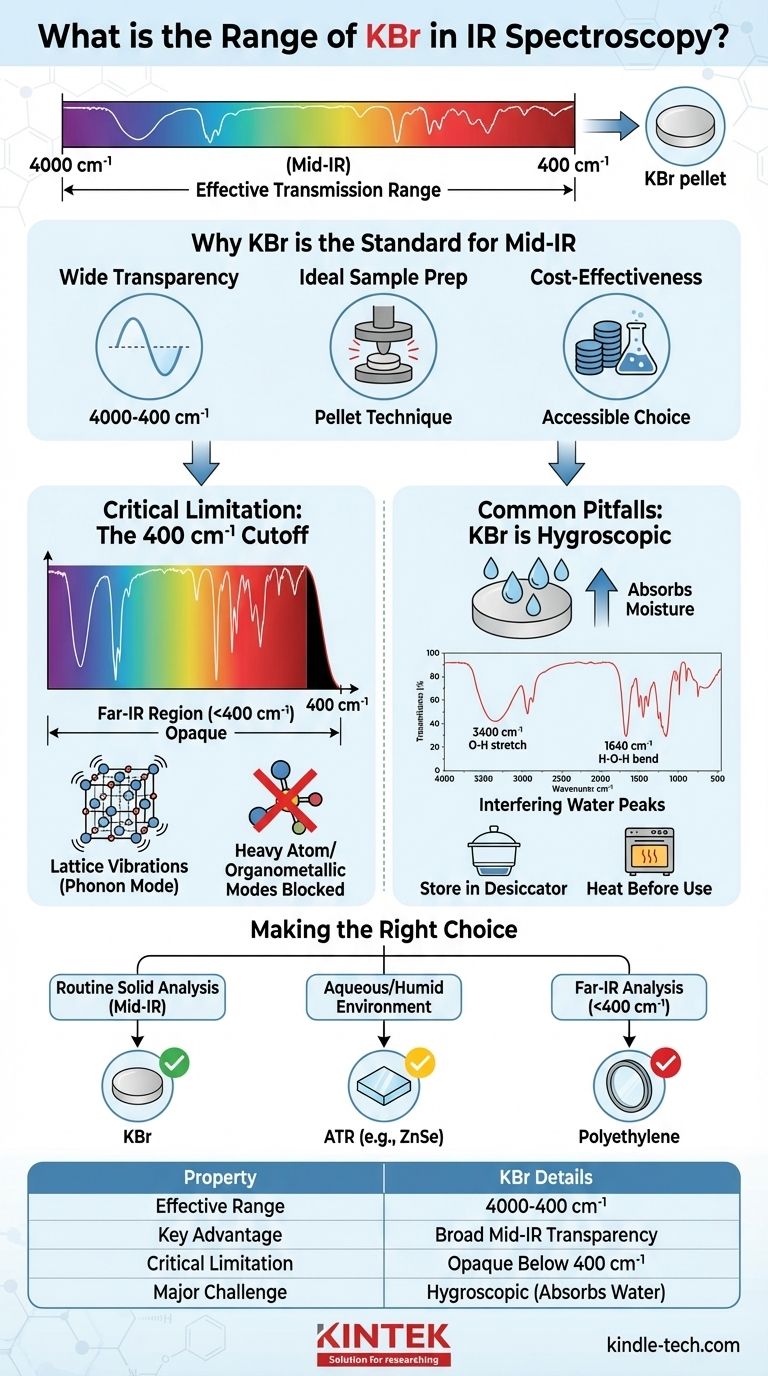
For infrared (IR) spectroscopy, the effective transmission range for Potassium Bromide (KBr) is approximately 4000 to 400 cm⁻¹ (wavenumbers). This broad transparency makes it the most common material for preparing solid samples and for use as optical windows in the Mid-IR region, where most fundamental molecular vibrations occur.
The core reason KBr is a standard in IR spectroscopy is its wide transparency across the crucial Mid-IR range. However, its usefulness is defined as much by this transparency as it is by its primary practical limitation: its tendency to absorb water (hygroscopicity), which can introduce significant interference in your spectrum.

Why KBr is the Standard for Mid-IR Spectroscopy
Potassium Bromide's dominance in routine IR analysis isn't accidental. It stems from a combination of excellent optical properties and practical, physical characteristics.
Wide Transparency Range
The most important feature of KBr is that it does not absorb infrared radiation in the Mid-IR region (4000 - 400 cm⁻¹).
This is the spectral window where the vast majority of organic and inorganic functional groups exhibit their characteristic vibrational absorptions, making KBr an ideal, non-interfering medium for analysis.
Ideal Physical Properties for Sample Prep
KBr is a soft, crystalline salt. Under pressure, it exhibits plastic flow, allowing it to form a thin, transparent, glass-like disc or "pellet" when mixed with a finely ground solid sample.
This KBr pellet technique is a foundational method for analyzing solid samples via transmission IR spectroscopy.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to more exotic optical materials, KBr is relatively inexpensive. This makes it a practical and accessible choice for high-throughput labs, academic research, and quality control applications.
Understanding the Critical Limitation: The 400 cm⁻¹ Cutoff
While KBr is excellent for the Mid-IR, it is not suitable for all spectral regions. Its utility abruptly ends around 400 cm⁻¹, rendering it opaque in the Far-IR region.
The Role of Lattice Vibrations
The cutoff is not arbitrary; it's a fundamental property of the material. The K-Br ionic bond in the crystal lattice has its own vibrational frequency.
This low-frequency vibration, known as a phonon mode, causes KBr itself to strongly absorb IR radiation below approximately 400 cm⁻¹. This absorption completely blocks any signal from your sample in that region.
The Impact on Far-IR Analysis
If your work involves studying low-frequency vibrations like heavy atom skeletal modes or organometallic bonds, KBr is unsuitable.
For analysis in the Far-IR region (<400 cm⁻¹), you must use a different window material, such as specially prepared polyethylene, which is transparent at these lower energies.
Common Pitfalls: KBr is Hygroscopic
The most significant practical challenge when working with KBr is its hygroscopic nature—it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. This can severely compromise the quality of your spectral data.
How Moisture Affects Your Spectrum
Water (H₂O) is a very strong IR absorber. If your KBr has absorbed moisture, you will see characteristic water peaks in your spectrum, even if your sample is perfectly dry.
These interfering peaks include a very broad absorption band around 3400 cm⁻¹ (O-H stretch) and a sharp band around 1640 cm⁻¹ (H-O-H bend). These can easily mask the peaks of your actual sample.
Proper Handling and Storage
To prevent moisture contamination, KBr powder must be stored in a desiccator. KBr optics (windows and pellets) should be stored under desiccation or in a low-humidity environment.
When preparing a KBr pellet, it is also common practice to heat the powder in an oven to drive off any adsorbed water just before use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the properties of KBr allows you to select the appropriate sampling technique for your specific analytical need.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis of solid organic or inorganic compounds: KBr is almost always the correct and most cost-effective choice for creating pellets in the Mid-IR range.
- If you are working with aqueous solutions or in a very humid environment: A KBr pellet is a poor choice. An Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) accessory, often with a water-insoluble Zinc Selenide (ZnSe) crystal, is a far superior method.
- If your analysis requires data below 400 cm⁻¹ (Far-IR): You must use a material other than KBr. Polyethylene windows and matrices are the standard for this spectral region.
Ultimately, choosing the right IR material is the first step toward acquiring a clean, accurate, and meaningful spectrum.
Summary Table:
| Property | Details for KBr in IR Spectroscopy |
|---|---|
| Effective Transmission Range | 4000 cm⁻¹ to 400 cm⁻¹ (Mid-IR) |
| Primary Use | Solid sample pellets, optical windows |
| Key Advantage | Broad transparency in the fundamental Mid-IR region |
| Critical Limitation | Strong absorption below 400 cm⁻¹ (Far-IR cutoff) |
| Major Practical Challenge | Hygroscopic (absorbs water, causing spectral interference) |
Need the right equipment for precise IR spectroscopy?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your spectroscopy needs. Whether you're preparing KBr pellets or require accessories for Far-IR analysis, our expertise ensures you get accurate and reliable results.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Customizable PTFE Wafer Carriers for Semiconductor and Lab Applications
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the minimum sample required for XRD analysis? Optimize Your Material Analysis
- What are the limitations of the IR spectroscopy? Understanding Its Boundaries for Accurate Analysis
- How should a sample holder be handled to ensure its longevity? Protect Your Lab Investment and Data Integrity
- What affects melting point chemistry? A Guide to Molecular Forces and Lattice Energy
- What is the difference between XRF and XRD techniques? A Guide to Choosing the Right Analytical Tool











