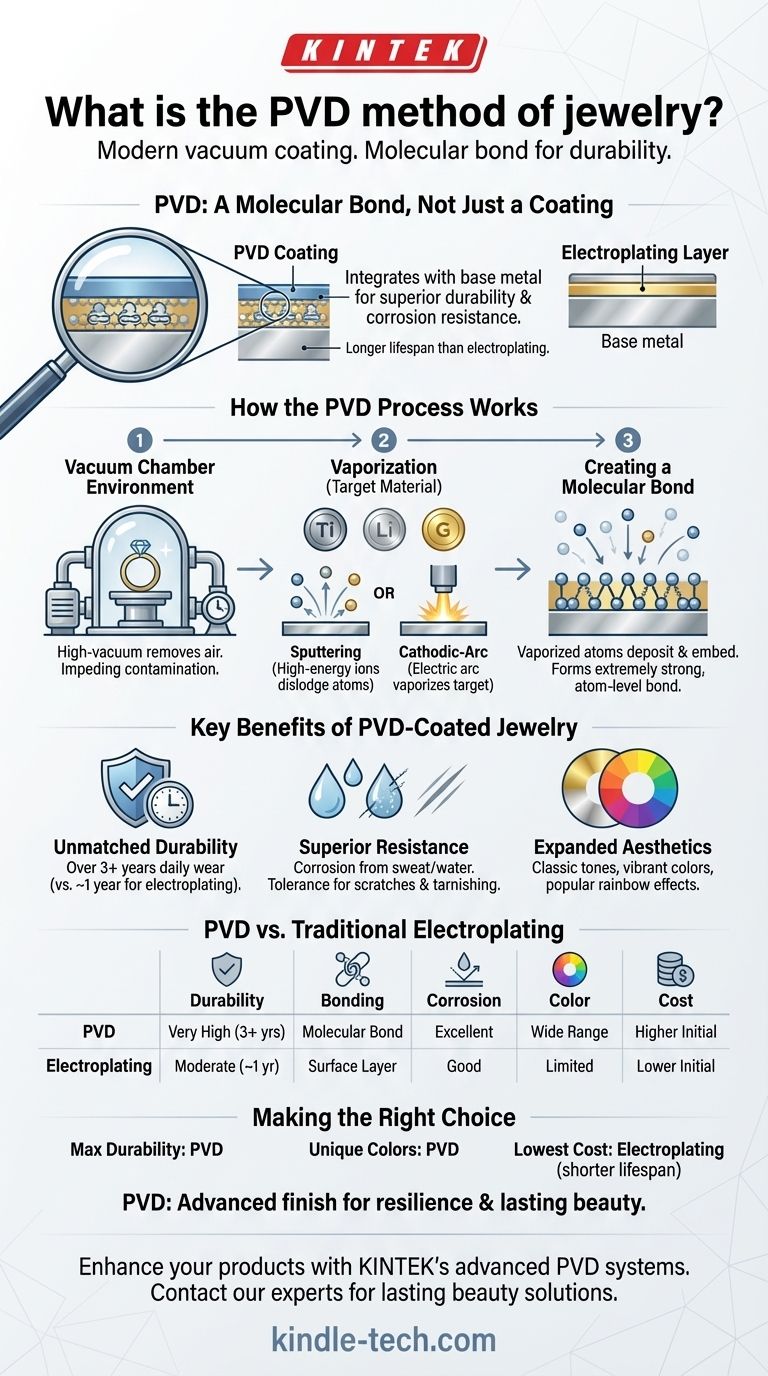
In the world of jewelry, PVD, or Physical Vapor Deposition, is a modern vacuum coating process that molecularly bonds a thin film of durable material onto a base metal. This technique creates a finish that is significantly more durable, long-lasting, and resistant to wear than traditional electroplating, offering both functional resilience and a wider range of aesthetic color options.
The critical difference with PVD is that it's not just a coating; it's a molecular bond. Unlike traditional electroplating which simply layers metal on top, PVD integrates the finish with the base metal, resulting in superior durability, corrosion resistance, and a longer lifespan for the jewelry's color and shine.
How the PVD Process Works
To understand why PVD is a superior finishing method, it's essential to grasp the fundamentals of the process itself. It's a high-tech procedure conducted in a specialized vacuum environment.
The Vacuum Chamber Environment
The entire PVD process takes place inside a high-vacuum chamber. The jewelry piece is placed inside, and the air is removed to create a near-perfect vacuum. This is critical to ensure the coating material can travel without being impeded or contaminated by air particles.
The Two Primary Methods
A target material—the substance that will form the coating, such as titanium or gold—is vaporized into a plasma state using one of two main techniques:
- Sputtering: This is the most common method. High-energy ions are fired at the target material, dislodging or "sputtering" atoms off its surface.
- Cathodic-Arc Evaporation (Arc-PVD): A high-current electric arc is used to vaporize the target material, creating a highly ionized vapor.
Creating a Molecular Bond
The vaporized atoms of the coating material then travel through the vacuum chamber and are deposited onto the jewelry. This isn't a simple layer of paint; the particles embed themselves onto the surface, forming an extremely strong, atom-level bond with the base metal.
Key Benefits of PVD-Coated Jewelry
The science behind PVD translates directly into tangible benefits for anyone who wears it. The result is a piece of jewelry that looks better for far longer.
Unmatched Durability and Longevity
PVD coatings are vastly more durable than traditional electroplated finishes. With proper care, a PVD finish can last over three years with daily wear, whereas a typical electroplated piece may only last for about one year before wearing away.
Superior Resistance to Wear
The molecular bond created by PVD makes the jewelry highly resistant to the common enemies of a beautiful finish. This includes increased resistance to corrosion from sweat and water, as well as a much higher tolerance for scratches and tarnishing.
Expanded Aesthetic Possibilities
PVD opens up a world of color options that are limited or impossible with precious metals alone. It can produce classic gold and silver tones, but also vibrant colors and even popular rainbow effects, giving designers immense creative freedom.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PVD is a superior technology, no process is without its considerations. An objective assessment requires understanding its limitations.
Higher Initial Cost
The specialized equipment and complex physics involved in the PVD process make it more expensive than traditional electroplating. This can translate to a higher retail price for the finished jewelry.
Complexity of Application
PVD is not a simple dip-and-dry process. It requires significant technical expertise and precisely controlled industrial machinery, making it less accessible for small-scale artisans compared to electroplating.
Repair and Re-coating Challenges
If a PVD-coated piece sustains a deep scratch that penetrates the coating, it cannot be spot-repaired. The entire piece would need to be stripped and put through the PVD process again, which is often not feasible or cost-effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to choose PVD-coated jewelry depends on your priorities for longevity, appearance, and budget.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and longevity: PVD is the superior choice, especially for everyday-wear items like rings and bracelets that face constant abrasion.
- If your primary focus is exploring unique colors: PVD offers a vast palette beyond traditional metals, including vibrant tones and rainbow finishes not achievable with other methods.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible cost for fashion jewelry: Traditional electroplating may be more budget-friendly, but you must accept a significantly shorter lifespan and lower resistance to wear.
Ultimately, investing in PVD-coated jewelry means choosing a technologically advanced finish designed for resilience and lasting beauty.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Coating | Traditional Electroplating |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Very High (3+ years daily wear) | Moderate (~1 year daily wear) |
| Bonding Method | Molecular Bond | Surface Layer |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Color Options | Wide range (gold, silver, rainbow) | Limited |
| Cost | Higher Initial Cost | Lower Initial Cost |
Ready to enhance your product line with durable, high-quality finishes? KINTEK specializes in advanced PVD coating systems and consumables for the jewelry industry. Our equipment ensures a superior molecular bond for finishes that last. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can bring lasting beauty and resilience to your jewelry designs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
People Also Ask
- Is sputtering a PVD? Discover the Key Coating Technology for Your Lab
- What is the RF frequency for sputtering? Unlocking the Standard for Insulating Materials
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- What does PVD sputtering mean? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Deposition
- How many types of vapor phase deposition techniques are present? PVD vs. CVD Explained



















