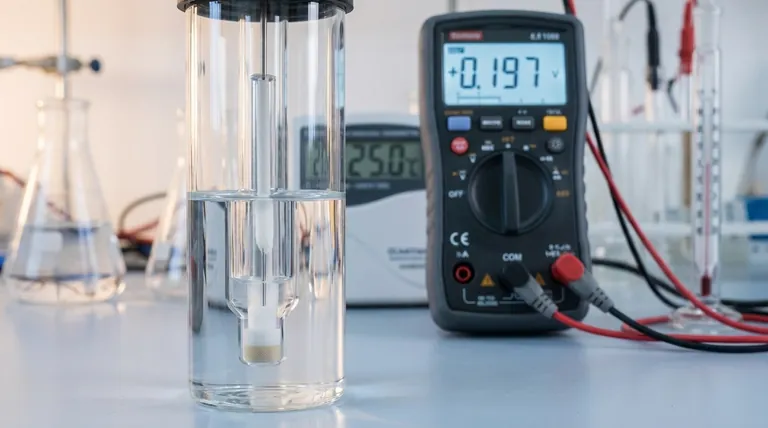
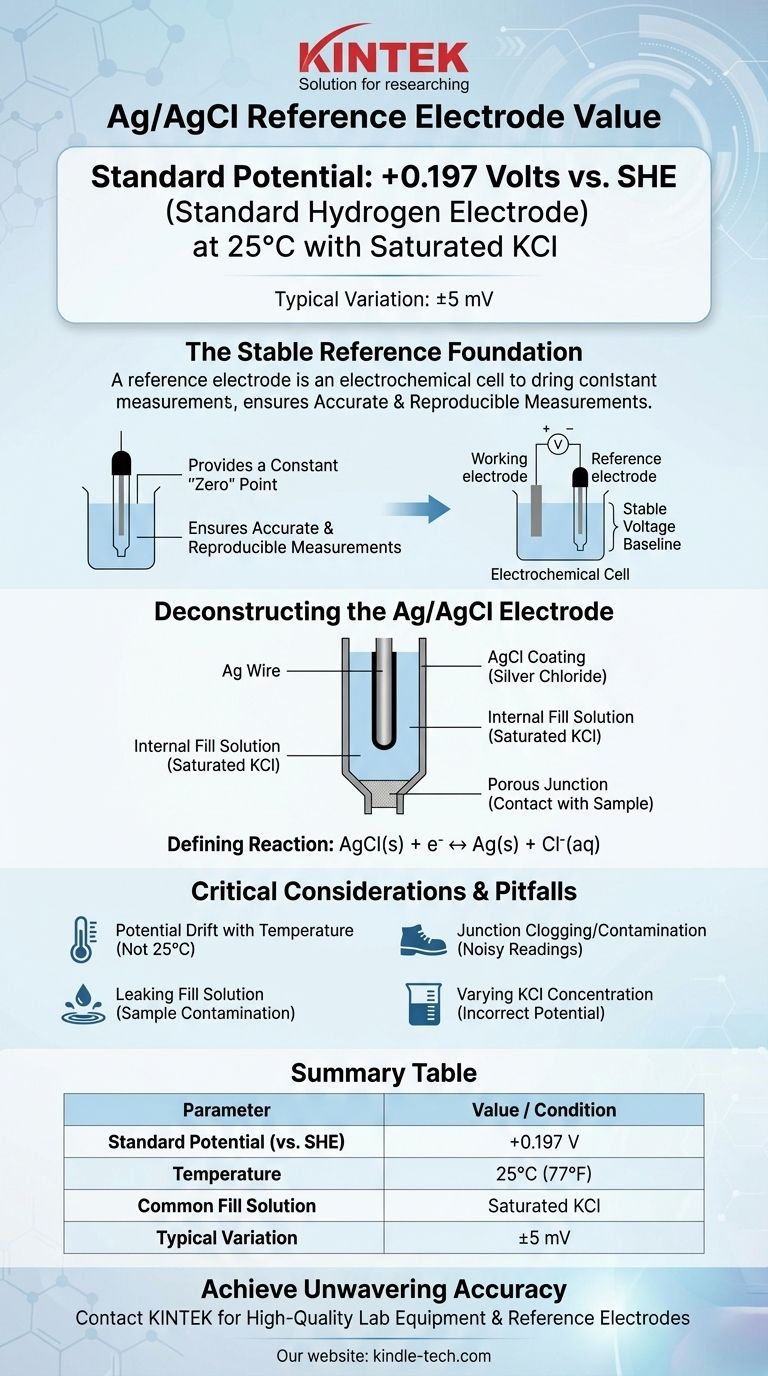
At its most common configuration, the silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) reference electrode has a potential of +0.197 Volts relative to the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) at 25°C. This value assumes the electrode is using a saturated potassium chloride (KCl) fill solution. Minor variations, often cited as +199 mV (±5mV), are common due to slight differences in preparation and conditions.
The core function of a reference electrode is to provide an unwavering, stable voltage baseline. Understanding that the Ag/AgCl electrode's potential is defined by a specific chemical equilibrium, and is sensitive to chloride concentration and temperature, is the key to using it for accurate and reproducible measurements.

The Role of a Stable Reference
Establishing a Zero Point
All voltage measurements are inherently a potential difference between two points. In electrochemistry, you cannot measure the absolute potential of a single working electrode.
A reference electrode provides a constant, known potential that serves as the stable "zero" point. All other potentials in your electrochemical cell are then measured relative to this unwavering reference.
How It Achieves Stability
An ideal reference electrode is described as "well-poised." This means its potential is governed by a fast, reversible chemical reaction that is not significantly disturbed by the tiny amount of current that flows during measurement.
For the Ag/AgCl electrode, this stability comes from the equilibrium between solid silver chloride and the silver and chloride ions.
Deconstructing the Ag/AgCl Electrode
The Core Components
A typical Ag/AgCl electrode consists of a silver (Ag) wire that has been coated with a layer of solid silver chloride (AgCl).
This entire assembly is immersed in an internal fill solution that contains a known, fixed concentration of chloride ions (Cl⁻), most commonly potassium chloride (KCl). A porous junction, often made of ceramic or cotton, allows electrical contact with the sample solution.
The Defining Electrochemical Reaction
The potential of the electrode is established by a simple and reversible half-cell reaction:
AgCl(s) + e⁻ ↔ Ag(s) + Cl⁻(aq)
The potential of this equilibrium is directly dependent on the activity (effectively, the concentration) of the chloride ions in the fill solution.
Why the Fill Solution Is Critical
Because the potential depends on the chloride concentration, its value must be fixed and known.
Saturated KCl is the most common choice because it's easy to prepare and maintain. As long as solid KCl crystals are present, the solution remains saturated, ensuring a constant chloride activity and thus a stable potential of +0.197 V.
Other concentrations, such as 3M or 1M KCl, are also used and will result in different reference potentials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Potential Drift with Temperature
The standard potential of +0.197 V is only valid at 25°C (77°F). The potential of the electrode will change predictably with temperature. For high-precision work, this temperature dependence must be accounted for or controlled.
Junction Clogging and Contamination
The porous junction is the most common point of failure. If it becomes clogged with sample material or if the internal electrolyte crystallizes within it, the electrical connection is broken, leading to noisy or completely unstable readings.
Leaking Fill Solution
The internal fill solution slowly leaks out through the junction by design. If your sample is sensitive to chloride or potassium ions, this leakage can cause contamination or undesirable side reactions, interfering with your measurement. In these cases, a double-junction electrode with a different outer electrolyte may be necessary.
Assuming Saturated KCl
Never assume your Ag/AgCl electrode uses a saturated KCl solution. Always verify the fill solution concentration, as using the wrong reference potential in your calculations is a fundamental source of error. An electrode with 3M KCl, for instance, has a potential closer to +0.210 V vs. SHE.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your measurements are sound, you must treat your reference electrode as the critical instrument it is.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis (e.g., pH measurement): Use a commercial, sealed electrode, store it properly in its designated storage solution to keep the junction wet, and replace it when readings become unstable.
- If your primary focus is high-precision research (e.g., corrosion studies): Always report the specific reference electrode used (e.g., Ag/AgCl, sat. KCl) alongside your data, monitor for drift, and consider calibrating it against a freshly prepared standard.
- If your primary focus is avoiding sample contamination: Select a double-junction electrode or one with a fill solution that is chemically compatible with your sample to prevent precipitation or interference at the liquid junction.
A reliable reference electrode is the foundation of any accurate electrochemical measurement.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Value / Condition |
|---|---|
| Standard Potential (vs. SHE) | +0.197 V |
| Temperature | 25°C (77°F) |
| Common Fill Solution | Saturated KCl |
| Typical Variation | ±5 mV |
Achieve Unwavering Accuracy in Your Lab
Your electrochemical measurements are only as reliable as your reference electrode. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise and stable Ag/AgCl reference electrodes your laboratory needs for reproducible results.
Let our experts help you select the perfect reference electrode for your application—whether it's routine analysis or high-precision research.
Contact KINTEK today to ensure your measurements are built on a solid foundation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
People Also Ask
- What is the common role of a platinum disk electrode? A Guide to Its Primary Use as a Working Electrode
- What is a common application for the platinum wire/rod electrode? The Essential Guide to Counter Electrodes
- What are the specifications of the Platinum-Titanium Functional Electrode? Maximize Electrochemical Performance
- How should a platinum wire/rod electrode be cleaned before use? A Guide to Reliable Electrochemical Data
- What is the difference between ring disk electrode and rotating disk electrode? Unlock Deeper Electrochemical Insights



















