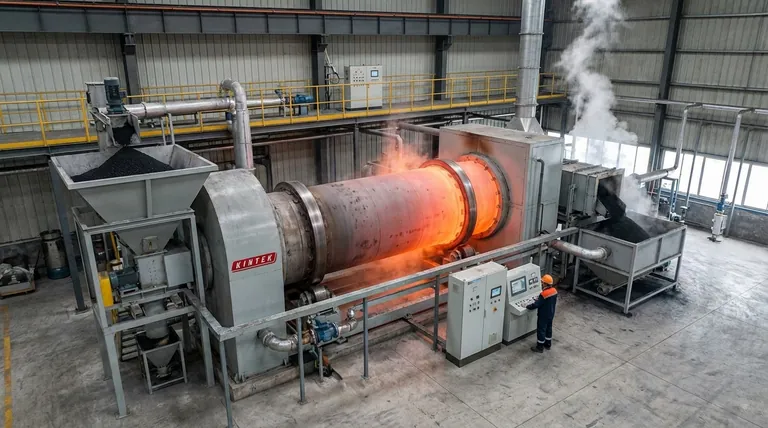
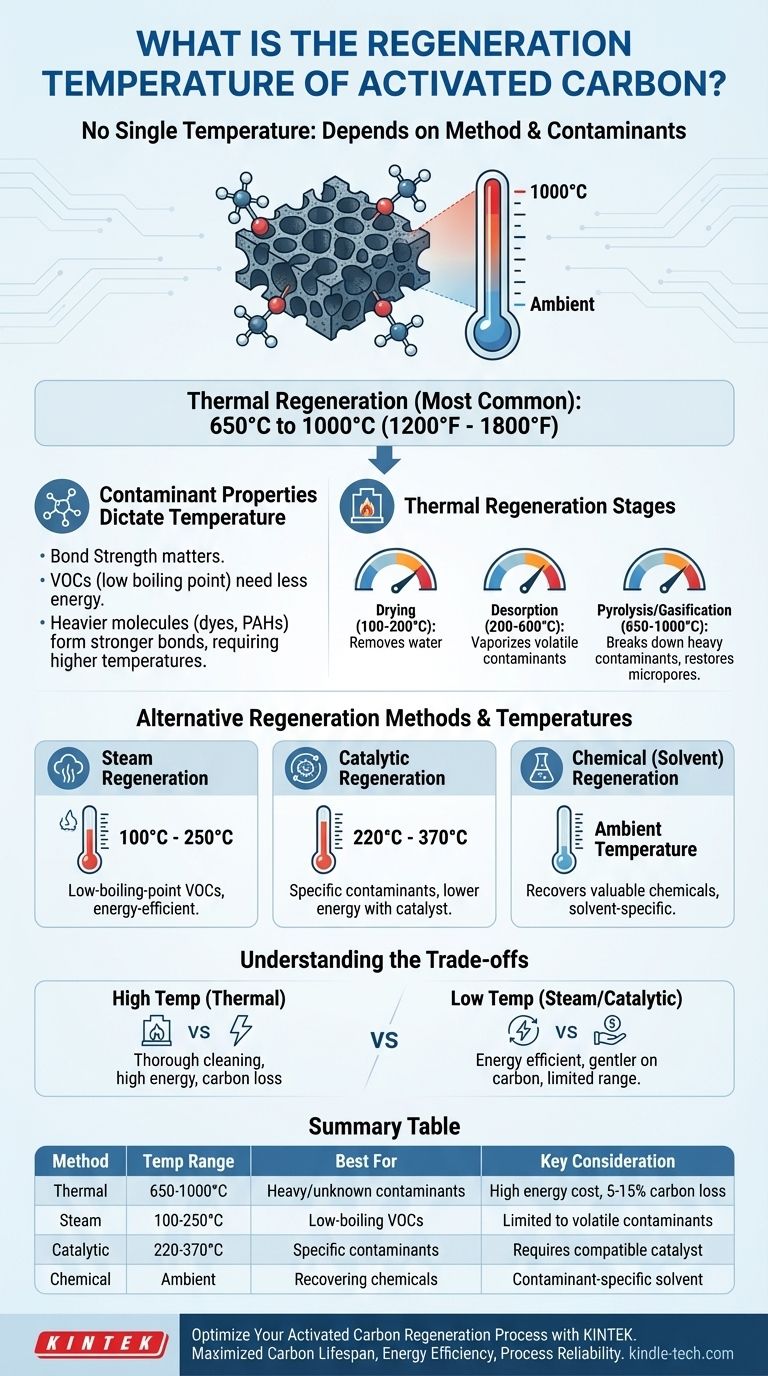
In short, there is no single regeneration temperature for activated carbon. The correct temperature depends entirely on the regeneration method and the specific contaminants being removed. For thermal regeneration, the most common industrial method, temperatures typically range from 650°C to 1000°C (1200°F to 1800°F).
Activated carbon regeneration is not about a single temperature but a process chosen to balance contaminant removal, energy cost, and carbon preservation. The goal is to break the bonds holding contaminants to the carbon's surface without destroying the carbon itself.

How Contaminant Properties Dictate Regeneration
Activated carbon works through adsorption, a process where contaminant molecules stick to its vast internal surface area. Regeneration is simply the process of reversing this, forcing the contaminants to detach.
The Role of Adsorption Energy
The strength of the bond between the contaminant and the carbon surface determines the energy needed for removal. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) with low boiling points are held by weaker forces and require less energy (lower temperatures) to release.
Heavier, more complex molecules like dyes or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) form stronger bonds and demand significantly more energy, pushing temperatures into the higher end of the thermal regeneration range.
Thermal Regeneration: The Brute-Force Method
This is the most common and robust method. It involves heating the spent carbon in a low-oxygen environment, typically a rotary kiln, to very high temperatures.
The process happens in stages:
- Drying (100-200°C): Removes residual water.
- Desorption (200-600°C): Vaporizes and boils off the more volatile contaminants.
- Pyrolysis/Gasification (650-1000°C): Breaks down the remaining, heavier contaminants into a char, which is then gasified by reacting with an oxidizing agent like steam or CO2. This final, high-temperature step is crucial for clearing the micropores and restoring the carbon's activity.
Alternative Regeneration Methods and Their Temperatures
While thermal regeneration is effective, its high energy cost and associated carbon loss (typically 5-15% per cycle) have led to other specialized methods.
Steam Regeneration
This method uses steam as both the heat source and a cleaning agent. It is most effective for regenerating carbon that has adsorbed volatile compounds with low boiling points.
Temperatures for steam regeneration are much lower than for thermal regeneration, generally in the range of 100°C to 250°C. It is faster and less energy-intensive but cannot remove heavy or strongly adsorbed contaminants.
Chemical (Solvent) Regeneration
In this process, a chemical solvent is used to wash the contaminants out of the carbon pores. The choice of solvent is critical and must be able to dissolve the specific adsorbate.
This method operates at or near ambient temperatures. Its effectiveness is highly dependent on the contaminant-solvent pairing and is often used in niche applications where the adsorbed substance is valuable and can be recovered from the solvent.
Catalytic Regeneration
This is an emerging technique that adds a catalyst to the carbon surface. The catalyst lowers the activation energy needed to break down adsorbed compounds.
Catalytic regeneration can occur at significantly lower temperatures than conventional thermal methods, often between 220°C and 370°C. This reduces energy consumption and minimizes damage to the activated carbon, but its application is specific to the contaminants the catalyst is designed for.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a regeneration method is a technical and economic decision. There is no universally "best" option.
High Temperature vs. Low Temperature
High-temperature methods like thermal regeneration offer near-complete restoration of adsorptive capacity but come with high energy costs, CO2 emissions, and a gradual loss of the carbon material itself.
Low-temperature methods like steam or catalytic regeneration are cheaper and gentler on the carbon but are only suitable for a limited range of volatile contaminants and may not fully restore the carbon's performance.
In-Situ vs. Off-Site
Steam and chemical regeneration can often be performed in-situ (on-site), reducing the logistical complexity of transporting the spent carbon.
Thermal regeneration almost always requires sending the carbon off-site to a specialized facility with the necessary high-temperature kilns and emissions control systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal regeneration strategy depends entirely on the application and operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is removing a wide range of unknown or heavy contaminants: High-temperature thermal regeneration (650-1000°C) is the most reliable and thorough method.
- If your primary focus is removing specific, low-boiling-point VOCs: Steam regeneration (100-250°C) is a much more energy-efficient and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is minimizing energy costs and preserving the carbon structure: Explore advanced options like catalytic regeneration (220-370°C) if a suitable catalyst exists for your contaminants.
- If your primary focus is recovering a valuable adsorbed chemical: Chemical regeneration at ambient temperatures is the only method that allows for recovery.
Ultimately, selecting the right regeneration temperature is about understanding the chemistry of your specific contaminants and the economic realities of your operation.
Summary Table:
| Regeneration Method | Typical Temperature Range | Best For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Regeneration | 650°C - 1000°C | Heavy/unknown contaminants, thorough cleaning | High energy cost, carbon loss (5-15%) |
| Steam Regeneration | 100°C - 250°C | Low-boiling-point VOCs, energy efficiency | Limited to volatile contaminants |
| Catalytic Regeneration | 220°C - 370°C | Specific contaminants, lower energy use | Requires a compatible catalyst |
| Chemical Regeneration | Ambient Temperature | Recovering valuable chemicals | Contaminant-specific solvent required |
Optimize Your Activated Carbon Regeneration Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right regeneration method is critical for your lab's efficiency, cost control, and sustainability. The wrong temperature can lead to incomplete cleaning, wasted energy, or damage to your valuable activated carbon.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables to support your specific regeneration needs. Whether you require robust thermal ovens for high-temperature processes or precise systems for lower-temperature methods, we provide reliable solutions that deliver:
- Maximized Carbon Lifespan: Minimize material loss and maintain adsorption capacity.
- Energy Efficiency: Reduce operational costs with optimized temperature control.
- Process Reliability: Ensure consistent, complete regeneration for accurate results.
Don't let an inefficient regeneration process compromise your research or operations. Contact our experts today to discuss your application, and we'll help you select the ideal equipment for your lab's unique requirements.
Contact KINTEK for a personalized solution
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Can you restore activated carbon? Understanding the Industrial Reactivation Process
- What is the temperature of a carbon regeneration kiln? Mastering the 750-800°C Reactivation Process
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the principles of a rotary kiln? Master the Mechanics of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the temperature for activated carbon regeneration? Key Ranges from 220°C to 900°C



















