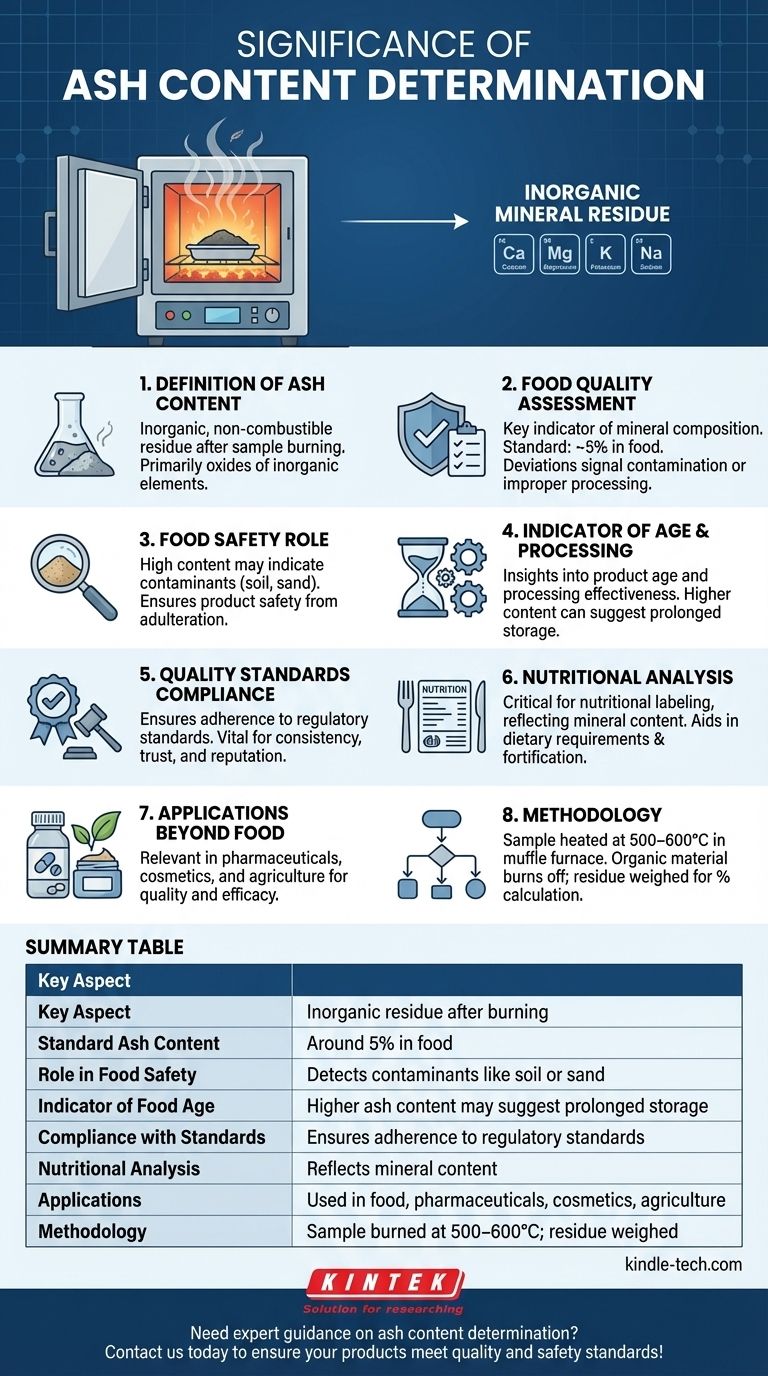
Ash content determination is a critical analytical process used to measure the inorganic mineral content in various products, particularly in food. It involves burning a sample to remove organic material, leaving behind non-combustible residues, which are primarily oxides of inorganic elements. This measurement is essential for assessing food quality, safety, and nutritional value. A standard acceptable ash content in food is around 5%, and deviations from this range can indicate issues such as contamination, aging, or improper processing. By determining ash content, manufacturers and regulators can ensure compliance with quality standards, identify potential adulteration, and maintain consumer trust in the product's safety and nutritional integrity.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition of Ash Content:
- Ash content refers to the inorganic, non-combustible residue left after a sample is completely burned. This residue primarily consists of oxides of inorganic elements like calcium, magnesium, potassium, and sodium.
- It is a direct measure of the mineral content in a product, as organic materials are burned away during the process.
-
Significance in Food Quality Assessment:
- Ash content is a key indicator of the mineral composition in food products. Minerals are essential nutrients, and their presence in appropriate amounts is crucial for maintaining food quality and nutritional value.
- A standard acceptable ash content in food is around 5%. Higher or lower levels can signal issues such as contamination, improper processing, or the age of the food.
-
Role in Food Safety:
- High ash content may indicate the presence of contaminants such as soil, sand, or other inorganic materials, which can compromise food safety.
- By monitoring ash content, manufacturers can detect adulteration or improper handling during production, ensuring that the final product is safe for consumption.
-
Indicator of Food Age and Processing:
- Ash content can provide insights into the age of food products. For example, higher ash content in certain foods may suggest prolonged storage or exposure to environmental factors that increase mineral content.
- It also helps evaluate the effectiveness of food processing methods, as improper processing can lead to undesirable changes in mineral composition.
-
Compliance with Quality Standards:
- Regulatory bodies often set standards for acceptable ash content in food products. Determining ash content ensures compliance with these standards, avoiding legal and reputational risks for manufacturers.
- It also helps maintain consistency in product quality, which is vital for consumer trust and brand reputation.
-
Nutritional Analysis:
- Ash content is a critical parameter in nutritional labeling, as it reflects the mineral content of the product. This information is valuable for consumers seeking to meet specific dietary requirements.
- It also aids in formulating balanced diets and developing fortified foods with enhanced mineral content.
-
Applications Beyond Food:
- While ash content determination is most commonly associated with food, it is also relevant in other industries, such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and agriculture, where mineral content plays a role in product quality and efficacy.
-
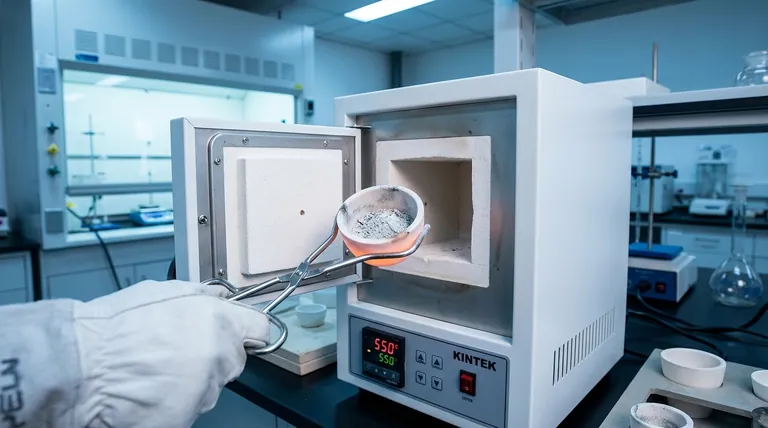
Methodology of Ash Content Determination:
- The process involves heating a sample at high temperatures (typically 500–600°C) in a muffle furnace until all organic material is burned off. The remaining residue is weighed to calculate the ash content as a percentage of the original sample.
- This method is standardized and widely used due to its simplicity and reliability.
By understanding the significance of ash content determination, manufacturers, regulators, and consumers can make informed decisions about product quality, safety, and nutritional value. This process plays a vital role in ensuring that products meet established standards and deliver the intended benefits to end-users.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Inorganic residue after burning a sample, primarily oxides of minerals. |
| Standard Ash Content | Around 5% in food; deviations indicate contamination or improper processing. |
| Role in Food Safety | Detects contaminants like soil or sand, ensuring safe consumption. |
| Indicator of Food Age | Higher ash content may suggest prolonged storage or environmental exposure. |
| Compliance with Standards | Ensures adherence to regulatory quality and safety standards. |
| Nutritional Analysis | Reflects mineral content, aiding dietary and labeling requirements. |
| Applications | Used in food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and agriculture. |
| Methodology | Sample burned in a muffle furnace at 500–600°C; residue weighed for ash %. |
Need expert guidance on ash content determination? Contact us today to ensure your products meet quality and safety standards!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the importance of melting process? Master the Foundation of Metal Production
- How do you cool a muffle furnace? Safeguard your equipment and samples from thermal shock.
- What happens in the muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- What are the roles of laboratory drying ovens and muffle furnaces in biomass analysis? Precision Thermal Treatment
- What is the mechanism of a muffle furnace? Master Precise, Contaminant-Free Heating



















