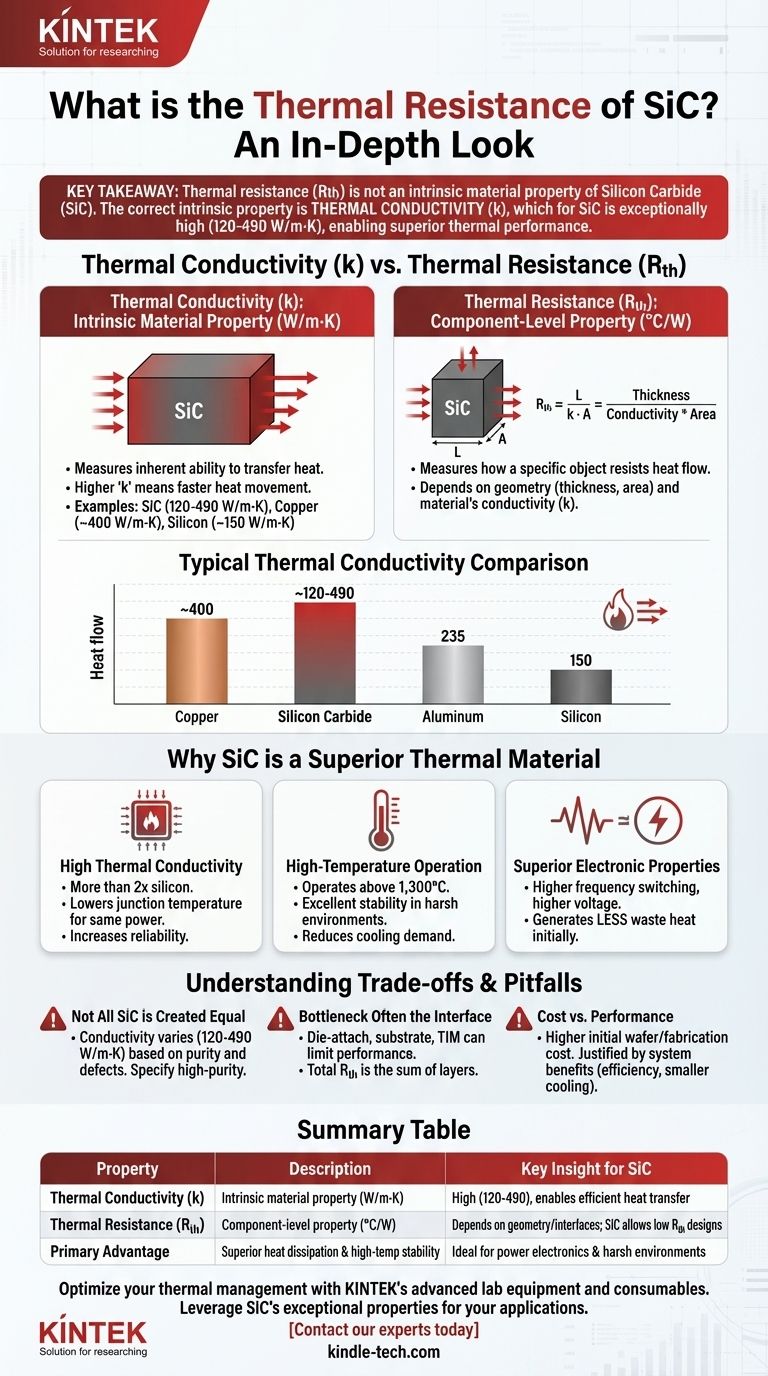
In short, you cannot assign a single thermal resistance value to Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a material. Thermal resistance is a property of a specific component's geometry and interfaces, not the material itself. The correct intrinsic property to consider is thermal conductivity (k), and for SiC, it is exceptionally high, typically ranging from 120 to 490 W/m·K, which is far superior to silicon and enables its excellent thermal performance.
The core issue is a common confusion between two different concepts: a material's intrinsic ability to conduct heat (conductivity) and a specific component's opposition to heat flow (resistance). Silicon Carbide's high thermal conductivity is the reason it is chosen for high-power and high-temperature applications, as it allows for the design of components with very low thermal resistance.
Thermal Conductivity vs. Thermal Resistance
To properly evaluate a material like SiC, it's critical to understand the distinction between these two thermal properties. They are related but fundamentally different.
Thermal Conductivity (k): An Intrinsic Material Property
Thermal conductivity, denoted as 'k', is a measure of a material's inherent ability to transfer heat. It is measured in watts per meter-Kelvin (W/m·K).
A material with a high 'k' value, like SiC, allows heat to move through it quickly and efficiently. This is a fundamental characteristic, like density or melting point.
For context, compare SiC's typical thermal conductivity (around 370 W/m·K for high-quality crystals) to other common materials:
- Copper: ~400 W/m·K
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): ~120 - 490 W/m·K
- Aluminum: ~235 W/m·K
- Silicon (Si): ~150 W/m·K
Thermal Resistance (Rth): A Component-Level Property
Thermal resistance, denoted as 'Rth', measures how much a specific object or interface resists the flow of heat. It is measured in degrees Celsius per watt (°C/W) or Kelvin per watt (K/W).
Unlike conductivity, resistance is not a material property. It depends entirely on the material's conductivity (k) and the component's geometry (its thickness and cross-sectional area). A thicker, narrower component will have higher thermal resistance than a thin, wide one made of the same material.
Why SiC is a Superior Thermal Material
The reason designers choose SiC is because its high thermal conductivity and other unique properties allow them to build devices that can handle extreme thermal loads.
High Thermal Conductivity
SiC's ability to conduct heat is more than twice that of traditional silicon. In a power semiconductor, this means heat generated in the tiny active region of the chip can be pulled away and spread to the packaging and heatsink much more effectively.
This directly results in a lower junction temperature for the same power dissipation, increasing device reliability and lifetime.
High-Temperature Operation
As your reference notes, SiC can operate at extremely high temperatures—well above 1,300°C for certain applications. This thermal stability is crucial not only for devices in harsh environments (like engines or industrial furnaces) but also for power electronics.
Because SiC can tolerate higher internal temperatures, it reduces the demand on the cooling system, potentially allowing for smaller, lighter, and less expensive heatsinks.
Superior Electronic Properties
For power electronics, SiC's thermal advantages are amplified by its wide bandgap electronic properties. SiC devices can switch at higher frequencies and operate at higher voltages with lower internal losses than silicon.
This means SiC devices generate less waste heat to begin with, easing the thermal management challenge from the start.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While SiC offers exceptional performance, it is not a simple drop-in solution. Objective analysis requires considering its limitations.
Not All SiC is Created Equal
The thermal conductivity of SiC can vary significantly—from ~120 W/m·K to over 490 W/m·K. This range is due to differences in crystal purity, defects, and manufacturing processes.
For demanding applications, specifying high-purity, single-crystal SiC is critical to achieving the expected thermal performance.
The Bottleneck is Often the Interface
In a real-world device, like a power module, the thermal resistance of the SiC die itself is only one part of the total equation. The overall system performance is often limited by other layers.
The thermal resistance of the die-attach material, the substrate, and the thermal interface material (TIM) between the package and the heatsink can be significant bottlenecks. A poorly designed package can easily negate the benefits of a high-conductivity SiC chip.
Cost vs. Performance
SiC wafers and the fabrication of SiC devices are currently more expensive than their silicon counterparts. The decision to use SiC often involves a system-level cost-benefit analysis.
The higher initial cost of SiC components may be justified by savings elsewhere, such as the need for a smaller cooling system, higher overall system efficiency, or improved reliability in demanding conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat dissipation in power electronics: Specify high-quality, single-crystal SiC and analyze the entire thermal path, optimizing the packaging and interface materials to minimize total thermal resistance.
- If your primary focus is performance in high-temperature environments: SiC's thermal stability is your key advantage, allowing reliable operation where silicon would fail.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost and performance: You must weigh the higher component cost of SiC against total system benefits, including higher efficiency, reduced cooling requirements, and greater power density.
By leveraging Silicon Carbide's outstanding thermal conductivity, you can design systems that are more efficient, reliable, and compact.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Insight for SiC |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity (k) | Intrinsic material property (W/m·K) | High (120-490 W/m·K), enabling efficient heat transfer |
| Thermal Resistance (Rth) | Component-level property (°C/W) | Depends on geometry and interfaces; SiC allows for low Rth designs |
| Primary Advantage | Superior heat dissipation and high-temperature stability | Ideal for power electronics and harsh environments |
Optimize your thermal management with KINTEK's advanced lab equipment and consumables.
Leverage Silicon Carbide's exceptional thermal conductivity in your high-power or high-temperature applications. Whether you're developing next-generation power electronics or need reliable performance in extreme conditions, KINTEK provides the precision tools and expertise to help you design systems that are more efficient, compact, and reliable.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your project's thermal performance and overall success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere
- What are the uses of silicon carbide rod? The Ultimate Heating Solution for Extreme Temperatures



















