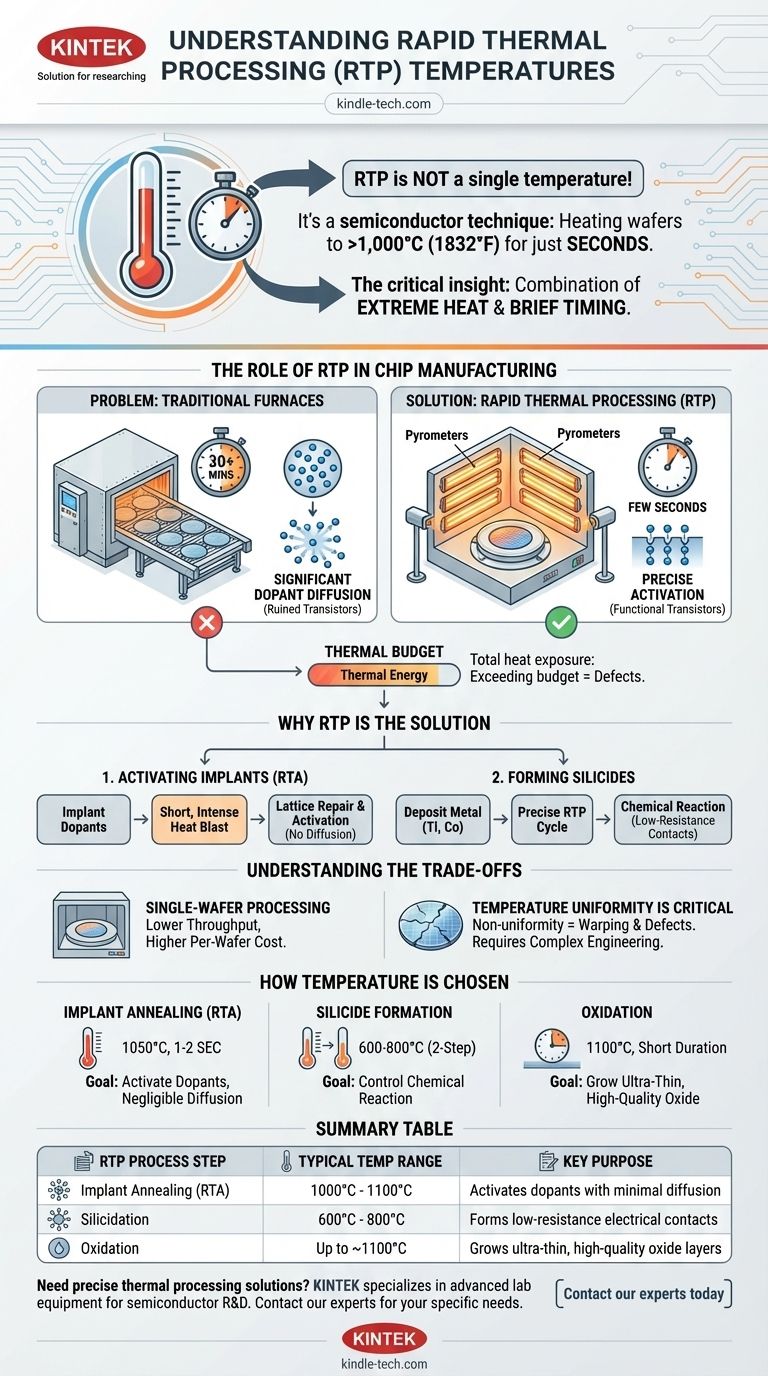
The term "RTP" does not refer to a single, specific temperature. Instead, Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) is a semiconductor manufacturing technique that involves heating wafers to very high temperatures, typically exceeding 1,000°C (1832°F), for extremely short durations, usually just a few seconds. The exact temperature is precisely controlled and tailored to the specific process step, such as implant annealing, silicidation, or oxidation.
The critical insight is not the temperature itself, but the combination of extreme heat and brief timing. RTP delivers a massive thermal budget in a short burst, enabling specific physical changes in the wafer while preventing unwanted side effects like dopant diffusion that would occur with prolonged heating.
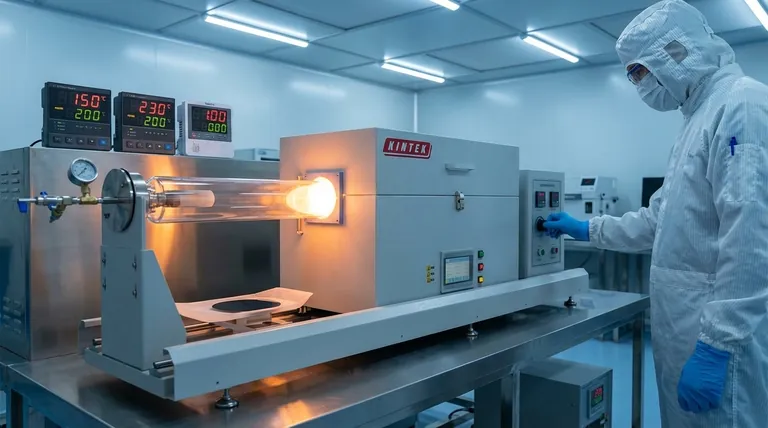

The Role of RTP in Chip Manufacturing
What is a "Thermal Budget"?
In semiconductor fabrication, the thermal budget is the total amount of thermal energy a wafer is exposed to throughout its entire manufacturing journey. It is a function of both temperature and time.
Every high-temperature step "spends" some of this budget. Exceeding the total budget can lead to defects and ruin the microscopic structures on the chip.
The Problem with Traditional Furnaces
Traditional batch furnaces heat hundreds of wafers simultaneously over long periods, often for 30 minutes or more.
While effective for some steps, this prolonged heating causes significant dopant diffusion. Dopants are impurities intentionally added to silicon to control its electrical properties. If they move or spread out too much, the resulting transistors will not function correctly, especially at the small scales of modern chips.
Why RTP is the Solution
Activating Implants Without Diffusion
After dopants are implanted into the silicon wafer, they sit in the crystal lattice in an electrically inactive state and cause structural damage. Heating is required to repair this damage and "activate" the dopants.
RTP provides a short, intense blast of heat. This is just enough time to repair the lattice and activate the dopants but is too short for them to diffuse significantly from their intended positions. This process is often called Rapid Thermal Annealing (RTA).
Forming Silicides
RTP is also used to form silicides, which are highly conductive compounds of metal and silicon. These are used to create low-resistance contacts for the source, drain, and gate of a transistor.
The process involves depositing a thin layer of metal (like titanium or cobalt) and then using a precise RTP cycle. The heat causes a chemical reaction that forms the silicide only where the metal touches the silicon, ensuring excellent electrical connections.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Single-Wafer Processing
Unlike batch furnaces that process many wafers at once, RTP systems process wafers one at a time. This results in lower throughput, making it a more expensive and time-consuming step on a per-wafer basis.
Temperature Uniformity is Critical
Heating a wafer from 20°C to over 1,000°C and back down in seconds presents an immense engineering challenge. Any non-uniformity in temperature across the wafer can cause stress, leading to warping or crystal defects called "slip dislocations," which destroy devices. Modern RTP systems use complex arrays of lamps and pyrometers to ensure uniformity within a few degrees.
How Temperature is Chosen for RTP
The specific temperature and time for an RTP step are not arbitrary. They are carefully selected based on the desired physical outcome.
- For Implant Annealing: The goal is to reach a temperature high enough (e.g., 1050°C) to activate the dopants but for a duration so short (e.g., 1-2 seconds) that diffusion is negligible.
- For Silicide Formation: This often involves a two-step RTP process at lower temperatures (e.g., 600-800°C) to control the chemical reaction and form the desired silicide phase.
- For Oxidation: RTP can be used to grow very thin, high-quality oxide layers at high temperatures (e.g., 1100°C). The short duration allows for nanometer-level control over the thickness.
Understanding RTP is about recognizing the strategic use of high heat for short times to solve critical fabrication challenges.
Summary Table:
| RTP Process Step | Typical Temperature Range | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Implant Annealing (RTA) | 1000°C - 1100°C | Activates dopants with minimal diffusion |
| Silicidation | 600°C - 800°C | Forms low-resistance electrical contacts |
| Oxidation | Up to ~1100°C | Grows ultra-thin, high-quality oxide layers |
Need precise thermal processing solutions for your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including thermal processing systems designed for semiconductor R&D and manufacturing. Our expertise ensures you achieve the temperature control and uniformity critical for processes like RTP. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in semiconductor fabrication and materials science.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- What is the role of a tube furnace in the thermal treatment of argyrodite electrolytes? Master Ionic Conductivity
- How does an industrial tube furnace ensure the required process conditions for supercritical fluid experimental devices?
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis
- Why are quartz tubes preferred for chromium powder combustion? Superior Heat Resistance & Optical Clarity



















