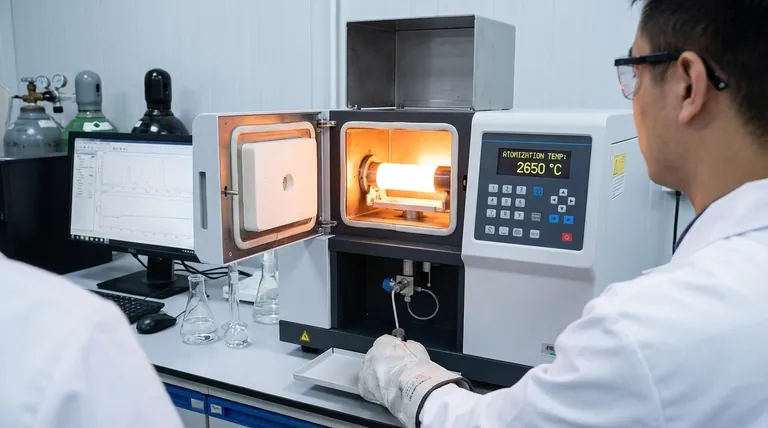
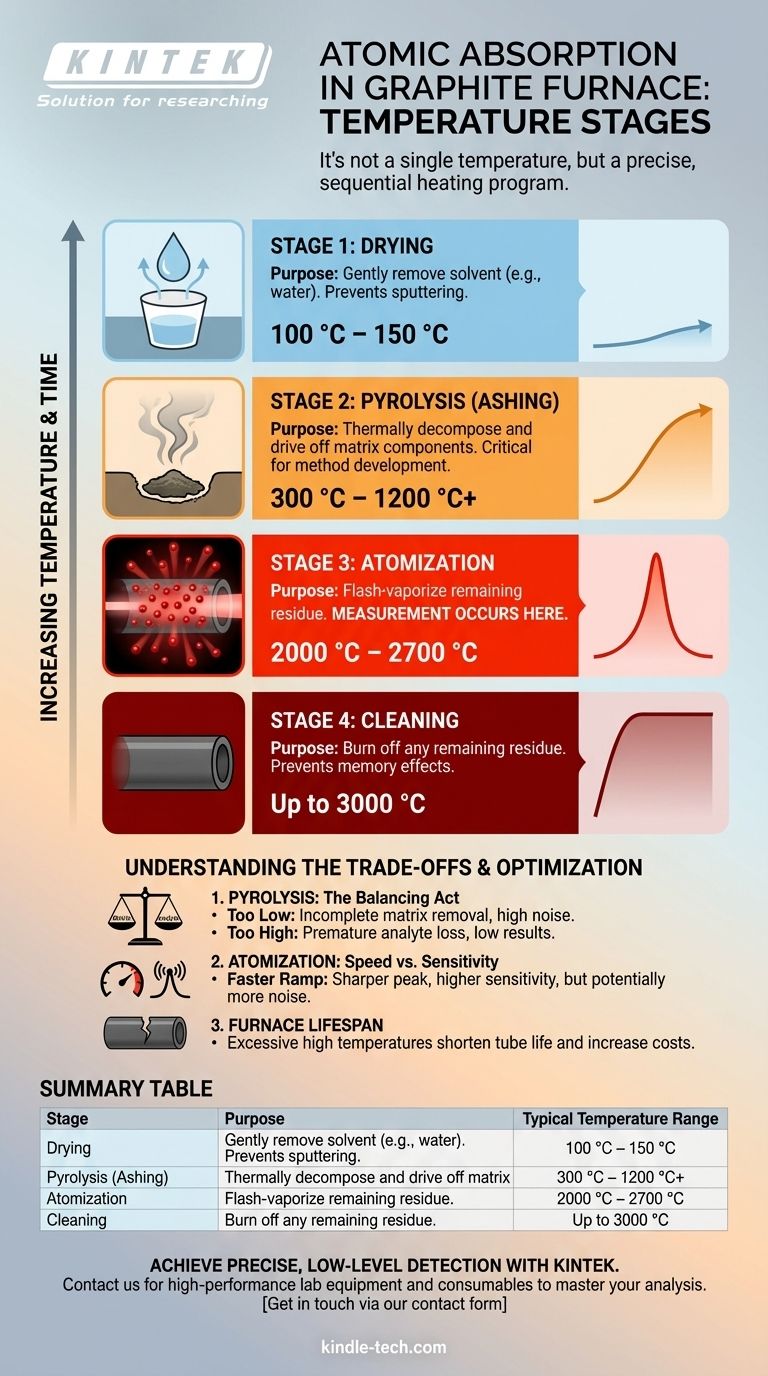
While a graphite furnace can reach temperatures up to 3000 °C, atomic absorption analysis does not occur at a single temperature. Instead, it relies on a precisely controlled, multi-stage heating program where the final, highest temperature step—atomization—is when the measurement actually takes place. This atomization temperature is specific to the element being measured but typically falls within the 2000 °C to 2700 °C range.
The core principle of graphite furnace analysis is not a single high temperature, but a sequential program of increasing temperatures. This program is designed to systematically remove the sample solvent and matrix before vaporizing the target element into a cloud of free atoms for measurement.

The Purpose of a Programmed Temperature Cycle
The primary goal of a graphite furnace is to achieve exceptionally low detection limits, often parts-per-billion or even parts-per-trillion.
This sensitivity is only possible if the instrument measures only the element of interest (the analyte) without interference from the rest of the sample (the matrix).
The temperature program is the method used to eliminate the matrix before the final measurement, ensuring a clean and accurate signal.
Deconstructing the GFAAS Temperature Program
A typical furnace program consists of three or four distinct heating stages, each with a specific purpose. The final temperature and duration of each stage are critical variables that must be optimized for each unique sample type and analyte.
Stage 1: The Drying Step (Low Temperature)
The first step gently removes the solvent (usually water or a dilute acid) from the sample.
This is typically done at a temperature slightly above the solvent's boiling point, often between 100 °C and 150 °C. A slow temperature ramp is used to prevent the sample from boiling violently and sputtering, which would cause a loss of sample and lead to inaccurate results.
Stage 2: The Pyrolysis Step (Medium Temperature)
Also known as the ashing step, this is often the most critical stage for method development. The temperature is raised significantly to thermally decompose and drive off the bulk of the organic and inorganic matrix components.
The pyrolysis temperature can range from 300 °C to over 1200 °C, depending on the matrix complexity and the volatility of the analyte. The goal is to use the highest possible temperature that removes the matrix without vaporizing and losing the analyte itself.
Stage 3: The Atomization Step (High Temperature)
This is the stage where the actual atomic absorption is measured. The furnace is heated as rapidly as possible to a very high temperature, typically between 2000 °C and 2700 °C.
This extreme heat flash-vaporizes the remaining sample residue, dissociating the analyte compounds into a dense cloud of free, ground-state atoms within the graphite tube. At this exact moment, light from the source lamp passes through the tube, and the amount of light absorbed by the atom cloud is measured.
Stage 4: The Cleaning Step (Maximum Temperature)
After the measurement is complete, the furnace is heated to its maximum or near-maximum temperature, often up to 3000 °C.
This final, brief step serves to burn off any remaining residue from the graphite tube, preventing contamination or "memory effects" between subsequent samples.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a furnace program requires balancing competing factors. An incorrect temperature at any stage can ruin the analysis.
Pyrolysis Temperature: The Critical Balancing Act
This is the most common challenge. If the pyrolysis temperature is too low, the matrix will not be fully removed, causing high background noise and chemical interferences during atomization. If it is too high, the target analyte will be prematurely vaporized and lost before the measurement step, leading to artificially low results.
Atomization Rate: Speed vs. Sensitivity
A faster temperature ramp to the atomization setpoint creates a denser, more concentrated cloud of atoms. This produces a sharper, taller absorption peak, which generally improves measurement sensitivity. However, extremely fast ramps can sometimes generate more background noise.
Furnace Lifespan and Cost
The graphite tube is a consumable component. Repeatedly firing the furnace to its absolute maximum temperature (3000 °C) will cause it to degrade more quickly. For analytes that atomize at lower temperatures (e.g., 2200 °C), using an unnecessarily high clean-out or atomization temperature will shorten the tube's life and increase operational costs.
Optimizing the Temperature for Your Analysis
Your approach to setting furnace temperatures depends directly on your analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is new method development: You must perform a pyrolysis temperature study, analyzing the same sample at various pyrolysis temperatures to find the highest possible temperature that yields a stable analyte signal before it begins to drop off.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis with a known method: Use the validated temperatures but monitor quality control standards closely. A sudden drop in recovery may indicate a loss of analyte, while an increase in background signal can point to an inefficient pyrolysis step.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum sensitivity: You will need to optimize for a high pyrolysis temperature (often with a chemical matrix modifier) and a very fast ramp to the ideal atomization temperature for your specific element.
Mastering the temperature program is the key to unlocking precise and reliable results in graphite furnace analysis.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Purpose | Typical Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Drying | Remove solvent | 100 °C – 150 °C |
| Pyrolysis | Remove matrix | 300 °C – 1200 °C+ |
| Atomization | Vaporize analyte for measurement | 2000 °C – 2700 °C |
| Cleaning | Remove residue | Up to 3000 °C |
Achieve precise, low-level detection with optimized graphite furnace methods.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including graphite furnaces and tubes. Our expertise helps laboratories master complex temperature programs for accurate atomic absorption analysis, ensuring maximum sensitivity and instrument longevity.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your analytical capabilities and streamline your workflow. Get in touch via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the industrial uses of graphite? Leverage Its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What is the graphite furnace method? Achieve Ultra-High Temperatures with Purity & Speed
- What does a graphite furnace do? Achieve Extreme Heat and Ultra-Sensitive Analysis
- What is the application of graphite furnace? Essential for High-Temp Material Processing & Synthesis
- Does graphite conduct electricity when melted? Discover the Secrets of Liquid Carbon Conductivity
- What are the stages of graphite furnace? A Guide to Precise Multi-Stage Temperature Programming
- What is the purpose of carbonization? Transform Organic Materials into Valuable Carbon Products
- Is graphite good for high temperature? Unlock Its Full Potential in Controlled Atmospheres



















