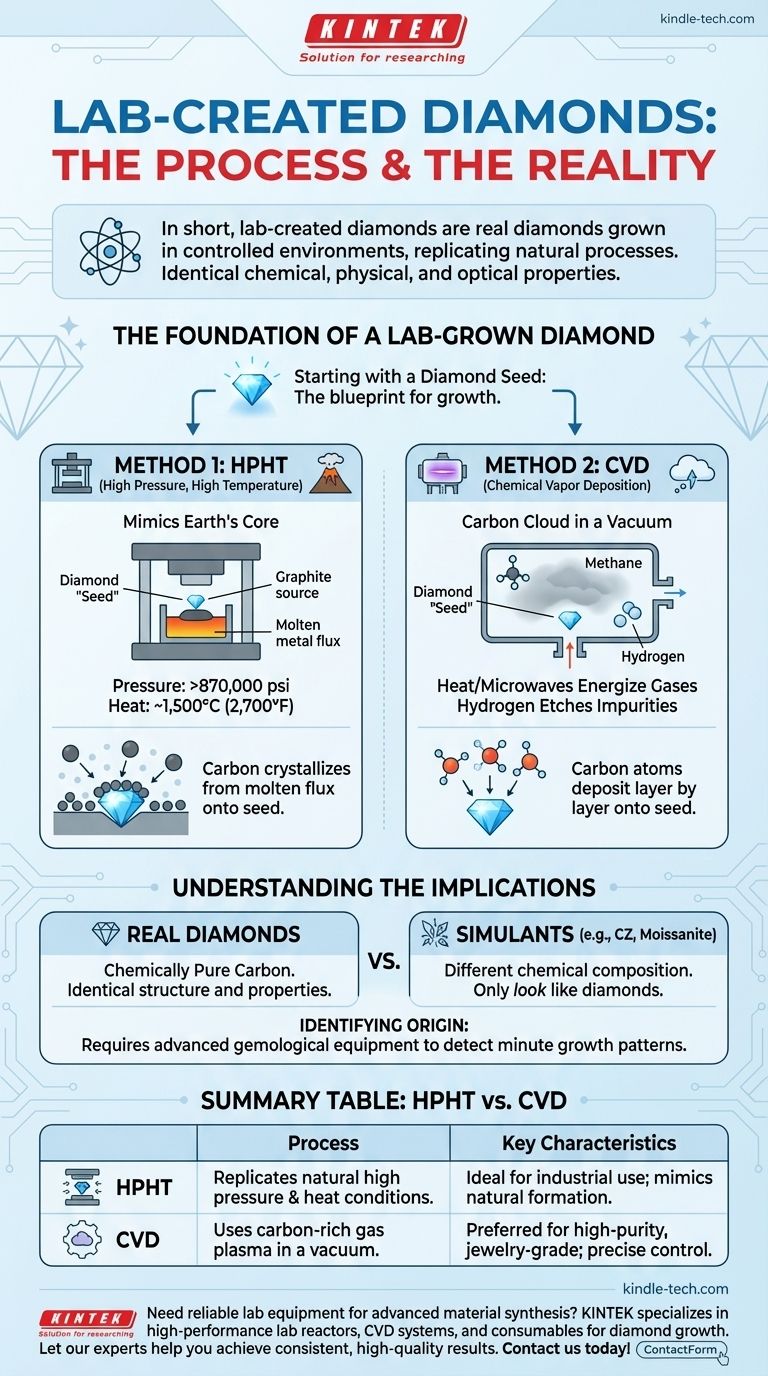
In short, lab-created diamonds are grown in highly controlled environments that replicate the natural diamond-forming process. These methods start with a tiny diamond "seed" and use advanced technology to add carbon atoms, layer by layer, until a full-sized rough diamond is formed. The two dominant industrial processes are High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The critical takeaway is that these laboratory processes do not create imitations; they produce real diamonds. Because they are grown from pure carbon in an identical crystal structure, lab-grown diamonds possess the same chemical, physical, and optical properties as their mined counterparts, making them indistinguishable without specialized gemological equipment.
The Foundation of a Lab-Grown Diamond
Before any growth process can begin, it requires a specific starting point. This foundation is the key to ensuring the final product is a genuine diamond.
Starting with a Diamond "Seed"
Every lab-grown diamond begins its life as a tiny sliver of a pre-existing diamond, known as a seed. This seed, which can be from either a natural or another lab-grown diamond, acts as the structural template.
The Goal: Replicating Nature's Blueprint
The objective of any lab-growing method is to create the precise conditions that encourage carbon atoms to bond to this seed. The seed's crystal lattice guides these new atoms into forming the same strong, tetrahedral structure that defines all diamonds.
The Two Primary Growth Methods
While other experimental methods exist, virtually all gem-quality lab diamonds available today are created using one of two highly refined processes.
Method 1: High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT)
The HPHT method directly mimics the intense conditions deep within the Earth where natural diamonds form.
The diamond seed is placed in a chamber along with a source of pure carbon, such as graphite. This chamber is then subjected to immense pressure—over 870,000 pounds per square inch—and extreme heat, reaching temperatures of around 1,500°C (2,700°F).
Under these conditions, the solid carbon source dissolves into a molten metal flux and crystallizes onto the diamond seed, building the diamond atom by atom.
Method 2: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is a newer technique that takes a different approach, often described as building the diamond from a "carbon cloud."
The diamond seed is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber. The chamber is then filled with a mixture of carbon-rich gases (like methane) and hydrogen.
This gas mixture is heated to a high temperature, often with microwaves, which energizes the gases and breaks them apart. These broken-down carbon atoms then "rain down" and deposit onto the cooler diamond seed, building up the diamond in successive layers. The hydrogen gas helps by selectively etching away any non-diamond carbon, ensuring high purity.
Understanding the Implications and Differences
The existence of these two methods and the lab-based origin raises important questions about the final product. Understanding the context is key to making an informed decision.
Why Two Different Methods?
HPHT is the original method for creating diamonds and is still widely used, particularly for industrial applications. CVD has gained immense popularity for producing high-quality, colorless jewelry-grade diamonds and allows for a high degree of control over the diamond's purity.
The Myth of "Fake" Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds are not simulants like cubic zirconia or moissanite. Simulants only look like diamonds but have entirely different chemical compositions and physical properties. Lab-grown diamonds are chemically pure carbon, just like mined diamonds.
Identifying the Origin
Because they are physically and optically identical, the only way to differentiate a lab-grown diamond from a natural one is with advanced scientific instruments. Gemological laboratories can detect minute differences in growth patterns and trace elements to definitively determine a diamond's origin.
How This Process Impacts Your Choice
Understanding that lab-grown diamonds are the result of a deliberate, highly technical manufacturing process clarifies the choice you face. It is not a matter of real vs. fake, but of different origins.
- If your primary focus is traditional rarity: A mined diamond's billion-year-old origin story and its journey from deep within the Earth is its defining characteristic.
- If your primary focus is value and transparency: Lab-grown diamonds offer identical physical quality and brilliance, often at a more accessible price point and with a fully documented, mine-free origin.
- If your primary focus is technical perfection: The controlled environment of the CVD process, in particular, allows for the creation of exceptionally pure diamonds with very high clarity and color grades.
Ultimately, understanding the process reveals that the choice between a lab-grown and a mined diamond is not one of quality, but of origin and the values you wish to prioritize.
Summary Table:
| Process | How It Works | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| HPHT | Replicates Earth's natural conditions with high pressure and heat to melt carbon onto a diamond seed. | Ideal for industrial use; mimics natural diamond formation. |
| CVD | Uses a carbon-rich gas plasma to deposit layers of carbon onto a diamond seed in a vacuum chamber. | Preferred for high-purity, jewelry-grade diamonds; offers precise control. |
Need reliable lab equipment for advanced material synthesis? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab reactors, CVD systems, and consumables tailored for diamond growth and other precision processes. Let our experts help you achieve consistent, high-quality results. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is CVD diamond? The Ultimate Guide to Lab-Grown Diamonds and Their Uses
- What is the future value of lab grown diamond? Understanding Its Depreciating Financial Worth
- What is the future of CVD diamond? Unlocking Next-Gen Electronics & Thermal Management
- What are the common sources of contamination during CVD diamond growth? Improve Purity and Quality Control
- What is the fluorescence of a CVD diamond? A Guide to Its Unique Glow and Purpose



















