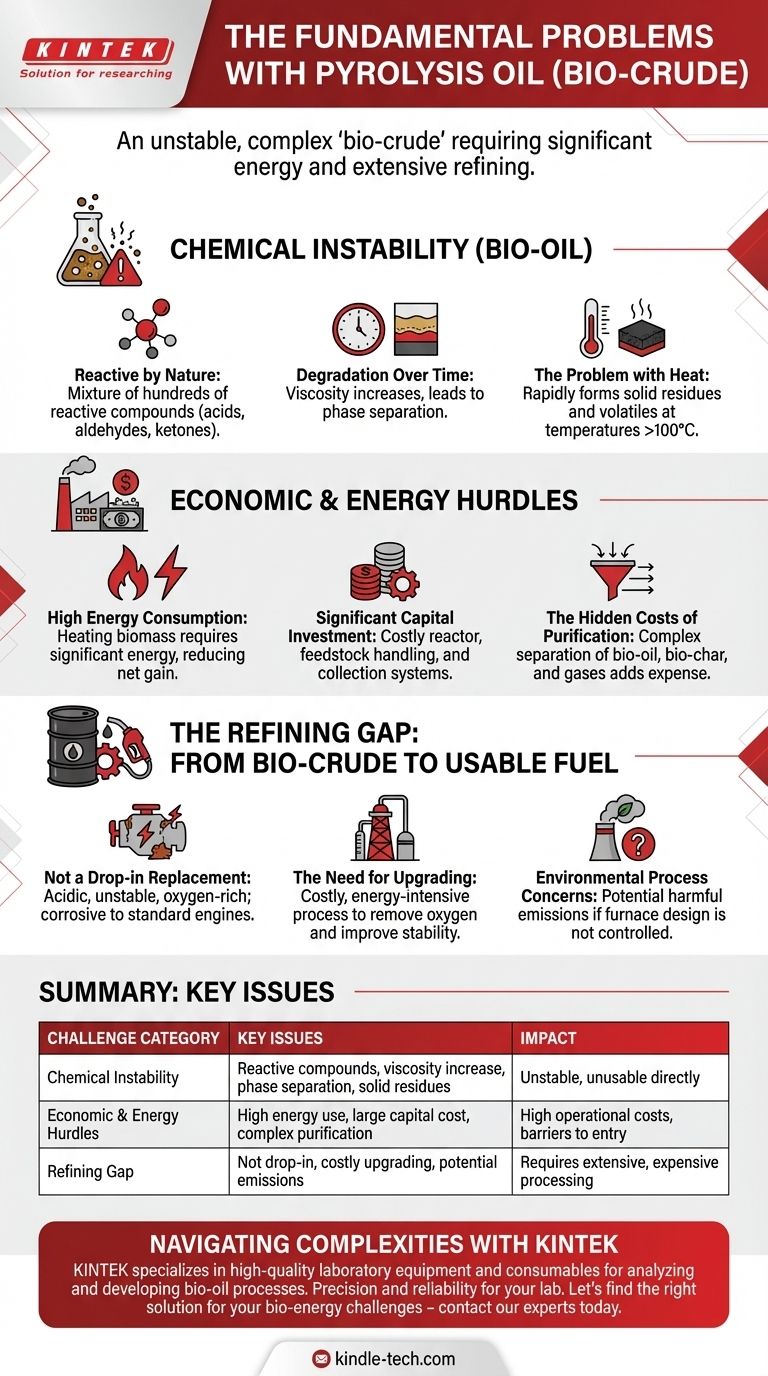
The fundamental problem with pyrolysis oil is that it is an unstable, chemically complex "bio-crude" that requires significant energy to produce and extensive refining before it can be used as a practical fuel. While a promising concept for converting waste to energy, it faces major hurdles in its chemical properties, production economics, and processing requirements.
While pyrolysis offers a way to turn biomass into a liquid energy carrier, the resulting oil is not a finished product. Its inherent instability and the high costs of production and upgrading are the primary barriers preventing its widespread adoption.

The Challenge of Chemical Instability
The most immediate problem with pyrolysis oil, also known as bio-oil, is its chemical nature. It is not a refined, stable product like diesel or gasoline.
Reactive by Nature
Pyrolysis oil is a mixture of hundreds of different organic compounds that are intermediate products of decomposition. Many of these compounds are highly reactive, including acids, aldehydes, and ketones.
Degradation Over Time
This reactivity means the oil is not stable during storage. Over time, these compounds react with each other, causing the oil's viscosity to gradually increase. This can eventually lead to phase separation, where the oil separates into unusable layers.
The Problem with Heat
Heating the oil, which is necessary for many fuel applications, accelerates these reactions dramatically. Temperatures of 100°C can cause the oil to rapidly form solid residues and volatile organic compounds, making it difficult to use in standard engines or burners without modification.
Understanding the Economic and Energy Hurdles
Beyond the oil's chemistry, the process of creating it is fraught with economic and energetic challenges that limit its viability, especially at smaller scales.
High Energy Consumption
The pyrolysis process requires heating biomass to high temperatures in the absence of oxygen. Maintaining these temperatures for the required duration consumes a significant amount of energy, which can negatively impact the net energy gain of the entire system.
Significant Capital Investment
The equipment and machinery required for a pyrolysis plant, including the reactor, feedstock handling, and product collection systems, are costly. This high initial capital cost is a major barrier to entry.
The Hidden Costs of Purification
The output of a pyrolysis reactor is not just oil; it's a mixed stream of liquid bio-oil, solid bio-char, and combustible gases. Efficiently separating and purifying these end products is a complex and expensive step that adds to the overall operational cost.
The Refining Gap: From Bio-Crude to Usable Fuel
A common misconception is that pyrolysis oil can be used directly as a transportation fuel. In reality, it is a "bio-crude" that is incompatible with modern engines without extensive upgrading.
Not a Drop-in Replacement
The acidic, unstable, and oxygen-rich nature of raw pyrolysis oil makes it corrosive and unsuitable for use in standard engines. It cannot simply be blended with conventional fuels.
The Need for Upgrading
To become a viable transportation fuel, the bio-oil must undergo further refining. This process, often called upgrading, is necessary to remove oxygen, reduce acidity, and improve stability, making it a costly and energy-intensive prerequisite.
Environmental Process Concerns
While often touted as environmentally friendly, the pyrolysis process itself can produce harmful emissions if not properly managed. The furnace design and operation must be carefully controlled to minimize air quality impacts, adding another layer of operational complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these challenges is critical for determining if pyrolysis is a suitable technology for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, drop-in fuel production: Be prepared for significant capital investment in both the core pyrolysis unit and the essential downstream refining infrastructure.
- If your primary focus is localized waste-to-energy: The oil's instability means it must likely be used on-site and quickly, making storage and transport a critical design constraint.
- If your primary focus is producing specialty chemical feedstocks: The complex purification stage is unavoidable and must be factored in as a major operational cost and technical challenge.
Ultimately, the viability of pyrolysis oil hinges on successfully navigating its inherent chemical, economic, and processing complexities.
Summary Table:
| Challenge Category | Key Issues |
|---|---|
| Chemical Instability | Reactive compounds, viscosity increase, phase separation, solid residue formation upon heating. |
| Economic & Energy Hurdles | High energy consumption, significant capital investment, complex purification costs. |
| Refining Gap | Not a drop-in fuel, requires costly upgrading to be engine-compatible, potential environmental emissions. |
Navigating the complexities of pyrolysis oil requires the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables for analyzing and developing bio-oil processes. Whether you are researching chemical stability, optimizing production, or testing upgrading methods, our solutions provide the precision and reliability your lab needs. Let's find the right solution for your bio-energy challenges – contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas










