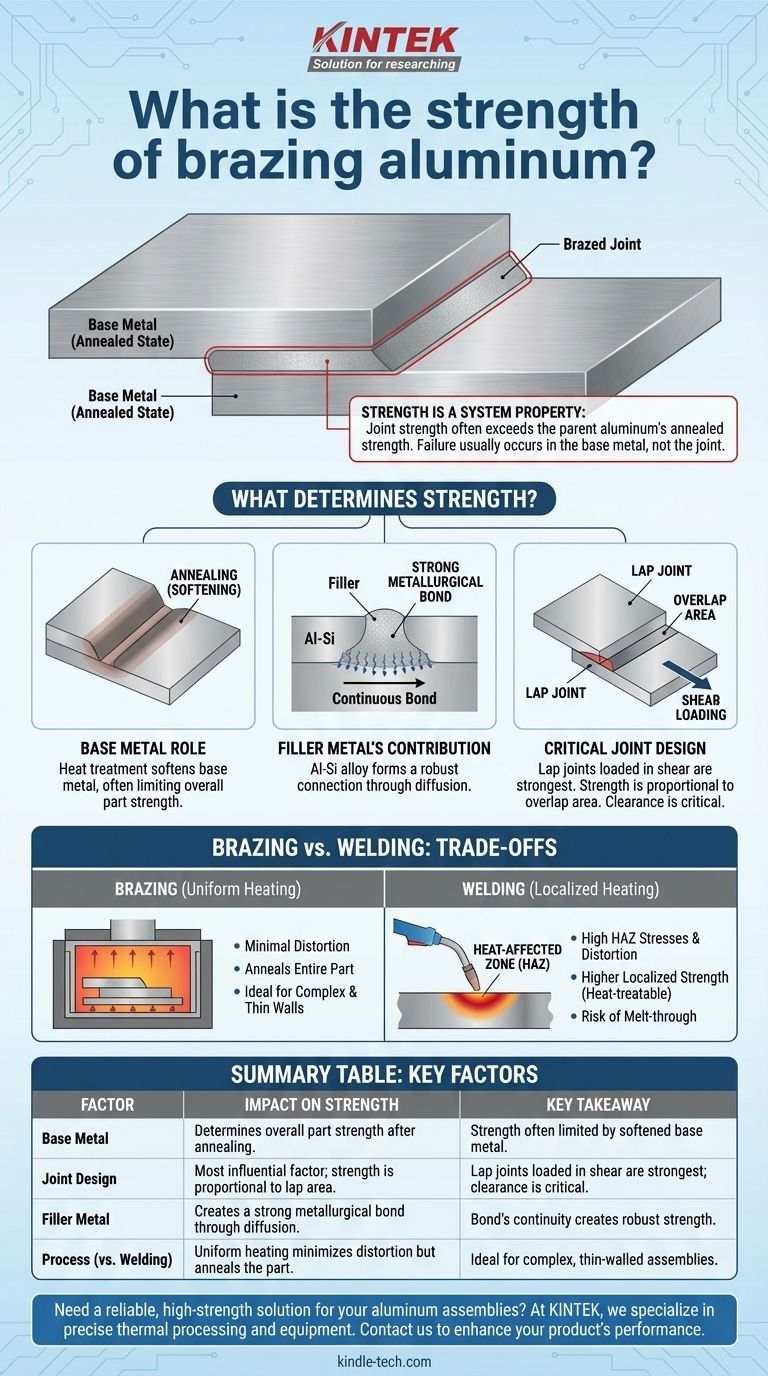
The strength of a brazed aluminum joint is not a single, fixed value. In a properly designed and executed joint, the shear strength can meet or exceed the strength of the parent aluminum alloy in its annealed (softened) state. This means that when tested to destruction, the base metal will often fail before the brazed joint itself does.
The core principle to understand is that brazing's strength comes not from the filler metal alone, but from the combination of a strong metallurgical bond and an optimized joint design. The focus shifts from the inherent strength of the filler to the shear strength distributed across the large surface area of a lap joint.

What Determines the Strength of a Brazed Joint?
The final strength of a brazed assembly is a system property, determined by the interaction of the base metal, the filler, and the joint's physical design.
The Role of the Base Metal
Brazing occurs at a temperature below the melting point of the aluminum base metal, but it is high enough to anneal it, which is a heat treatment that softens the metal. This is the most critical factor to understand.
The strength of the overall part is often limited by the annealed strength of the base aluminum, not the brazed joint. Even if the joint is technically stronger, the component will bend or break in the softened areas adjacent to the joint.
The Filler Metal's Contribution
Aluminum brazing typically uses an aluminum-silicon (Al-Si) alloy as the filler metal. This filler has a lower melting point than the parent material.
While the filler alloy itself is not as strong as many high-strength aluminum alloys, its purpose is to wet the surfaces and form a strong, continuous metallurgical bond through diffusion. This bond, when spread over a sufficient area, creates an incredibly robust connection.
The Critical Importance of Joint Design
This is the most influential factor you can control. Brazed joints are engineered to be strongest when loaded in shear. Attempting to use them in pure tension (a butt joint) is poor practice and will yield a much weaker result.
The most common and effective design is the lap joint, where two surfaces overlap. The strength of this joint is directly proportional to the overlapping surface area. A longer lap provides a stronger joint.
Joint clearance, the gap between the two overlapping parts, is also critical. Too small a gap prevents the filler metal from flowing in, while too large a gap can lead to voids and lower strength. Typical clearances are in the range of 0.002 to 0.006 inches (0.05 to 0.15 mm).
Understanding the Trade-offs: Brazing vs. Welding
Engineers often weigh brazing against welding. The choice has significant implications for strength and manufacturing.
Strength and the Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)
Welding creates an intense, localized heat-affected zone (HAZ), which can significantly alter the properties of the base metal in that small area. This can lead to high residual stresses and distortion.
Brazing, especially furnace brazing, heats the entire assembly uniformly. This results in minimal distortion but anneals the entire part, which may reduce its overall strength compared to its pre-brazed temper. However, this uniformity can be a significant advantage.
Design Complexity and Material Thickness
Brazing excels at joining complex, multi-joint assemblies or components with very thin walls, such as heat exchangers. The gentle, uniform heating makes it possible to create intricate and leak-tight structures that would be impossible to weld reliably.
It is also superior for joining dissimilar thicknesses of aluminum, as the risk of melting through the thinner section is much lower than with welding.
Post-Processing and Heat Treatment
For heat-treatable aluminum alloys (like the 6xxx series), it is possible to perform a post-braze heat treatment (solution treating and aging) to recover a significant portion of the base metal's original strength. This adds cost and complexity but can be essential for high-performance applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if brazing is strong enough, you must evaluate your design goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength in a simple, linear joint: Welding a heat-treatable alloy and managing the HAZ may yield a higher localized strength.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex, leak-tight assembly (like a radiator or chassis): Brazing is the superior method, and its strength is maximized through proper lap joint design.
- If your primary focus is joining very thin materials or dissimilar thicknesses: Brazing provides better thermal control and is often the more reliable and structurally sound option.
Ultimately, designing for the specific joining process from the beginning is the key to achieving a robust and reliable aluminum assembly.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Strength | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Base Metal | Determines overall part strength after annealing. | Strength is often limited by the softened base metal, not the joint. |
| Joint Design | Most influential factor; strength is proportional to lap area. | Lap joints loaded in shear are strongest; joint clearance is critical. |
| Filler Metal | Creates a strong metallurgical bond through diffusion. | The bond's continuity over a large area creates robust strength. |
| Process (vs. Welding) | Uniform heating minimizes distortion but anneals the part. | Ideal for complex, thin-walled, or leak-tight assemblies like heat exchangers. |
Need a reliable, high-strength solution for your aluminum assemblies?
Brazing is the superior method for creating complex, leak-tight components like heat exchangers, radiators, and chassis. At KINTEK, we specialize in the precise thermal processing and equipment needed to achieve optimal brazed joint strength and integrity. Our expertise ensures your lab or production facility can reliably join even thin or dissimilar materials.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our brazing solutions can enhance your product's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- What is the sintering process in engineering? A Guide to High-Performance Materials
- What is the temperature and time for annealing? A Tailored Guide for Your Material
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum furnace with a flexible membrane? High-Precision Titanium Bonding Explained
- What technical advantages does a high-temperature furnace with a graphite heater offer for steam oxidation experiments?
- What is the process of vacuum brazing? Achieve High-Purity, Strong Metal Joining
- Which furnace can produce high temperature? Choose the Right High-Temp Furnace for Your Process
- How is hydrogen produced in pyrolysis? A Low-Carbon, Energy-Efficient Path to Clean Hydrogen



















