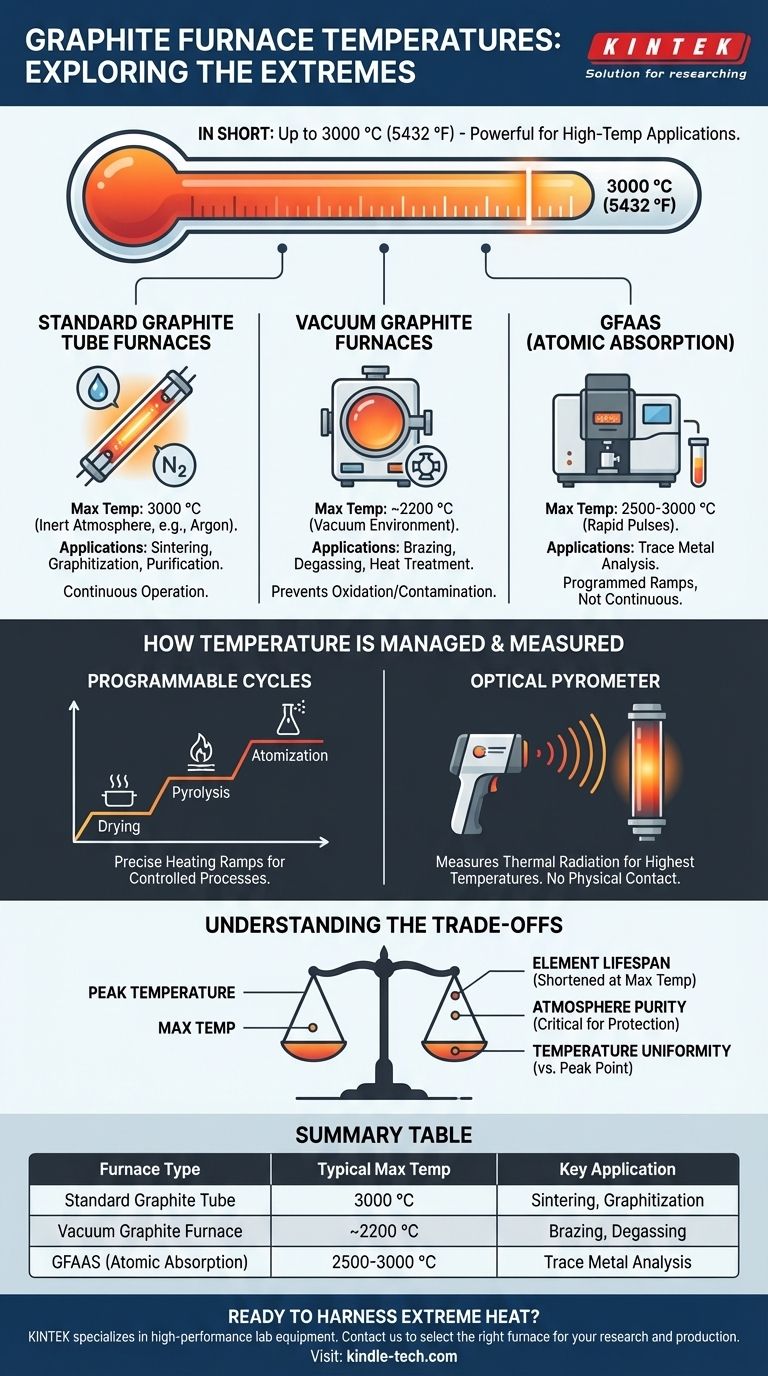
In short, a graphite furnace can reach temperatures up to 3000 °C (5432 °F). This capability makes it one of the most powerful tools for high-temperature applications in both industrial processing and laboratory analysis. However, the specific maximum temperature and how it is used depend heavily on the furnace's design and purpose.
The key takeaway is not a single temperature, but a range. The achievable temperature of a graphite furnace is dictated by its specific type—such as a tube furnace for material processing or a system for atomic absorption—and whether it operates under a vacuum or a controlled atmosphere.

Maximum Temperature by Furnace Type
The term "graphite furnace" can refer to several different pieces of equipment, each optimized for a specific task. Their temperature capabilities vary accordingly.
Standard Graphite Tube Furnaces
These furnaces are designed for processing materials at extremely high temperatures. They are commonly used for applications like sintering, graphitization, and purification.
The heating element is a graphite tube through which an electrical current is passed. These systems can consistently and reliably achieve a maximum operating temperature of 3000 °C in a controlled, inert atmosphere like argon.
Vacuum Graphite Furnaces
When a process must be performed in a vacuum to prevent oxidation or contamination, a vacuum graphite furnace is used. These are common for brazing, degassing, and certain types of heat treatment.
The presence of a vacuum changes the thermal dynamics and design constraints. As a result, these furnaces typically have a slightly lower maximum temperature, often rated around 2200 °C.
Graphite Furnaces for Atomic Absorption (GFAAS)
In analytical chemistry, GFAAS is used to detect trace metals. Here, the graphite furnace is a small, rapidly heated tube designed to vaporize and then atomize a tiny liquid sample.
While these systems also reach temperatures of 2500-3000 °C, they do so for only a few seconds during the "atomization" step. The process involves a programmed temperature ramp, not continuous operation at the peak temperature.
How Temperature is Managed and Measured
Achieving and verifying these extreme temperatures requires sophisticated control and measurement systems. The method used is a direct indicator of the temperature range being targeted.
Programmable Heating Cycles
Graphite furnaces do not simply turn on to a single temperature. They follow a precise, programmed heating ramp with multiple steps. This allows for controlled processes like drying a sample at a low temperature before rapidly heating it to a much higher one.
Measurement with Pyrometers
Standard thermocouples are not suitable for the highest temperatures inside a graphite furnace, as they would be destroyed. Instead, an optical pyrometer is used.
A pyrometer measures the thermal radiation (the light and heat) emitted by the hot graphite tube and calculates its temperature without making physical contact. For lower temperature stages, a thermocouple may be used.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Operating at such extreme temperatures involves significant compromises that are critical to understand for practical applications.
Temperature vs. Element Lifespan
The single biggest trade-off is component lifespan. The graphite heating element is a consumable part. Operating it near its maximum temperature of 3000 °C drastically shortens its life, increasing operational costs and downtime.
Atmosphere and Purity
The type of gas inside the furnace (typically an inert gas like argon) is not just a detail—it is fundamental. It prevents the hot graphite from oxidizing and burning away instantly. The purity of this gas is critical for both protecting the furnace and preventing contamination of the sample.
Uniformity vs. Peak Temperature
Achieving a high peak temperature at one point inside the furnace is different from achieving a stable, uniform temperature across a larger work zone. For material processing, temperature uniformity is often more important than the absolute maximum temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace requires matching its capabilities to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is industrial heat treatment or material synthesis: You need a tube furnace rated for continuous operation at your target temperature, potentially up to 3000 °C.
- If your primary focus is vacuum brazing or degassing: A dedicated vacuum graphite furnace with a maximum temperature around 2200 °C is the purpose-built tool.
- If your primary focus is trace element analysis: You require a GFAAS system capable of precise, rapid, and repeatable temperature pulses, not just a high continuous temperature.
Understanding these distinctions is the key to leveraging the immense power of graphite furnace technology for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Graphite Tube Furnace | 3000 °C | Sintering, Graphitization |
| Vacuum Graphite Furnace | ~2200 °C | Brazing, Degassing |
| GFAAS (Atomic Absorption) | 2500-3000 °C | Trace Metal Analysis |
Ready to harness the power of extreme heat for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including graphite furnaces tailored for industrial processing and precise analytical chemistry. Our experts will help you select the right furnace to meet your specific temperature and application requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and production processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Temperatures for Advanced Materials
- What are the advantages of graphite furnace? Achieve High-Temperature Precision and Purity
- Can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking its extreme 3,600°C potential in inert environments
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite
- What are the advantages of graphite? Unlock Superior Performance in High-Temperature Processes



















