significant refining or "upgrading" before it can be used as a transportation fuel. This extra step makes the overall fuel production process less cost-effective.
Common Pitfalls and Environmental Concerns
A realistic assessment of pyrolysis must also account for its operational risks and potential environmental impact.
Risk of Harmful Emissions
If not properly managed, the process can release pollutants into the atmosphere. These include fine particulate matter and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are environmental and health concerns.
Overlooking Product Instability
A common mistake is treating bio-oil as a finished product. Its tendency to thicken and degrade means it cannot be stored or transported like conventional fuels without risking equipment fouling and product loss.
How to Evaluate Pyrolysis for Your Application
Successfully implementing a pyrolysis project requires matching the technology's capabilities with a clear, well-defined goal.
- If your primary focus is large-scale fuel production: The economic viability hinges on securing a consistent, low-cost feedstock and integrating an efficient, on-site upgrading process.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Prioritize robust system designs that can tolerate feedstock variability and have a clear, immediate use-case or disposal plan for the unstable bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is producing high-value chemicals: Be prepared for highly complex and expensive downstream purification processes that are typically only feasible at a significant industrial scale.
Understanding these fundamental challenges is the first step toward developing a truly viable and sustainable pyrolysis operation.
Summary Table:
| Challenge Category | Key Issue | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Barrier | High capital & operating costs, expensive purification | Difficult to compete with traditional fuels |
| Technical Hurdles | Inconsistent feedstock, catalyst limitations, contaminant sensitivity | Unreliable and inefficient operations |
| Product Quality | Bio-oil is chemically unstable and degrades over time | Requires costly upgrading before use |
| Environmental & Operational | Risk of harmful emissions, product instability during storage | Adds complexity and potential liabilities |
Ready to overcome your pyrolysis challenges? KINTEK specializes in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables to help you optimize your pyrolysis processes, from R&D to scale-up. Our solutions are designed to handle high temperatures and complex reactions, giving you the reliability and data you need to improve yield and product stability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application and help you achieve a more viable operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs


















