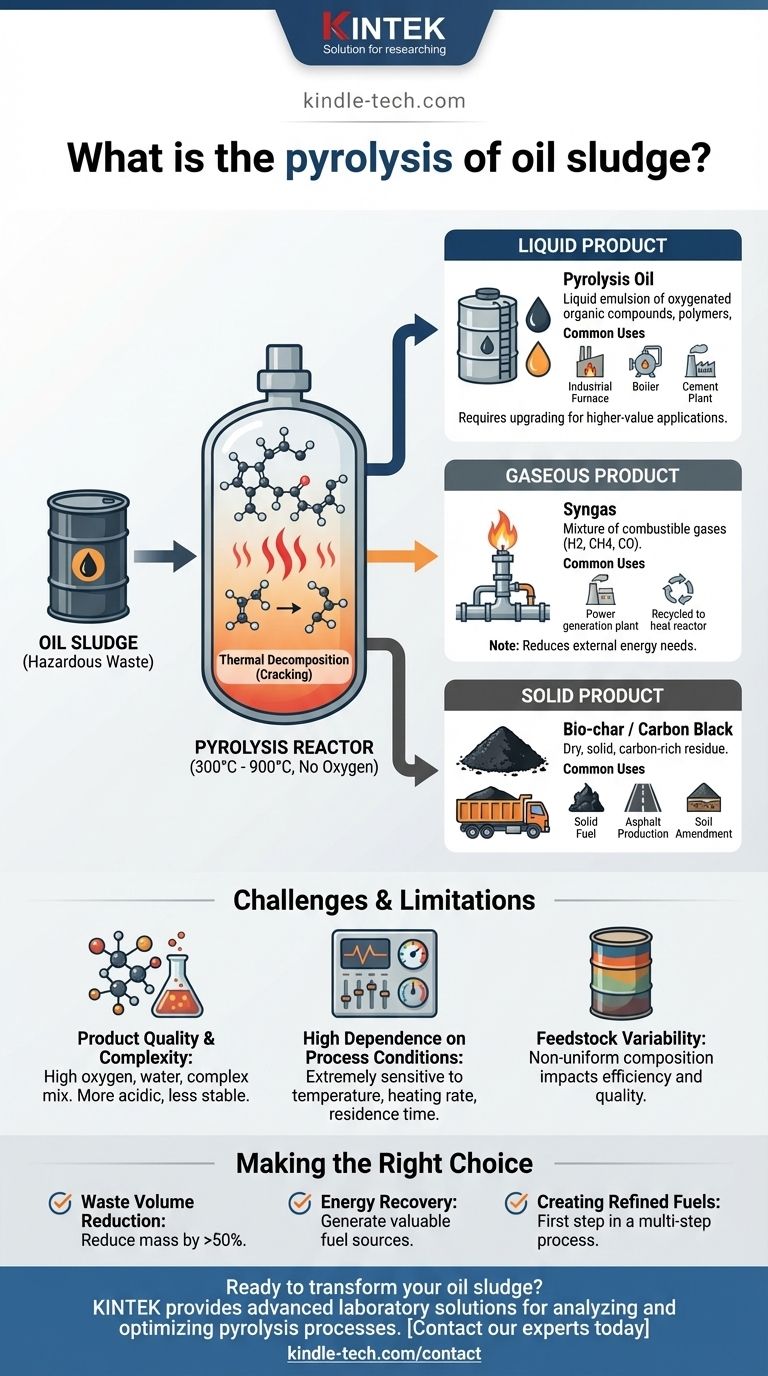
In essence, the pyrolysis of oil sludge is a thermal decomposition process used to treat this hazardous waste. The sludge is heated to high temperatures in a sealed, oxygen-free environment, which causes the long-chain hydrocarbon molecules to "crack" or break down into smaller, more valuable components without actually burning. This method transforms a problematic industrial byproduct into recoverable resources.
The core challenge with oil sludge is its hazardous nature and complex composition, making traditional disposal difficult and expensive. Pyrolysis addresses this not by simply destroying the waste, but by converting it into usable fuel oil, combustible gas, and a solid carbon residue, turning an environmental liability into a potential asset.

How Oil Sludge Pyrolysis Works
Pyrolysis leverages a fundamental chemical principle to deconstruct waste. The name itself offers a clue: "pyro" means heat, and "lysis" means to break apart.
The Core Principle: Thermal Cracking Without Oxygen
The process involves heating oil sludge in a reactor, typically between 300°C and 900°C. The key is the absence of oxygen.
Without oxygen, the material cannot combust or burn. Instead, the intense heat provides the energy to break the large, complex chemical bonds in the hydrocarbons, reforming them into smaller, more stable, and often more valuable molecules.
The Three Main Products
This thermal cracking process results in three distinct outputs: a liquid, a gas, and a solid. The specific yield and quality of each depend heavily on the process conditions and the initial composition of the sludge.
A Breakdown of the Pyrolysis Outputs
The value of pyrolysis lies in the utility of its end products. Each component has a potential application, contributing to a more circular economic model for waste management.
The Liquid Product: Pyrolysis Oil
This is often the most sought-after product. It is a liquid emulsion of oxygenated organic compounds, polymers, and water.
This oil can be used directly as a heavy fuel oil in industrial furnaces, boilers, or cement plants. However, it is chemically complex and differs from conventional crude oil, often requiring further refining or upgrading for higher-value applications.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas
The process releases a mixture of non-condensable gases, collectively known as synthesis gas or syngas. This is primarily composed of combustible gases like hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide.
A key advantage is that this syngas can be recycled back into the system to provide the heat for the pyrolysis reactor, significantly reducing the external energy required and making the process more self-sustaining.
The Solid Product: Bio-char / Carbon Black
After the volatile components have been driven off, a dry, solid, carbon-rich residue remains. This material is often referred to as bio-char or carbon black.
Its applications vary. It can be used as a low-grade solid fuel, a component in asphalt production, or as a soil amendment to improve soil structure and water retention.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While promising, pyrolysis technology is not a silver bullet. A clear understanding of its limitations is crucial for any practical application.
Product Quality and Complexity
The resulting pyrolysis oil is not a drop-in replacement for diesel or gasoline. As the references note, it contains a high concentration of oxygenated compounds, water, and a complex mix of chemicals. This makes it more acidic and less stable than conventional petroleum products, necessitating specialized handling and often costly upgrading to produce refined fuels.
High Dependence on Process Conditions
The outcome of pyrolysis is extremely sensitive to operating parameters. Factors like temperature, heating rate, and residence time in the reactor dramatically alter the proportions of oil, gas, and char produced. This requires sophisticated process control to consistently achieve the desired output.
The Feedstock Problem
Oil sludge is not a uniform material. Its composition can vary widely, with fluctuating amounts of oil, water, and solid sediments. This variability in the input feedstock directly impacts the efficiency of the process and the quality of the end products, posing a significant operational challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating pyrolysis requires aligning its capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Pyrolysis is an excellent solution, as it can reduce the total mass of hazardous sludge by over 50%, converting much of it into stable, more manageable products.
- If your primary focus is energy recovery: The technology is highly effective, as the pyrolysis oil and syngas serve as valuable fuel sources, often making the entire facility a net energy producer.
- If your primary focus is creating refined fuels: Be prepared for a multi-step process. Pyrolysis is the first crucial step, but the resulting oil will almost certainly require further investment in upgrading and refining technology.
By understanding its principles and limitations, you can properly assess pyrolysis as a strategic tool for converting industrial waste into a recoverable resource.
Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis Oil | Liquid emulsion of oxygenated organic compounds | Industrial fuel for furnaces, boilers; requires upgrading for refined fuels |
| Syngas | Mixture of combustible gases (H2, CH4, CO) | Recycled to heat the pyrolysis reactor, reducing external energy needs |
| Bio-char / Carbon Black | Dry, solid, carbon-rich residue | Solid fuel, asphalt component, soil amendment |
Ready to transform your oil sludge from a liability into an asset? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for analyzing and optimizing pyrolysis processes. Whether you're researching product yields, testing feedstock variability, or scaling up for energy recovery, our solutions provide the precision and reliability your lab needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your waste-to-resource goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum welding system used for sealing zirconium alloy cladding? Ensure Precise Surface Oxidation Results
- What is the necessity of heat treatment after carburizing? Unlock Superior Hardness and Toughness
- Under what pressure value does vacuum system operate in instrumentation? Find the Perfect Range for Your Lab
- In what ways can you detect leaks in vacuum system? Master Leak Detection for Optimal Performance
- Why must copper foil electrodes undergo high-temperature drying in a vacuum oven? Optimize Li6PS5Cl Cell Assembly
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum drying oven for Ga0.25Zn4.67S5.08? Protect Your Material’s Integrity.
- What are the materials for vacuum hardening? A Guide to High-Performance Steel Selection
- How is radiation responsible for heat transfer through vacuum? Unlocking the Science of Thermal Radiation



















