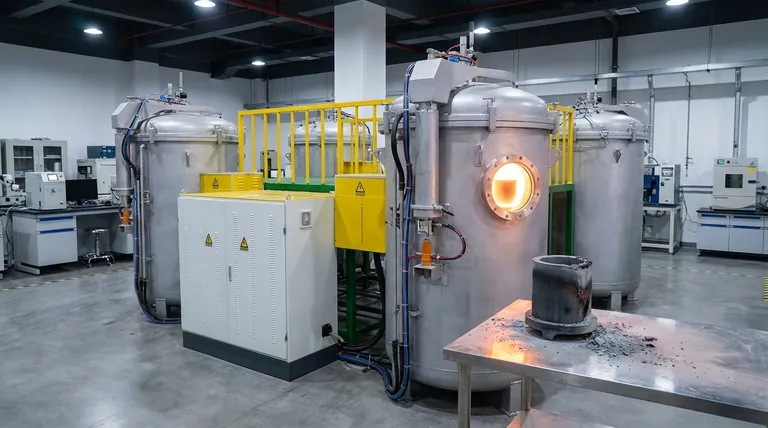
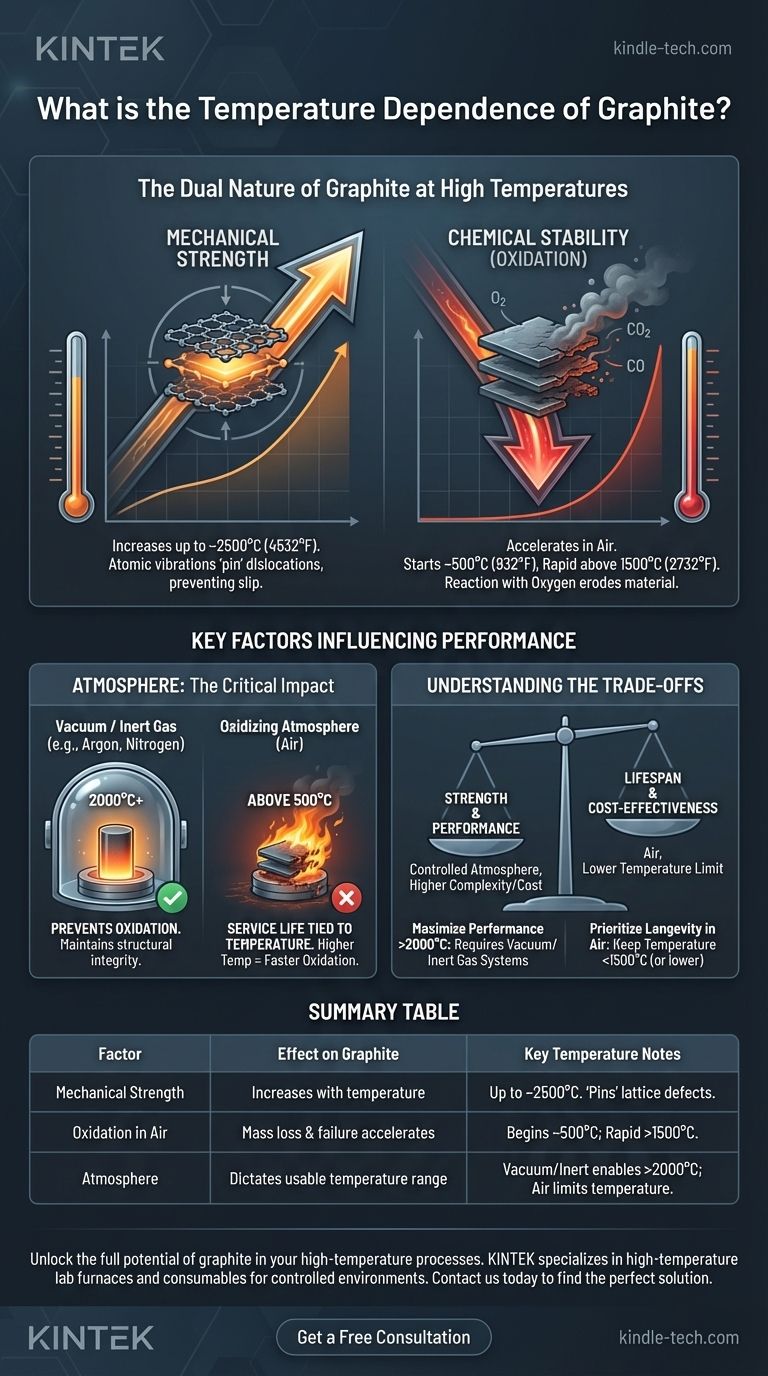
At its core, graphite exhibits a unique and often misunderstood relationship with temperature. Unlike metals that weaken as they get hotter, graphite's mechanical strength actually increases with temperature, but this remarkable property is in direct conflict with its vulnerability to oxidation, which also accelerates with heat.
The practical temperature limit of graphite is not defined by its loss of strength, but by the environment in which it operates. Its exceptional high-temperature mechanical properties can only be fully realized in a vacuum or an inert atmosphere that prevents oxidative degradation.

The Dual Nature of Graphite at High Temperatures
To use graphite effectively, you must understand two competing behaviors that occur as temperature rises: one mechanical and one chemical.
Mechanical Strength: A Counter-intuitive Increase
Graphite's layered atomic structure is the source of its unique thermal properties. As temperature increases, the bonds within its hexagonal layers become more active.
This increased atomic vibration helps to "pin" dislocations, or imperfections, in the crystal lattice. This makes it more difficult for the atomic layers to slip past one another, resulting in a material that is measurably stronger and stiffer. This strengthening effect continues up to temperatures around 2500°C (4532°F).
Chemical Stability: The Role of Oxidation
The primary limitation of graphite at high temperatures is its reaction with oxygen. This process, known as oxidation, begins to occur at a meaningful rate around 450-500°C (842-932°F).
In an oxygen-rich environment like air, the carbon atoms of the graphite combine with oxygen to form carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) gas. This reaction effectively erodes the material, causing a direct loss of mass, a reduction in structural integrity, and ultimately, component failure.
Key Factors Influencing Performance
The "temperature dependence" of graphite is therefore not a single number, but a function of its operating conditions.
The Critical Impact of Atmosphere
The atmosphere is the single most important factor. In a vacuum or an inert gas environment (like argon or nitrogen), oxidation is prevented. Here, graphite can be used to its full potential, maintaining structural integrity well above 2000°C.
In an oxidizing atmosphere (air), the service life is directly tied to temperature. The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of oxidation and the shorter the component's lifespan.
The Temperature Threshold for Oxidation
While oxidation starts at lower temperatures, the rate increases exponentially with heat.
The reference to 1500°C (2732°F) marks a point of rapid acceleration. Above this temperature in the open air, the oxidation rate becomes so aggressive that the lifespan of a graphite component can be reduced from hundreds of hours to just a few.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using graphite in high-temperature applications requires balancing its strengths against its environmental weaknesses.
Strength vs. Lifespan
In the presence of air, you face a direct trade-off. Pushing the temperature higher to gain more mechanical strength will simultaneously and dramatically shorten the component's operational life due to oxidation.
For any long-term application in air, the operational temperature must be kept low enough to manage the rate of material loss.
Performance vs. System Complexity
Achieving graphite's maximum performance potential (i.e., using it above 2000°C) necessitates operating in a controlled atmosphere.
This requires systems like vacuum furnaces or inert gas purging, which add significant cost, complexity, and maintenance requirements to the overall design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your ideal operating temperature for graphite depends entirely on your primary goal and the surrounding environment.
- If your primary focus is leveraging maximum mechanical strength: You must operate in a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere to prevent oxidation at extreme temperatures (above 2000°C).
- If your primary focus is longevity and cost-effectiveness in air: You must keep the graphite's surface temperature well below the point of accelerated oxidation, ideally below 1500°C and often much lower for sustained use.
Ultimately, mastering the interplay between graphite's internal strength and its external chemical environment is the key to unlocking its exceptional high-temperature performance.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Graphite | Key Temperature Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Increases up to ~2500°C | Atomic vibrations 'pin' lattice defects, making it stronger. |
| Oxidation in Air | Mass loss & failure accelerates | Begins at ~500°C; rapid acceleration above 1500°C. |
| Atmosphere | Dictates usable temperature range | Vacuum/inert gas enables use >2000°C; air limits temperature for longevity. |
Unlock the full potential of graphite in your high-temperature processes. The right lab equipment is crucial for creating the controlled environments (vacuum or inert gas) needed to leverage graphite's peak performance. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab furnaces and consumables designed for such demanding applications. Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs and ensure your materials perform reliably at extreme temperatures.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is brazing in safety? Managing Toxic Fumes, Fire, and Chemical Hazards
- What would be an advantage of biomass over the use of coal? A Cleaner, Carbon-Neutral Energy Source
- Why is a multi-step cleaning process involving acetone and ethanol necessary? Ensure Pure Electrode Surface Integrity
- What additional technological features do ULT freezers offer? Maximize Sample Security and Efficiency
- What are the important parameters in thin film deposition with magnetron sputtering technique? Master Your Film's Properties
- What is the process of making bio-oil? Convert Biomass to Liquid Fuel via Pyrolysis
- How does sintering work in metals? A Guide to Solid-State Diffusion for Strong Parts
- What is the function of a heating reaction system in benzoic acid esterification? Master Precision Thermal Control



















