At its core, thermal evaporation is a process for creating exceptionally thin films of material. It works by heating a source material inside a high-vacuum chamber until its atoms turn into a vapor. This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto a cooler target surface, known as a substrate, building a uniform, thin coating one atom at a time.
Thermal evaporation is a foundational thin-film deposition technique that uses resistive heating to vaporize a material in a vacuum. Its value lies in its relative simplicity, low cost, and ability to precisely coat surfaces, making it a cornerstone for manufacturing many modern electronic and optical devices.
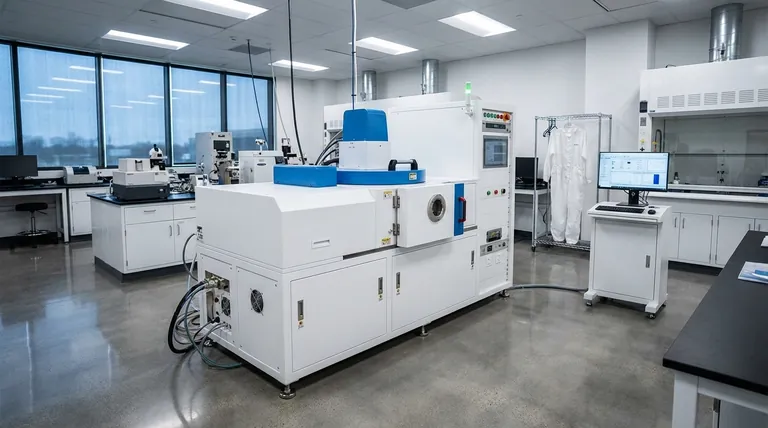

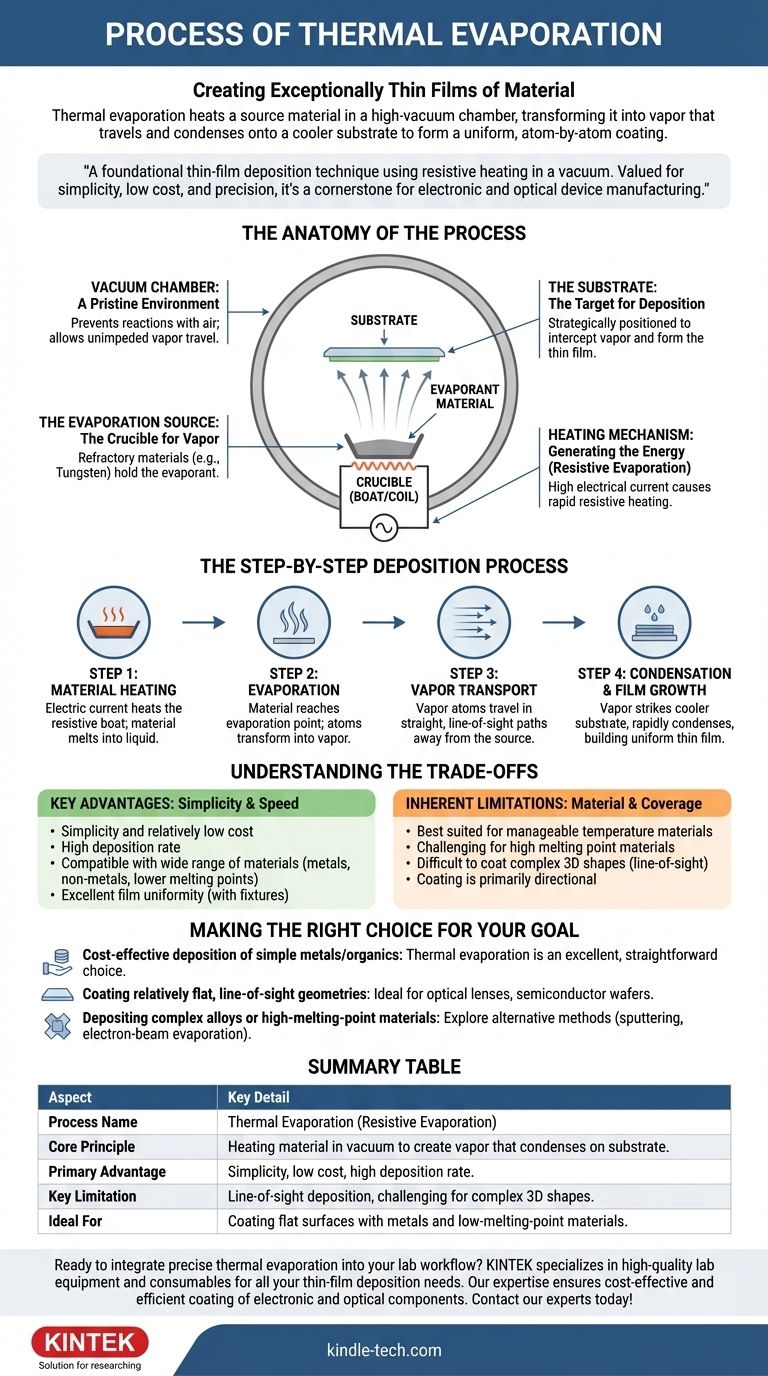
The Anatomy of the Process
To understand how thermal evaporation works, it’s essential to recognize its key components and the role each one plays. The entire process is a carefully controlled sequence within a specialized environment.
The Vacuum Chamber: A Pristine Environment
The process must occur in a high-vacuum chamber, typically made of stainless steel. The vacuum is critical for two reasons: it prevents the hot source material from reacting with air, and it allows the vaporized atoms to travel directly to the substrate without colliding with other gas molecules.
The Evaporation Source: The Crucible for Vapor
The material to be deposited, known as the evaporant, is placed in a container often called a "boat" or "coil." These sources are made from refractory materials like tungsten or molybdenum that can withstand extreme heat without melting or contaminating the evaporant.
The Heating Mechanism: Generating the Energy
This method is often called resistive evaporation because of how heat is generated. A high electrical current is passed through the evaporation source (the boat or coil). The source's natural electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly, transferring thermal energy directly to the evaporant material held within it.
The Substrate: The Target for Deposition
The substrate is the object or surface that receives the coating. It is strategically positioned above the evaporation source to intercept the flow of vaporized atoms, allowing them to condense and form the desired thin film.
The Step-by-Step Deposition Process
The creation of a thin film via thermal evaporation follows a clear, sequential path from solid material to a precision coating.
Step 1: Material Heating
An electric current is applied to the resistive boat containing the solid source material. As the current increases, the boat heats up intensely, causing the material to first melt into a liquid.
Step 2: Evaporation
As the temperature continues to rise, the material reaches its evaporation point. Its atoms gain enough thermal energy to break free from the liquid surface and transform into a vapor, filling the space around the source.
Step 3: Vapor Transport
Within the high vacuum, the vaporized atoms travel in straight, line-of-sight paths away from the source. The absence of air molecules ensures their journey is unimpeded.
Step 4: Condensation and Film Growth
When the vapor atoms strike the cooler surface of the substrate, they rapidly lose energy and condense back into a solid state. This process builds up layer by layer, forming a highly uniform and controlled thin film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any technical process, thermal evaporation has distinct advantages and limitations that make it suitable for specific applications.
Key Advantages: Simplicity and Speed
The primary strength of thermal evaporation is its simplicity and relatively low cost. The equipment is less complex than many alternative deposition methods.
It offers a high deposition rate and is compatible with a wide range of materials, including both metals and non-metals, particularly those with lower melting points. With proper substrate fixtures, it can achieve excellent film uniformity.
Inherent Limitations: Material and Coverage
The process is best suited for materials that evaporate at manageable temperatures. Depositing materials with very high melting points can be challenging for standard resistive sources.
Because the vapor travels in a straight line, it can be difficult to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with sharp corners or undercuts. The coating is primarily line-of-sight.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method depends entirely on your material, substrate, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective deposition of simple metals or organics: Thermal evaporation is an excellent, straightforward choice for creating high-quality films.
- If your primary focus is coating relatively flat, line-of-sight geometries: The directional nature of this process is ideal for applications like optical lenses or semiconductor wafers.
- If your primary focus is depositing complex alloys or high-melting-point materials: You may need to explore alternative methods like sputtering or electron-beam evaporation.
By understanding these core principles, you can determine if this foundational technique is the most efficient path for achieving your thin-film deposition goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Name | Thermal Evaporation (Resistive Evaporation) |
| Core Principle | Heating a material in a vacuum to create a vapor that condenses on a substrate. |
| Primary Advantage | Simplicity, low cost, and high deposition rate. |
| Key Limitation | Line-of-sight deposition, challenging for complex 3D shapes. |
| Ideal For | Coating flat surfaces with metals and low-melting-point materials. |
Ready to integrate precise thermal evaporation into your lab workflow? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your thin-film deposition needs. Our expertise ensures you get the right tools for cost-effective and efficient coating of electronic and optical components. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and how we can support your research and production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
People Also Ask
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing



















