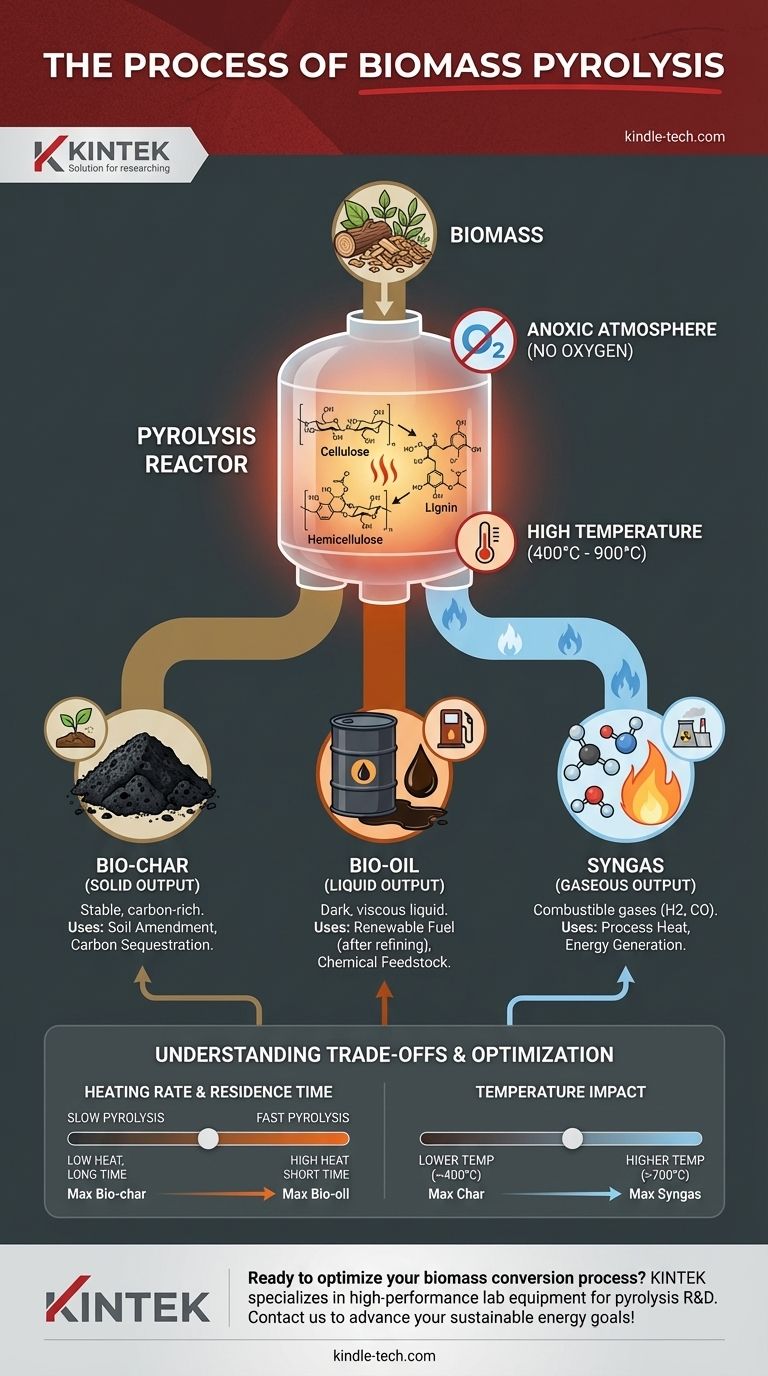
Biomass pyrolysis is the process of thermally decomposing organic materials at high temperatures in an oxygen-deprived environment. Unlike combustion, which burns material, pyrolysis uses intense heat to chemically break down biomass into a solid, a liquid, and a gas. This allows for the capture of carbon and energy in stable, usable forms.
Pyrolysis is not burning; it is a controlled thermal deconstruction. By removing oxygen from the equation, you force the biomass to break apart into its core components—bio-char, bio-oil, and syngas—rather than simply turning into ash and heat.

The Core Principle: Deconstruction Without Combustion
To truly understand pyrolysis, you must grasp its fundamental goal: to transform low-density, unstable biomass into high-value, stable products. This is achieved by carefully controlling the core parameters of the reaction.
What "Absence of Oxygen" Really Means
The defining characteristic of pyrolysis is the anoxic (oxygen-free) atmosphere inside the reactor. This is critical because it prevents the biomass from burning.
Combustion requires fuel, heat, and oxygen. By removing oxygen, the process can't complete the burning reaction, forcing the complex organic polymers in the biomass to fracture into simpler, more stable molecules.
The Building Blocks of Biomass
The process works by breaking down the primary components of all plant-based material.
These are cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. Each of these components decomposes at different temperatures and rates, which influences the final ratio of products.
The Role of High Temperature
Heat is the engine of pyrolysis, providing the energy needed to sever the chemical bonds within the biomass.
Reactors typically operate between 400°C and 900°C (750°F to 1650°F). The specific temperature used is one of the most important factors in determining the final product yields.
The Three Primary Products and Their Purpose
The output of a pyrolysis system is not a single product but a portfolio of materials, each with a distinct use case. The process separates the original biomass into solid, liquid, and gaseous forms.
The Solid Output: Bio-char
Bio-char is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after the volatile components have been driven off. It is similar in appearance to charcoal.
Its primary applications are in agriculture as a soil amendment to improve water retention and as a method for long-term carbon sequestration, locking carbon into the soil for centuries.
The Liquid Output: Bio-oil
Bio-oil (also known as pyrolysis oil or tar) is a dark, viscous liquid created by cooling and condensing the volatile gases from the reactor. It is a complex mixture of oxygenated organic compounds.
After upgrading and refining, bio-oil has the potential to be used as a renewable liquid fuel or as a source for specialty chemicals.
The Gaseous Output: Syngas
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a mixture of combustible gases (primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide) that do not condense with the bio-oil.
This gas has a low-to-medium energy value and is often re-routed to provide heat for the pyrolysis reactor, making the process more energy-efficient and potentially self-sustaining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The yields of bio-char, bio-oil, and syngas are not fixed. They can be manipulated by adjusting process conditions, creating a significant trade-off between the three outputs.
Slow vs. Fast Pyrolysis
The heating rate and residence time (how long the biomass stays in the reactor) are crucial.
Slow pyrolysis uses lower temperatures and longer residence times to maximize the production of bio-char. In contrast, fast pyrolysis uses very high heating rates and short residence times (often less than 2 seconds) to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil.
The Impact of Temperature
Temperature directly influences which products are favored.
Lower temperatures (around 400°C) tend to produce more char. As the temperature increases toward 500-550°C, bio-oil production is typically optimized. At very high temperatures (above 700°C), the process favors the production of syngas.
Feedstock Consistency
The type and condition of the input biomass—its moisture content, particle size, and chemical composition—will significantly impact the efficiency of the process and the quality of the final products. A consistent feedstock is key to a predictable output.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The versatility of pyrolysis means the "best" approach depends entirely on your desired outcome. You must tune the process to match the product you value most.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration and soil improvement: A slow pyrolysis process at lower temperatures is the correct path to maximize bio-char yield.
- If your primary focus is producing renewable liquid fuels: Fast pyrolysis with rapid heating and quick vapor quenching is necessary to maximize bio-oil production.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-energy and self-sufficiency: A system designed to capture and burn its own syngas is the most efficient design.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a powerful and flexible platform for converting biomass into a portfolio of valuable, carbon-based products.
Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Bio-char | Carbon-rich solid residue | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
| Bio-oil | Dark, viscous liquid from condensed gases | Renewable liquid fuel, chemical feedstock |
| Syngas | Mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and other gases | Process heat, energy generation |
Ready to optimize your biomass conversion process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're scaling up bio-char production for agriculture or refining bio-oil for renewable energy, our solutions ensure precise temperature control and consistent results. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can advance your sustainable energy goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds

















