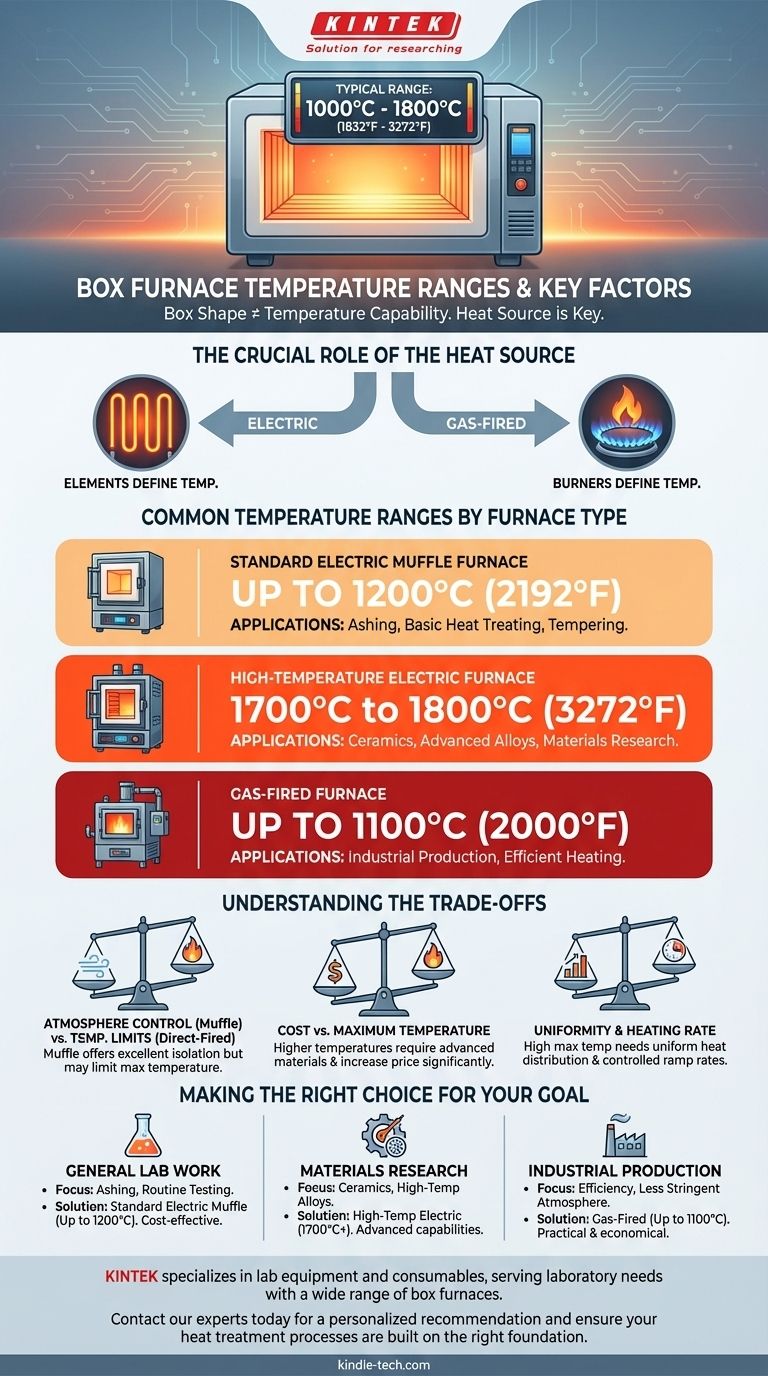
The typical temperature range of a box furnace is between 1000°C (1832°F) and 1800°C (3272°F). However, this range is broad because "box furnace" describes the physical shape, not the heating technology inside. The specific maximum temperature is determined entirely by the furnace's heat source, whether it's electric heating elements or a gas burner.
A box furnace's temperature capability is not defined by its box-like shape, but by its underlying heating mechanism. To understand its limits, you must look at the specific type of furnace, such as a muffle, induction, or gas-fired model.

What Defines a Box Furnace's Temperature?
A box furnace is simply an insulated chamber with a door, characterized by its rectangular, box-like interior. This simple design is versatile, but the factors that dictate its performance are internal.
The General "Box" Design
The name refers to the geometry of the heating chamber. This shape is convenient for loading and unloading samples and provides a uniform heating environment when properly designed.
The Crucial Role of the Heat Source
The true determinant of a furnace's temperature range is how it generates heat. Different methods have vastly different capabilities.
Common Temperature Ranges by Furnace Type
The specific model and its components are what truly matter. The most common types of box furnaces fall into distinct temperature classes based on their heating technology.
Standard Electric Muffle Furnaces
Many lab-grade box furnaces are muffle furnaces. These models often use metallic heating elements and can reliably reach up to 1200°C (2192°F). They are ideal for applications like ashing, tempering, and general heat treating.
High-Temperature Electric Furnaces
For more demanding applications involving ceramics or advanced materials, high-temperature models are required. These furnaces use specialized ceramic heating elements (like silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide) and can achieve maximum temperatures of 1700°C to 1800°C (3092°F to 3272°F).
Gas-Fired Furnaces
In some industrial settings, box furnaces are heated by natural gas burners. These units can typically reach temperatures around 1100°C (2000°F) and are valued for their operational efficiency in certain production environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace based on maximum temperature alone is a common mistake. The right choice involves balancing performance, cost, and specific application needs.
Temperature vs. Atmosphere Control
A muffle furnace is designed to isolate the material being heated from the direct heat source or combustion byproducts. This provides excellent atmosphere control but can sometimes limit the maximum achievable temperature compared to direct-fired designs.
Cost vs. Maximum Temperature
There is a direct and steep correlation between cost and temperature. Furnaces capable of exceeding 1200°C require more advanced insulation, power controllers, and significantly more expensive heating elements, which increases their price substantially.
Uniformity and Heating Rate
A high maximum temperature is only useful if the heat within the chamber is uniform. Furthermore, consider the ramp rate—how quickly the furnace can reach its setpoint. Some high-temperature materials take longer to heat up, which can affect process times.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct furnace, match its technical specifications to the primary requirements of your work.
- If your primary focus is general lab work like ashing or basic heat treating: A standard electric muffle furnace reaching up to 1200°C is typically sufficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is materials research with ceramics or high-temp alloys: You will need a high-temperature model capable of reaching 1700°C or more.
- If your primary focus is industrial production with less stringent atmosphere needs: A gas-fired furnace operating around 1100°C can be a practical and economical choice.
Understanding that the heating technology, not the shape, dictates performance is the key to selecting the correct tool for your work.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Electric Muffle Furnace | Up to 1200°C (2192°F) | Ashing, basic heat treating, tempering |
| High-Temperature Electric Furnace | 1700°C to 1800°C (3272°F) | Ceramics, advanced alloys, materials research |
| Gas-Fired Furnace | Up to 1100°C (2000°F) | Industrial production, efficient heating |
Selecting the right furnace is critical for your lab's success. The specific heating technology—not just the box shape—determines performance, cost, and suitability for your application. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with a wide range of box furnaces. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between temperature, atmosphere control, and budget to find the perfect solution for your work, whether it's routine testing or cutting-edge research.
Contact our experts today for a personalized recommendation and ensure your heat treatment processes are built on the right foundation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature muffle furnace utilized in SDC-carbonate synthesis? Master Calcination for High-Purity Powders
- What role does a high-temperature box furnace play in the densification of high-entropy alloys? Achieve Peak Density.
- Why is a high-precision muffle furnace required for the thermal decomposition of siderite to produce nano-iron oxide?
- What is the primary function of an electric muffle furnace during CNT synthesis? Unlock High-Performance Catalysts
- How does the sintering furnace contribute to the production of granular titanium dioxide photocatalysts? Guide
- What is a muffle furnace used for in microbiology? Essential for Depyrogenation and Ashing
- How does the liquid environment in a molten salt furnace control carbon pore size? Master Precision Carbonization
- How does a ceramic high-temperature furnace ensure experimental validity? Stabilize 100-Hour Molten Salt Corrosion Tests



















