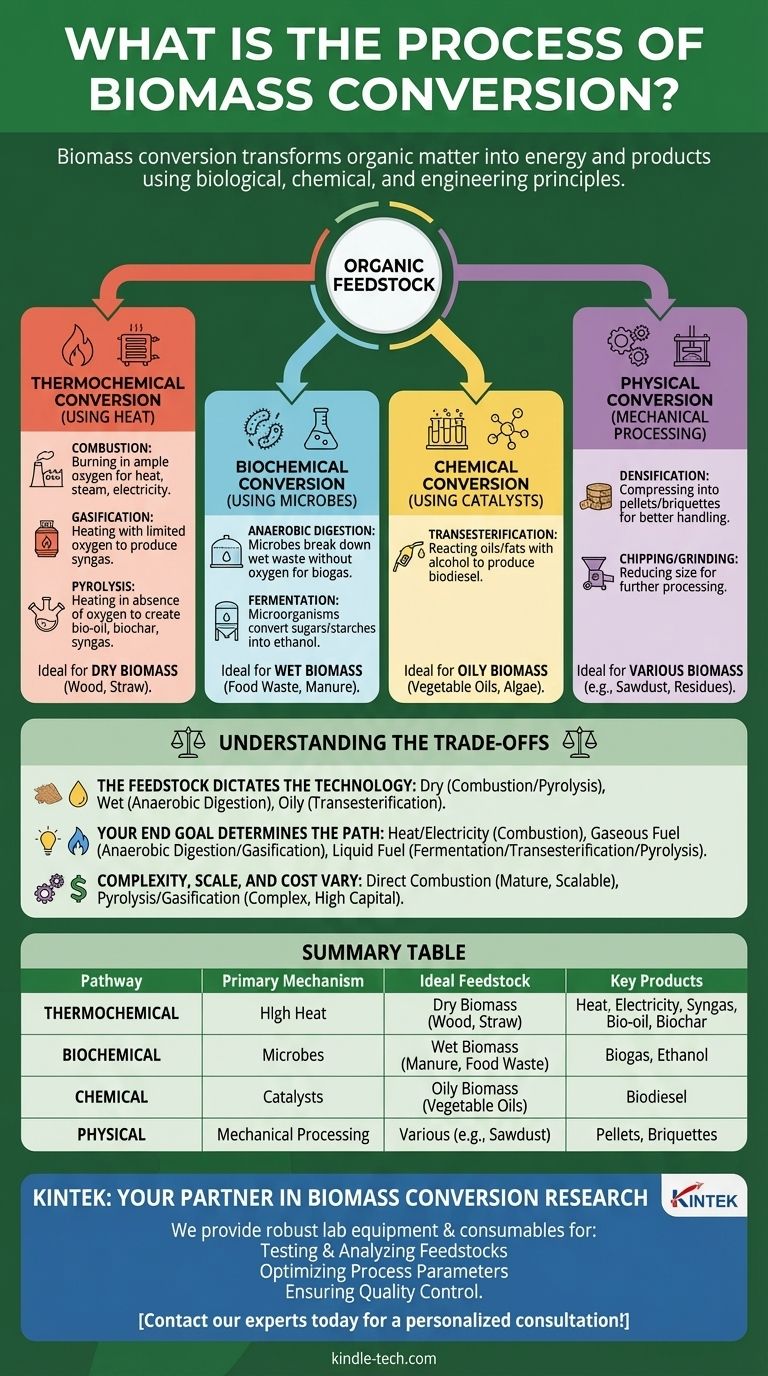
In essence, biomass conversion is the technological process of transforming organic matter—such as plants, agricultural residues, or municipal waste—into usable energy and valuable products. This is achieved by leveraging principles from biology, chemistry, and engineering to unlock the energy stored within these materials, creating everything from electricity and heat to liquid biofuels and bio-based chemicals.
The critical takeaway is that "biomass conversion" is not a single method, but an umbrella term for several distinct pathways. The right process depends entirely on two factors: the type of organic material you start with (the "feedstock") and the final product you need to create.

The Four Primary Conversion Pathways
Understanding biomass conversion means understanding the four fundamental ways we can break down organic matter. Each pathway is suited for different types of biomass and yields different results.
Thermochemical Conversion (Using Heat)
This family of processes uses heat to break down the chemical structure of biomass. These methods are most effective with dry feedstocks like wood, straw, or other fibrous plant material.
- Combustion: This is the most direct and common method. Biomass is simply burned in the presence of ample oxygen to generate heat, which can be used directly for industrial processes or to boil water, create steam, and turn turbines to generate electricity.
- Gasification: This process involves heating biomass with a limited amount of oxygen. Instead of burning completely, the biomass converts into a flammable gas mixture called synthesis gas (or "syngas"), which can be burned to run a gas engine or used as a chemical building block.
- Pyrolysis: This is the process of heating biomass in the complete absence of oxygen. It decomposes the material into three distinct products: a liquid called bio-oil (which can be upgraded to biofuel), a solid, carbon-rich charcoal called biochar, and a syngas.
Biochemical Conversion (Using Microbes)
This pathway uses microorganisms like bacteria and yeast to digest and break down biomass. It is best suited for wet organic materials with high moisture content.
- Anaerobic Digestion: Microorganisms break down wet organic waste (like food scraps, manure, or sewage) in an oxygen-free environment. The primary output is biogas, a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide, which can be used for heat and power generation.
- Fermentation: This classic biological process uses yeast or bacteria to convert the sugars and starches in biomass (like corn, sugarcane, or cellulosic material) into ethanol, a widely used biofuel.
Chemical Conversion (Using Catalysts)
These processes use chemical agents to convert biomass components into specific, desired products.
- Transesterification: This is the most common process for creating biodiesel. It reacts vegetable oils or animal fats with an alcohol (like methanol) in the presence of a catalyst to produce biodiesel and a glycerin co-product.
Physical Conversion (Mechanical Processing)
While not a conversion process in the chemical sense, physical processing is a critical preparatory step. It changes the physical characteristics of biomass to make it easier to handle, transport, and convert.
- Densification: This involves compressing loose biomass, such as sawdust or crop residues, into uniform, high-density pellets or briquettes. This greatly improves its energy density and handling for combustion.
- Chipping/Grinding: Reducing the size of large biomass like logs or wood waste makes it suitable for use in advanced thermochemical reactors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right conversion pathway is a matter of strategic trade-offs. There is no single "best" method; the optimal choice is determined by your resources and your goals.
The Feedstock Dictates the Technology
The nature of your raw material is the most important constraint.
- Dry biomass (e.g., wood chips, straw) is not suitable for biochemical digestion but is ideal for thermochemical processes like combustion, gasification, and pyrolysis.
- Wet biomass (e.g., food waste, manure) is a poor candidate for burning but is the perfect feedstock for anaerobic digestion, which thrives on high moisture content.
- Oily biomass (e.g., vegetable oils, algae, fats) is specifically required for the chemical process of transesterification to produce biodiesel.
Your End Goal Determines the Path
The product you want to create narrows the options further.
- For direct heat and electricity: Combustion is the most mature and straightforward technology.
- For a gaseous fuel: Anaerobic digestion (producing biogas) or gasification (producing syngas) are the primary routes.
- For a liquid transportation fuel: Fermentation for ethanol, transesterification for biodiesel, or pyrolysis for bio-oil are your main choices.
Complexity, Scale, and Cost
The pathways vary significantly in their technological maturity and capital requirements.
- Direct combustion is a highly developed, scalable technology, but requires effective emissions controls.
- Anaerobic digestion is ideal for decentralized waste management but can be sensitive to feedstock contamination.
- Pyrolysis and gasification are highly flexible but are more technologically complex and capital-intensive, making them better suited for industrial-scale facilities aiming to produce high-value fuels and chemicals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct process, you must align your available feedstock with your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is generating base-load power or heat: Direct combustion of dry, densified biomass is the most established and direct pathway.
- If your primary focus is managing wet organic waste: Anaerobic digestion is the ideal solution to produce biogas for energy and a nutrient-rich digestate as fertilizer.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid transportation fuels: Fermentation of sugar/starch crops for ethanol or transesterification of oils for biodiesel are the most mature technologies.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced biofuels or specialty bio-chemicals: Pyrolysis and gasification offer flexible platforms but require higher capital investment and technical expertise.
By understanding these distinct pathways and their associated trade-offs, you can effectively navigate the landscape of biomass conversion to unlock the value hidden within organic resources.
Summary Table:
| Pathway | Primary Mechanism | Ideal Feedstock | Key Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermochemical | High Heat | Dry Biomass (Wood, Straw) | Heat, Electricity, Syngas, Bio-oil, Biochar |
| Biochemical | Microbes | Wet Biomass (Manure, Food Waste) | Biogas, Ethanol |
| Chemical | Catalysts | Oily Biomass (Vegetable Oils) | Biodiesel |
| Physical | Mechanical Processing | Various (e.g., Sawdust) | Pellets, Briquettes |
Ready to implement the right biomass conversion technology for your operation?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the robust lab equipment and consumables needed for research, development, and quality control in biomass conversion processes. Whether you are developing new biofuels, optimizing anaerobic digestion, or analyzing bio-oil, our solutions support your innovation.
We help you:
- Test and analyze different feedstocks.
- Optimize process parameters for pyrolysis, gasification, and more.
- Ensure quality control for your final bio-products.
Let's discuss how KINTEK can support your biomass conversion goals. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty



















