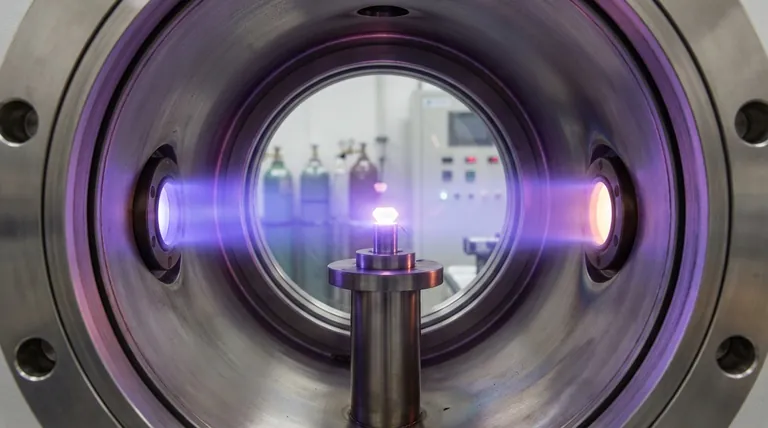
The process of creating a CVD diamond is a method of atomic construction. It begins by placing a small diamond "seed" crystal into a vacuum chamber, which is then heated and filled with a mixture of hydrogen and a carbon-containing gas like methane. A source of energy, typically microwaves, energizes the gas into a plasma, breaking the molecules apart and freeing carbon atoms. These carbon atoms then deposit onto the diamond seed, extending its crystal lattice and growing a larger, high-purity diamond atom by atom over several weeks.
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is not about mimicking the earth's pressure but about meticulously building a diamond from the ground up. The true genius of the process lies in using hydrogen gas as a purifier to selectively etch away any non-diamond carbon, ensuring only a perfect crystal structure is formed.
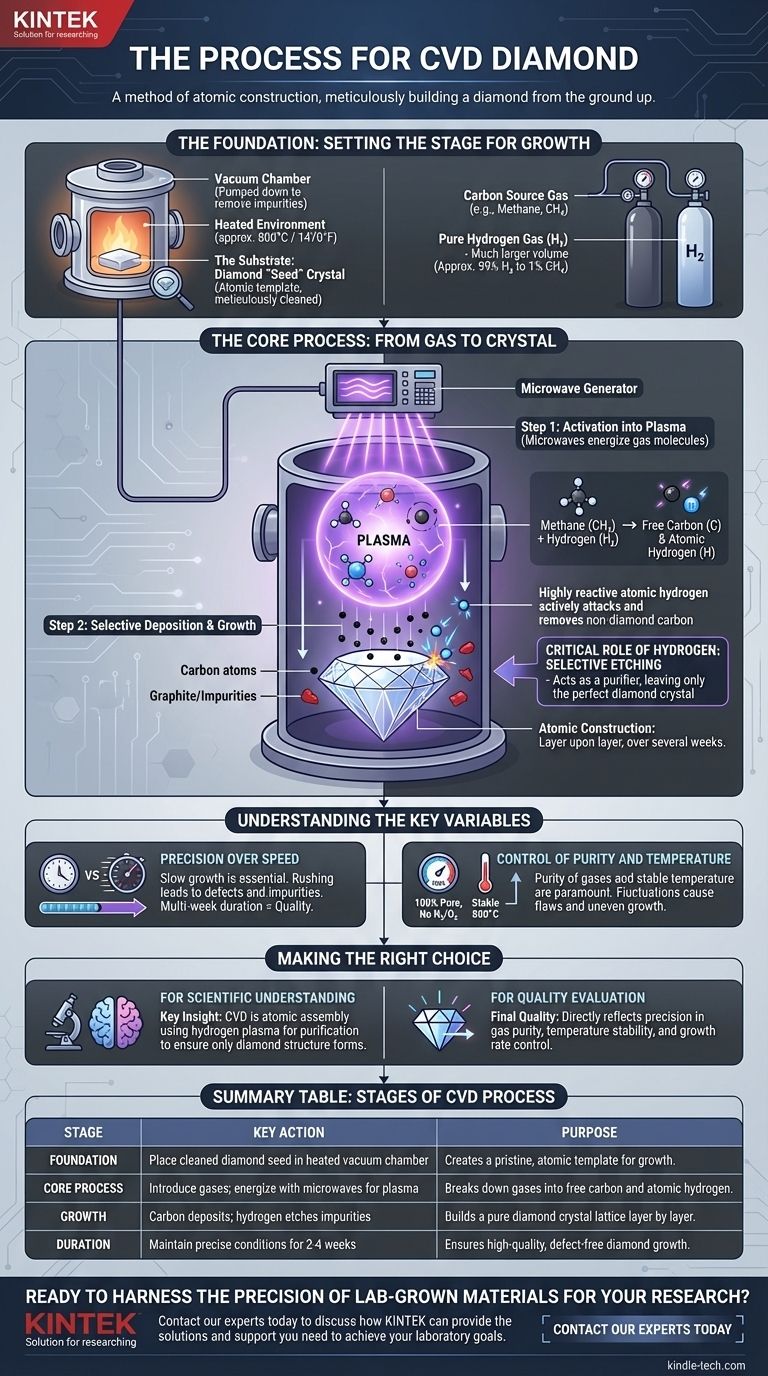
The Foundation: Setting the Stage for Growth
The quality of a CVD diamond is determined long before the growth process even begins. The initial setup requires an environment of extreme precision and cleanliness.
The Substrate: The 'Seed' Crystal
The entire process starts with a substrate, which is almost always a thin slice of a high-quality existing diamond, either natural or lab-grown. This "seed" provides the atomic template for the new diamond to grow upon.
Before being placed in the reactor, this seed must be meticulously cleaned to remove any microscopic contaminants that could disrupt the crystal growth.
The Chamber: A Controlled Environment
The diamond seed is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber. The chamber is pumped down to remove all air and impurities, creating a pristine environment.
Once sealed, the chamber is heated to a precise temperature, typically around 800°C (1,470°F). This temperature is high enough to facilitate the necessary chemical reactions but low enough to avoid the formation of graphite.
The Ingredients: Carbon and Hydrogen Gas
The primary ingredients are introduced into the chamber in a carefully controlled ratio. These are a carbon-source gas (usually methane, CH₄) and a much larger volume of pure hydrogen (H₂) gas.
A common ratio is approximately 99% hydrogen to 1% methane. This hydrogen-rich mixture is fundamental to the success of the process.
The Core Process: From Gas to Crystal
With the stage set, the active growth phase begins. This is a sequence of chemical reactions at the atomic level, managed by energizing the gases.
Step 1: Activation into Plasma
Energy, most commonly in the form of microwaves, is beamed into the chamber. This energy is powerful enough to strip electrons from the gas molecules, creating a glowing ball of superheated gas known as plasma.
Within this plasma, the methane (CH₄) and hydrogen (H₂) molecules break down into their constituent atoms: free carbon (C) and atomic hydrogen (H).
Step 2: Selective Deposition
The free carbon atoms are naturally drawn to the relatively cooler surface of the diamond seed crystal. There, they bond with the seed's existing carbon atoms, perfectly aligning with its crystal lattice structure.
This process repeats continuously, adding layer upon layer of carbon atoms and "growing" the diamond in size. The entire growth cycle can take two to four weeks, depending on the desired size and quality.
The Critical Role of Hydrogen
The abundance of hydrogen is not accidental; it is the key to creating high-purity diamond. As carbon atoms rain down on the substrate, some may try to form weaker, non-diamond bonds (like graphite).
The highly reactive atomic hydrogen in the plasma acts as a chemical "purifier." It selectively etches, or cleans away, any graphite or other non-diamond carbon formations much faster than it etches diamond, leaving only the pure, correctly bonded diamond crystal to grow.
Understanding the Key Variables
The CVD process is a delicate balance of multiple factors. A failure to control any one of them can compromise the final product, leading to inclusions, structural flaws, or undesirable color.
Precision Over Speed
CVD is an intentionally slow process. Attempting to accelerate growth by altering gas ratios or increasing carbon concentration often results in the formation of more defects and non-diamond carbon, overwhelming the hydrogen's ability to purify the crystal. The multi-week duration is a necessary trade-off for quality and control.
Control of Purity and Temperature
The purity of the introduced gases is paramount. Any contaminants, such as nitrogen or oxygen, can be incorporated into the diamond's crystal structure, impacting its color and clarity.
Likewise, maintaining a stable temperature across the substrate is crucial. Fluctuations can cause uneven growth or internal stress, which may require the diamond to be treated after growth to improve its quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the fundamentals of the CVD process empowers you to evaluate the technology and its resulting products more effectively.
- If your primary focus is scientific understanding: The key insight is that CVD is an atomic assembly process defined by the use of a hydrogen plasma to selectively etch away impurities, ensuring only the desired diamond crystal structure forms.
- If your primary focus is quality evaluation: The final diamond's clarity, color, and structural integrity are a direct reflection of the precision used during the growth process—specifically the control over gas purity, temperature stability, and growth rate.
By mastering the manipulation of gases and energy, the CVD process transforms simple carbon atoms into one of nature's most extraordinary materials.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Foundation | Place a cleaned diamond seed in a heated vacuum chamber. | Creates a pristine, atomic template for growth. |
| Core Process | Introduce methane/hydrogen gas; energize with microwaves to create plasma. | Breaks down gases into free carbon and atomic hydrogen. |
| Growth | Carbon atoms deposit onto the seed; hydrogen etches away non-diamond carbon. | Builds a pure diamond crystal lattice layer by layer. |
| Duration | Maintain precise conditions for 2-4 weeks. | Ensures high-quality, defect-free diamond growth. |
Ready to harness the precision of lab-grown materials for your research?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the advanced equipment and consumables that power cutting-edge laboratory processes like CVD. Whether you are developing new materials or require reliable lab supplies, our expertise supports your innovation.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can provide the solutions and support you need to achieve your laboratory goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs


















