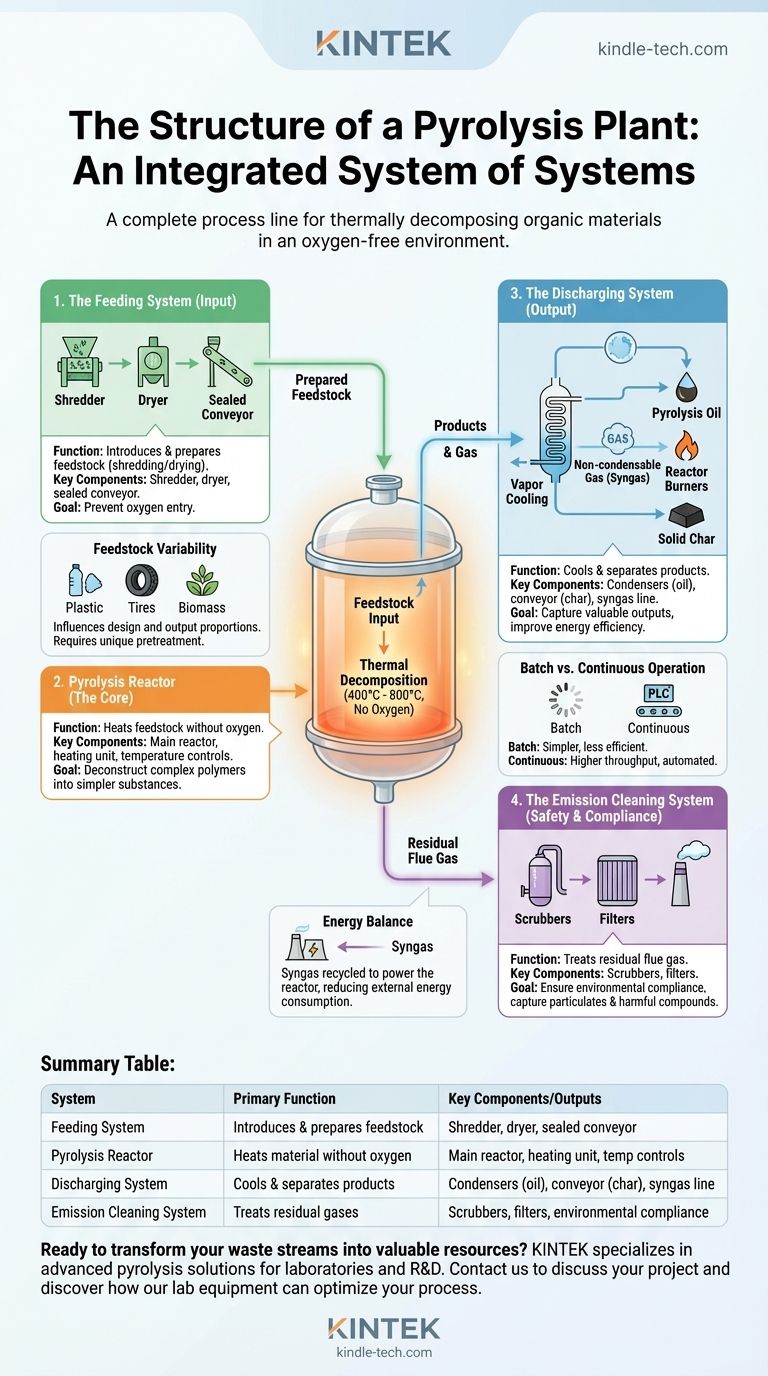
At its core, a pyrolysis plant is structured around four primary, interconnected systems. These are the feeding system, the pyrolysis reactor line, the product discharging system, and the emission cleaning system. Together, they form an integrated facility designed to thermally decompose organic materials like plastic, tires, or biomass in an oxygen-free environment, transforming waste into valuable outputs.
A pyrolysis plant is not a single machine but a complete process line. Its structure is engineered to manage a controlled chemical reaction: safely introducing feedstock, heating it without oxygen, separating the resulting products, and cleaning any emissions.

The Core Principle: What is Pyrolysis?
Before examining the plant's structure, it's crucial to understand the process it's built to facilitate.
A Controlled Thermal Reaction
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical treatment where organic materials are subjected to high temperatures in a near-total absence of oxygen.
This lack of oxygen is critical. Instead of burning (combusting), the material's chemical bonds break apart due to the intense heat, a process known as thermal cracking.
The Goal of Transformation
The goal of this process is to deconstruct complex organic polymers into simpler, more valuable substances.
The primary outputs are typically a liquid fuel known as pyrolysis oil, a solid carbon-rich residue called char (or carbon black), and a mixture of non-condensable syngas.
A Breakdown of the Four Key Systems
Each part of the plant is designed to execute one phase of the pyrolysis process efficiently and safely.
1. The Feeding System (Input)
This system is responsible for introducing raw materials, or feedstock, into the reactor. For many materials, this involves a pretreatment stage, such as shredding tires or drying biomass.
The feeding mechanism must be sealed to prevent oxygen from entering the reactor, which would cause the material to burn instead of pyrolyze.
2. The Pyrolysis Reactor (The Core)
This is the heart of the plant where the thermal decomposition occurs. The reactor heats the feedstock to temperatures often ranging from 400°C to 800°C.
The design of the reactor ensures uniform heating and an oxygen-starved environment, allowing the chemical breakdown to proceed correctly.
3. The Discharging System (Output)
Once the reaction is complete, this system cools and separates the different products.
Gaseous products are cooled in condensers, which turns the condensable vapors into liquid pyrolysis oil. The remaining non-condensable gas (syngas) is often redirected to fuel the reactor's burners, improving energy efficiency. The solid char is removed separately, typically through a sealed cooling conveyor.
4. The Emission Cleaning System (Safety & Compliance)
This final system treats any residual flue gas before it is released into the atmosphere.
Its purpose is to capture particulates and scrub harmful compounds, ensuring the plant operates without releasing damaging byproducts and complies with environmental regulations.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
The specific design of a pyrolysis plant can vary significantly based on its intended purpose and the feedstock it processes.
Feedstock Variability
The type of feedstock—be it plastic, tires, or wood waste—heavily influences the plant's design.
Different materials require unique pretreatment steps and can yield vastly different proportions of oil, char, and gas. A plant optimized for plastic may be inefficient for processing tires.
Batch vs. Continuous Operation
Pyrolysis plants can operate in batch mode (loading, processing, and unloading one set at a time) or continuous mode.
Batch systems are simpler and less expensive upfront, but less efficient. Continuous systems, often controlled by a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), offer much higher throughput but require more sophisticated engineering and investment.
Energy Balance
While pyrolysis requires a significant energy input to reach operating temperature, a well-designed plant becomes partially self-sustaining.
The syngas produced during the process is a combustible fuel that is almost always recycled to power the reactor's heating system, reducing external energy consumption.
Matching Plant Design to Your Goal
Understanding this structure helps in selecting or designing a plant that aligns with your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Your priority should be a robust and versatile feeding and pretreatment system capable of handling mixed or contaminated feedstock.
- If your primary focus is high-quality fuel production: The design of the reactor and the sophistication of the discharging and condensing systems are most critical for controlling output quality.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: A fully continuous, automated plant is the only viable option to ensure efficient, large-scale processing with minimal downtime.
Ultimately, viewing the pyrolysis plant as an integrated system of systems is the key to appreciating its design and operational logic.
Summary Table:
| System | Primary Function | Key Components/Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Feeding System | Introduces & prepares feedstock | Shredder, dryer, sealed conveyor |
| Pyrolysis Reactor | Heats material without oxygen | Main reactor, heating unit, temperature controls |
| Discharging System | Cools & separates products | Condensers (pyrolysis oil), conveyor (char), syngas line |
| Emission Cleaning System | Treats residual gases | Scrubbers, filters, ensures environmental compliance |
Ready to transform your waste streams into valuable resources?
KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis solutions for laboratories and R&D facilities. Our equipment is engineered for precise control, safety, and high-quality output, whether you're processing plastics, biomass, or tires for research or small-scale production.
We provide the right technology to match your goal—from waste management to high-quality fuel production.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your project and discover how our lab equipment can optimize your pyrolysis process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
People Also Ask
- What are three potential solutions to the plastic waste problem? A Guide to Recycling, Bioplastics & Upcycling
- What are the advantages of rotary vane pumps? Unlock Cost-Effective, High-Performance Vacuum
- How much does a biochar production facility cost? From $100k to $10M+ for Your Project
- What are the considerations of powder metallurgy? Key Factors for Manufacturing Success
- How does a precision heating system influence the coating quality of soft magnetic composite materials? Expert Insights
- How do ULT freezers maintain a uniform temperature? Achieve Stable Sample Storage with Advanced Cooling
- What are the advantages of XRF analysis? Achieve Superior Accuracy with Pressed Pellet Preparation
- What is the application of annealing process? Enhance Workability and Material Stability


















