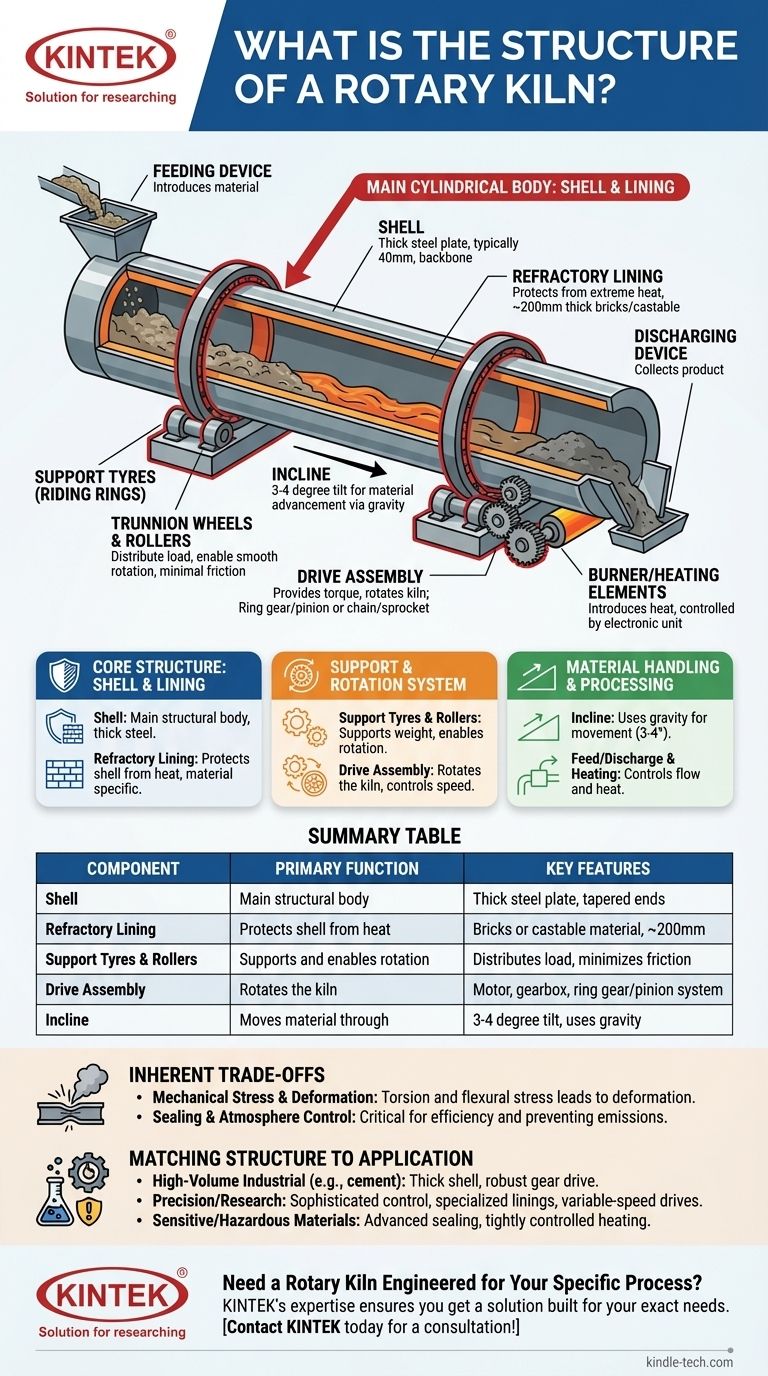
In essence, a rotary kiln is a long, cylindrical furnace that is slightly inclined and rotates slowly on its axis. Its fundamental structure consists of the main cylindrical body, known as the shell, which is protected from high temperatures by an internal refractory lining. This entire assembly is supported by a system of rollers and is turned by a powerful drive assembly, allowing material to tumble and flow from one end to the other as it is processed.
A rotary kiln’s structure is not just a collection of parts, but an engineered system designed for a single purpose: to contain extreme thermal and mechanical stress while precisely controlling the movement and chemical transformation of materials.

The Core Structure: Shell and Lining
The primary body of the kiln is responsible for containing the entire process. Its design is a balance between structural integrity and thermal resistance.
The Kiln Shell
The kiln shell is the main structural component, a large tube typically fabricated from thick steel plate (often around 40mm). It is the backbone of the entire apparatus.
Because it bears immense weight and stress, the steel is often thicker near the support points. The ends may be conically tapered to facilitate a smoother flow of material in and out of the kiln.
The Refractory Lining
Inside the steel shell is a thick layer of refractory bricks or castable material, often around 200mm thick.
This lining's sole purpose is to protect the steel shell from the extreme internal processing temperatures, which would otherwise weaken and destroy it. The choice of refractory material is critical and depends entirely on the material being processed.
The Support and Rotation System
A kiln's immense weight must be supported and its rotation must be controlled with precision. This is the function of the mechanical support and drive systems.
Support Tyres (Riding Rings)
Attached to the outside of the shell are massive steel rings known as support tyres or riding rings.
These components act as the interface between the rotating kiln shell and the stationary support structure, distributing the kiln's load evenly.
Trunnion Wheels and Rollers
The support tyres rest on sets of heavy-duty rollers, often called trunnion wheels.
These rollers function like bearings, allowing the massive kiln shell to rotate smoothly with minimal friction. Thrust rollers are also used to prevent the inclined kiln from sliding downhill.
The Drive Assembly
The drive assembly provides the torque needed to rotate the kiln. This system typically consists of a large motor, a reduction gearbox, and a final drive mechanism.
Common drive types include a large ring gear that encircles the kiln and is driven by a small pinion gear, or a chain and sprocket system. The speed of rotation is a critical process variable.
Material Handling and Processing Components
The kiln's structure is designed to move material through a controlled thermal environment.
The Incline
Every rotary kiln is set at a slight incline, typically between 3 and 4 degrees from horizontal.
This tilt is fundamental to its operation. As the kiln rotates, gravity causes the material inside to slowly tumble and advance from the higher feeding end to the lower discharge end.
Feed and Discharge Systems
Specialized equipment is used at both ends of the kiln. A feeding device introduces raw material at the upper end, while a discharging device collects the finished product as it exits the lower end.
The shape of the shell and the design of these systems are crucial for preventing material spillage and ensuring a controlled flow.
Heating and Control Systems
Heat is introduced by a burner positioned at the discharge end or through external electric heating elements surrounding the shell.
An electronic control unit manages all of these components—regulating the fuel or power, rotation speed, and tilt to create a precise heat pattern that matches the product's requirements.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
The design of a rotary kiln is a series of engineering compromises to manage extreme operating conditions.
Mechanical Stress and Deformation
The combination of immense weight and high temperatures subjects the kiln shell to constant torsion and flexural stress.
Over time, this can lead to an "ellipsoidal deformation," where the circular shell slightly flattens. This deformation can stress and damage the internal refractory lining, impacting the kiln's operational lifespan.
Sealing and Atmosphere Control
Sealing the gap between the rotating kiln and the stationary feed and discharge hoods is a significant engineering challenge.
Effective seals are critical for maintaining the internal atmosphere, improving thermal efficiency, and preventing the release of dust or gases. However, achieving a perfect seal on such a large, dynamic piece of equipment is difficult and requires constant maintenance.
Matching Structure to Application
The specific design of a rotary kiln's components is dictated by its intended use.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial processing (e.g., cement): Your key components are a thick steel shell, a robust gear drive, and an extremely durable refractory lining built for continuous, high-stress operation.
- If your primary focus is precision or research: The critical elements are a sophisticated control system, specialized linings to prevent contamination, and variable-speed drives for maximum experimental flexibility.
- If your primary focus is handling sensitive or hazardous materials: The most important structural features are advanced sealing systems and a tightly controlled heating mechanism to ensure process integrity and safety.
Understanding this purpose-driven design allows you to evaluate any rotary kiln not as a static object, but as a dynamic processing solution.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Shell | Main structural body | Thick steel plate, tapered ends for material flow |
| Refractory Lining | Protects shell from heat | Bricks or castable material, ~200mm thick |
| Support Tyres & Rollers | Supports and enables rotation | Distributes load, minimizes friction, includes thrust rollers |
| Drive Assembly | Rotates the kiln | Motor, gearbox, ring gear/pinion system for speed control |
| Incline | Moves material through the kiln | 3-4 degree tilt, uses gravity for material advancement |
Need a Rotary Kiln Engineered for Your Specific Process?
Whether your laboratory requires a high-volume industrial kiln or a precision unit for research, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment ensures you get a solution built for your exact needs—from robust refractory linings to sophisticated control systems. Let our specialists help you select the right structure for maximum efficiency and safety.
Contact KINTEL today for a consultation on your laboratory's kiln requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste



















