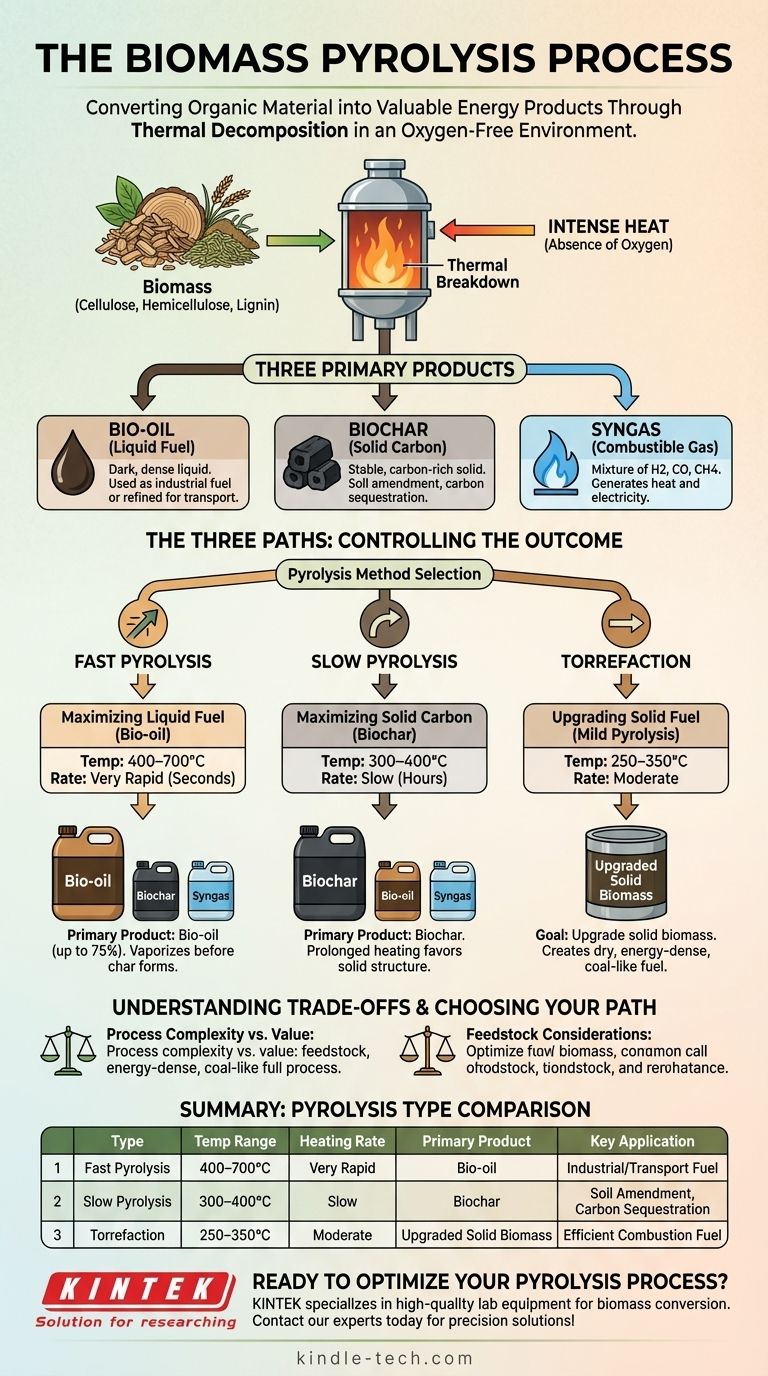
In essence, pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of organic material, like biomass, at high temperatures in a controlled, oxygen-free environment. Unlike combustion, which burns material with oxygen to produce heat and ash, pyrolysis chemically breaks down the complex structures of biomass into a mix of a liquid fuel (bio-oil), a solid carbon-rich product (biochar), and a combustible gas (syngas).
The key to understanding pyrolysis is that it is not a single process, but a set of controlled "recipes." By carefully managing temperature and heating rate, you can intentionally steer the reaction to maximize the output of either liquid fuel, solid char, or an upgraded solid fuel, depending on your end goal.
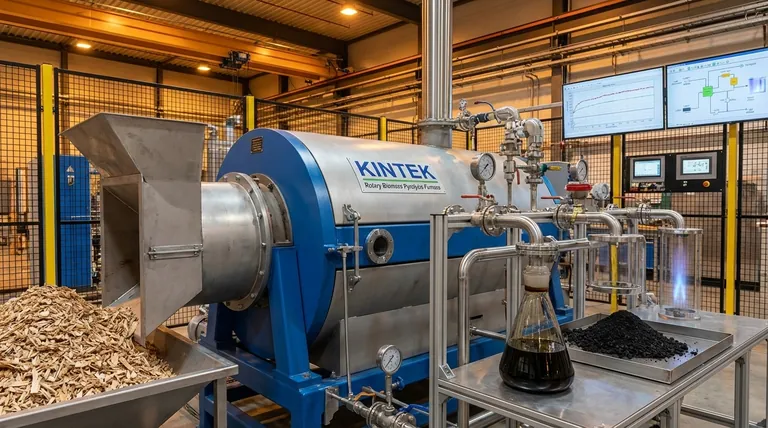

The Core Mechanism: How Pyrolysis Works
A Reaction Without Oxygen
The defining characteristic of pyrolysis is the absence of oxygen. This prevents the biomass from burning.
Instead of combusting, the intense heat breaks the long, complex polymer chains of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin—the primary components of biomass—into smaller, more valuable molecules.
The Three Primary Products
The process fundamentally sorts the original biomass into three distinct states: a liquid, a solid, and a gas. The proportion of each is not random; it is dictated by the specific pyrolysis method used.
- Bio-oil: A dark, dense liquid that can be used as an industrial fuel oil or further refined into transportation fuels and chemicals.
- Biochar: A stable, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal. It is highly valued as a soil amendment to improve fertility and for carbon sequestration.
- Syngas (Synthesis Gas): A mixture of combustible gases (primarily hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane) that can be burned to provide heat for the pyrolysis process itself or used to generate electricity.
The Three Paths of Pyrolysis: Controlling the Outcome
The specific conditions of the pyrolysis process determine which of the three products is maximized. This choice is deliberate and is based entirely on the desired output.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Liquid Fuel (Bio-oil)
Fast pyrolysis uses very high temperatures (400–700°C) and an extremely rapid heating rate. The biomass is heated in mere seconds.
This "thermal shock" vaporizes the organic material before it can break down into char. The vapors are then rapidly cooled and condensed to form the primary product: bio-oil, which can make up to 75% of the product mass.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Solid Carbon (Biochar)
In contrast, slow pyrolysis uses lower temperatures (300–400°C) and a much slower heating rate, often lasting several hours.
This prolonged, gentle heating process favors the formation of a stable, carbon-rich solid structure. The primary product here is biochar, which is the main goal. Bio-oil and syngas are produced in smaller quantities as byproducts.
Torrefaction: Upgrading Solid Fuel
Torrefaction, sometimes called "mild pyrolysis," operates at the lowest temperature range (250–350°C).
The goal is not to create a liquid or char, but to upgrade the solid biomass itself. The process drives off water and volatile compounds, creating a final product that is dry, brittle, energy-dense, and water-resistant, making it much easier to store, transport, and burn like coal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pyrolysis method involves balancing process complexity against product characteristics and feedstock limitations.
Process Complexity vs. Product Value
Fast pyrolysis yields a high-value, energy-dense liquid fuel, but it requires sophisticated reactors capable of extremely fast heat transfer and rapid quenching.
Slow pyrolysis is technologically simpler and less demanding, but its main product, biochar, has a different market (agriculture, carbon credits) than the energy sector.
Feedstock Considerations
The type and condition of the biomass are critical. Materials like wood chips and nut shells are ideal due to their low moisture content.
Conversely, wet feedstocks like agricultural waste or food waste require significant energy for pre-drying before they can be effectively processed, which impacts the overall energy balance of the system.
The Bio-oil Challenge
It is important to recognize that bio-oil is not a "drop-in" replacement for petroleum fuels. It is typically acidic, corrosive, and chemically unstable. It requires significant secondary processing (known as "upgrading") to be converted into stable transportation fuels like gasoline or diesel, adding cost and complexity to the overall process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your objective dictates the correct pyrolysis strategy.
- If your primary focus is producing a transportable liquid fuel: Fast pyrolysis is the correct path, but be prepared for the costs and challenges of upgrading the resulting bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is creating a valuable soil amendment and sequestering carbon: Slow pyrolysis is your ideal choice, as it is specifically designed to maximize the yield and quality of biochar.
- If your primary focus is improving the handling and combustion properties of solid biomass: Torrefaction is the most effective method for creating a coal-like, energy-dense solid fuel.
By understanding these distinct pathways, you can align the pyrolysis process with your specific energy or material goals.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Temperature Range | Heating Rate | Primary Product | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fast Pyrolysis | 400–700°C | Very Rapid | Bio-oil (Liquid Fuel) | Industrial fuel, transportation fuel refining |
| Slow Pyrolysis | 300–400°C | Slow (Hours) | Biochar (Solid Carbon) | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
| Torrefaction | 250–350°C | Moderate | Upgraded Solid Biomass | Coal-like solid fuel for efficient combustion |
Ready to implement pyrolysis technology for your biomass conversion needs? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're optimizing bio-oil production, characterizing biochar, or scaling up your process, our solutions provide the precision and reliability you need. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's biomass energy projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success















