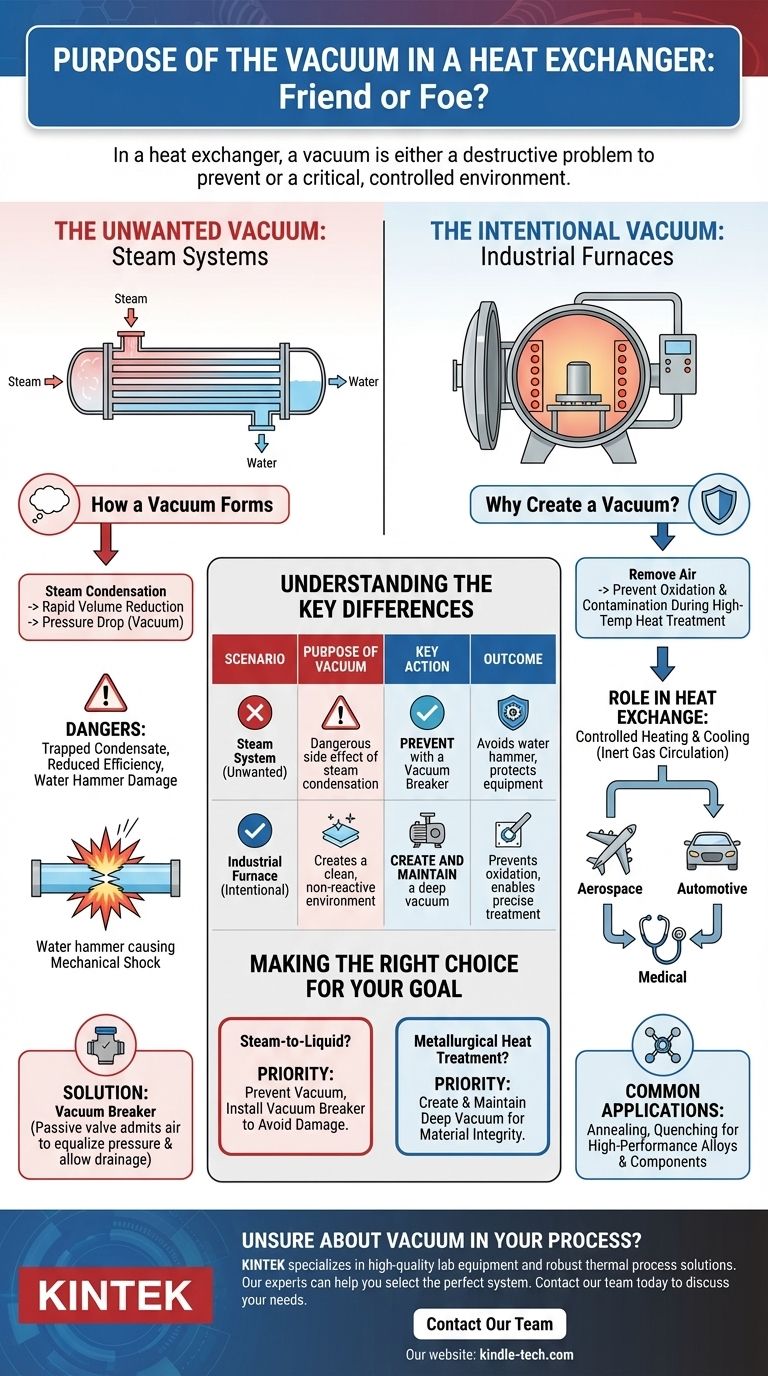
In the context of a heat exchanger, the role of a vacuum is fundamentally twofold: it is either a highly destructive problem that must be prevented or a highly controlled, intentional environment required for a specific industrial process. In common steam-to-water systems, an unwanted vacuum can form that traps water, leading to violent water hammer and tube damage. Conversely, in specialized applications like heat treatment furnaces, a vacuum is deliberately created to protect materials from oxidation at high temperatures.
Understanding the purpose of a vacuum in your heat exchanger system first requires identifying your application. In most HVAC and process heating systems, a vacuum is a dangerous side effect to be eliminated, whereas in advanced metallurgy, it is the essential operating environment.

The Unwanted Vacuum: Steam Systems
In many common heat exchangers, particularly those using steam to heat water or another liquid, a vacuum is not a feature but a critical failure condition that must be actively prevented.
How a Vacuum Forms During Condensation
When steam transfers its energy to the colder fluid in the heat exchanger, it condenses back into water. The volume of this resulting water (condensate) is drastically smaller than the volume of the steam it came from. This rapid, massive reduction in volume inside a sealed shell creates a pressure drop, often falling well below atmospheric pressure, forming a vacuum.
The Dangers of an Unwanted Vacuum
This vacuum actively works against the system, preventing condensate from draining properly out of the heat exchanger shell. The trapped water then creates two major problems: it reduces the surface area available for new steam to condense, drastically lowering efficiency, and it sets the stage for water hammer—a destructive phenomenon where incoming high-velocity steam collides with the stationary slug of trapped water, causing a violent mechanical shock that can damage or even rupture the equipment.
The Solution: The Vacuum Breaker
To solve this, steam-to-liquid heat exchangers are fitted with a vacuum breaker. This is a simple, passive check valve installed on the steam shell. If the internal pressure drops below the external atmospheric pressure, the valve automatically opens, allowing air to enter and "break" the vacuum. This equalizes the pressure, allowing the condensate to drain freely by gravity as intended.
The Intentional Vacuum: Industrial Furnaces
In stark contrast to steam systems, some industrial processes use vacuum furnaces for highly specialized heat treatments. Here, the vacuum is not a problem but the core requirement for the process to succeed.
Why Create a Vacuum?
In applications like annealing or quenching heat-resistant alloys (such as those used in aerospace), heating the metal in the presence of air would cause it to oxidize and become contaminated. A deep vacuum is pulled to remove nearly all the air and other gases from the furnace chamber before the heat treatment begins. This creates a clean, non-reactive environment.
The Role of Heat Exchange in a Vacuum
Within these furnaces, heating elements bring the target materials up to extreme temperatures. The system must also be able to cool them at a controlled rate. This often involves flowing an inert gas into the chamber after the heating cycle, which is then circulated through an internal heat exchanger to remove heat. The entire process—heating and cooling—occurs within this tightly controlled vacuum environment.
Common Applications
This method is crucial for manufacturing high-performance components that must withstand extreme stress and heat. You will find vacuum heat treatment used extensively in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries for parts like engine turbines, exhaust components, and surgical tools.
Understanding the Key Differences
It is critical to distinguish between these two scenarios, as they represent opposite operational goals.
Heat Transfer vs. Material Protection
In a steam system, the goal is maximum heat transfer from the steam to the liquid. A vacuum hinders this process. In a vacuum furnace, the primary goal is material protection from atmospheric reaction; heat transfer is simply part of the treatment process within that protected environment.
Pressure as a Fault vs. a Feature
For a steam heat exchanger, sub-atmospheric pressure is a fault condition that indicates poor drainage and imminent risk of damage. For a vacuum furnace, sub-atmospheric pressure is the primary operational state required for a successful outcome.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine whether a vacuum is a friend or foe in your system, you must first identify the fundamental purpose of your equipment.
- If you are working with a steam-to-liquid heat exchanger: Your priority is to prevent vacuum formation using a correctly installed vacuum breaker to ensure proper condensate drainage and avoid equipment damage.
- If you are involved in metallurgical heat treatment: Your priority is to create and maintain a deep vacuum using a robust pumping system to protect the integrity of the material during its thermal processing.
Ultimately, understanding the core objective of your thermal process will tell you whether a vacuum is a dangerous problem to be solved or a critical environment to be created.
Summary Table:
| Scenario | Purpose of Vacuum | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steam System (Unwanted) | A dangerous side effect of steam condensation | Prevent with a Vacuum Breaker | Avoids water hammer, ensures proper drainage, protects equipment |
| Industrial Furnace (Intentional) | Creates a clean, non-reactive environment | Create and Maintain a deep vacuum | Prevents material oxidation, enables precise heat treatment |
Unsure if a vacuum is a problem or a requirement for your process? The right equipment is critical for safety and performance. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including robust solutions for demanding thermal processes. Our experts can help you select the perfect system for your application, whether you need to prevent a damaging vacuum or create a controlled one.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and ensure optimal results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- Why is a heated laboratory hydraulic press necessary for composite laminates? Achieve Void-Free Structural Integrity
- What is vacuum lamination? Achieve a Flawless, Durable Finish on Complex Shapes
- What is the advantage by using hot press forming? Achieve Stronger, More Complex Parts
- What is hot press lamination? The Ultimate Guide to Strong, Durable Material Bonding
- What is hot press moulding? Achieve Superior Density and Complex Shapes with Heat and Pressure












