In short, the quality of CVD diamonds can be exceptional. These lab-grown diamonds are chemically, physically, and optically identical to their natural counterparts. Because they are created in a highly controlled environment, they have the potential to achieve a level of clarity and perfection that is often superior to many rough diamonds found in nature.
The key to understanding CVD diamond quality is recognizing that it's a direct result of a precise manufacturing and refinement process. The crucial factor for a buyer is not whether it's "lab-grown," but understanding the specific post-growth treatments it may have undergone, which are always disclosed on its certificate.

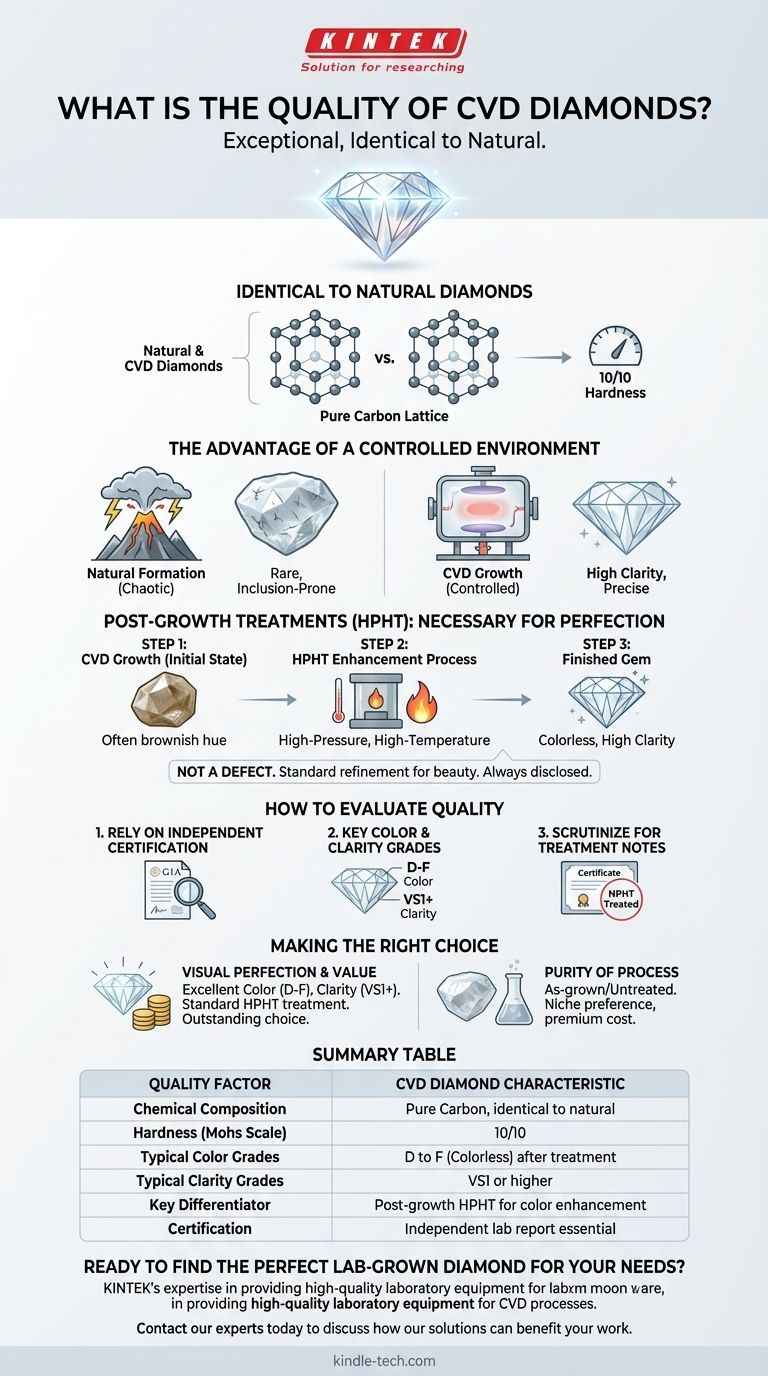
What Defines CVD Diamond Quality?
To properly evaluate a CVD diamond, it's essential to understand the factors that contribute to its final state. The process is one of deliberate engineering rather than geological chance.
Identical to Natural Diamonds
At a molecular level, CVD diamonds share the exact same internal crystal structure and chemical makeup as mined diamonds.
They are composed of pure carbon atoms arranged in a crystal lattice. This means they possess the same hardness, scoring a 10 on the Mohs scale, and exhibit the same intense brilliance and sparkle.
The Advantage of a Controlled Environment
Natural diamonds form under chaotic conditions, making high-quality, inclusion-free stones relatively rare.
CVD diamonds are grown in a vacuum chamber under strict supervision. This controlled process allows for precise management of variables, creating an environment conducive to forming diamonds with very high clarity and color.
The Initial Growth State
The Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process involves growing the diamond crystal in layers over several weeks.
It's common for these diamonds to initially have a brownish hue and rough graphite edges as a byproduct of the growth method. This initial state is why a secondary finishing process is often a critical step in achieving gem quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Post-Growth Treatments
The most misunderstood aspect of CVD diamond quality involves post-growth treatments. This is not a defect, but a standard and necessary step for refining many of these stones.
Why Treatments are Often Necessary
The brown coloration that can occur during growth is often removed to enhance the diamond's beauty. This is a permanent and stable enhancement.
The HPHT Enhancement Process
Many CVD diamonds undergo a High-Pressure, High-Temperature (HPHT) process after they are grown.
This secondary treatment effectively "finishes" the diamond, improving its clarity and color grade. It turns a potentially brown, industrial-grade stone into a bright, colorless gem suitable for fine jewelry.
Treated vs. Untreated: The Key Distinction
An untreated CVD diamond that grew perfectly colorless from the start is rare and highly valued for its "purity."
However, a CVD diamond that has been treated with HPHT to achieve a D color grade is often visually superior to an untreated diamond that has a lower G or H color grade. The critical factor is full disclosure. An independent certificate will always state if the diamond has undergone post-growth treatment.
How to Evaluate a High-Quality CVD Diamond
You should evaluate a CVD diamond using the same criteria as a natural diamond, with a special focus on certification.
Rely on Independent Certification
This is non-negotiable. The diamond's certificate from a reputable gemological lab is your objective proof of its quality. It details the cut, color, clarity, and carat weight.
Key Color and Clarity Grades
For the best combination of visual perfection and value, look for CVD diamonds with color grades between D and F and clarity grades of VS1 or higher.
Stones in the SI1 clarity range can also offer excellent value, provided the inclusions are not visible to the naked eye.
Scrutinize for Treatment Notes
Always check the comments section of the certificate for any mention of post-growth treatment. Knowing a diamond has been treated is not a red flag; it is an expected part of the process for many high-quality CVD diamonds and allows you to make an informed purchase.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be guided by your specific priorities, whether they are visual appeal, the purity of the process, or overall value.
- If your primary focus is visual perfection and value: A certified CVD diamond with excellent color (D-F) and clarity (VS1+) that has undergone standard post-growth treatment is an outstanding and logical choice.
- If your primary focus is the 'purity' of the growth process: Seek out a certified "as-grown" or untreated CVD diamond, but be aware this is a niche preference that may come with a premium.
Ultimately, understanding the science behind CVD diamonds empowers you to select a stone with confidence, knowing it is every bit a true diamond.
Summary Table:
| Quality Factor | CVD Diamond Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Carbon, identical to natural diamonds |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 10/10 |
| Typical Color Grades | D to F (Colorless) after treatment |
| Typical Clarity Grades | VS1 or higher |
| Key Differentiator | Post-growth HPHT treatment for color enhancement |
| Certification | Independent lab report (e.g., GIA, IGI) is essential |
Ready to find the perfect lab-grown diamond for your needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables. Whether you are a researcher developing new CVD processes or a jeweler seeking to understand the materials you work with, our expertise supports the entire lifecycle of these exceptional stones.
Let us help you achieve precision and perfection in your lab. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary advantages of the CVD method for growing diamonds? Engineering High-Purity Gems and Components
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What are the challenges of lab-grown diamonds? Navigating Value, Perception & Technical Limits
- How do lab-grown diamonds compare to natural diamonds? Uncover the Truth About Origin, Price, and Value
- Which lab grown diamond process is best? Focus on Quality, Not the Method

















