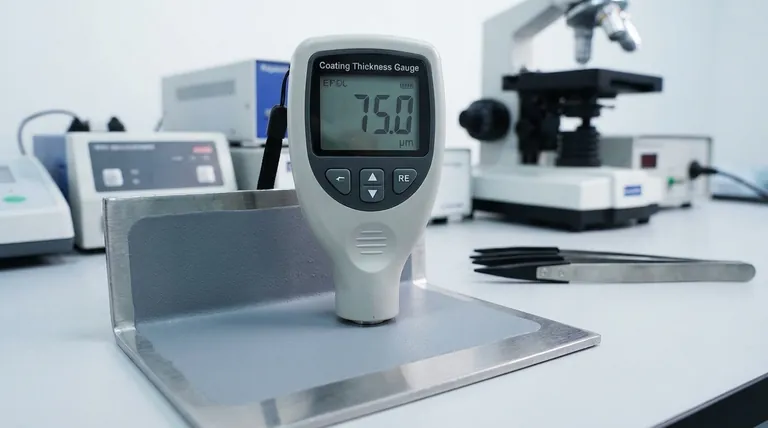
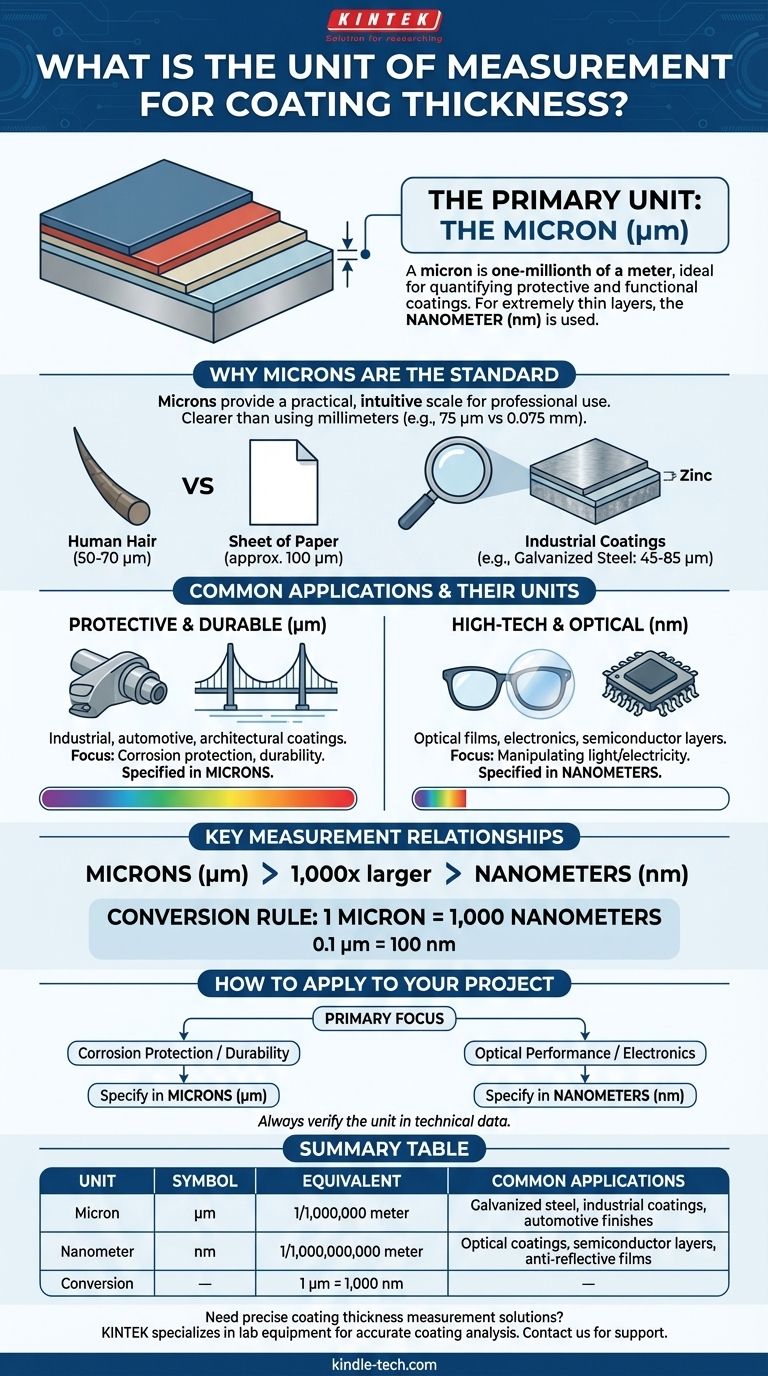
The primary unit of measurement for coating thickness is the micron. A micron, also known as a micrometer (μm), is one-millionth of a meter, making it ideal for quantifying the microscopic scale of most protective and functional coatings. For the extremely thin layers found in optics or electronics, the even smaller nanometer (nm) is also commonly used.
The choice of unit—microns or nanometers—is driven by the need for a practical way to express the microscopic dimensions of a coating. Using standard units like millimeters would result in impractical decimals, obscuring the precision required in engineering and quality control.

Why Microns Are the Standard
To understand why microns are the default unit for coatings, we must first appreciate the scale at which these layers are applied. Coatings are engineered to be incredibly thin yet highly effective.
Putting the Scale into Perspective
A micron (μm) is exceptionally small. To give this context, a typical human hair is between 50 and 70 microns thick. A sheet of office paper is about 100 microns.
Most industrial coatings, such as the zinc layer on galvanized steel, fall squarely within this range. This makes the micron a perfectly scaled and intuitive unit for professionals.
The Language of Engineering Precision
Using microns provides a clear, whole-number language for specifications. Communicating a coating thickness as "75 microns" is far more direct and less prone to error than its equivalent, "0.075 millimeters."
In manufacturing and quality assurance, where tiny deviations can lead to product failure, this clarity is non-negotiable.
Common Applications and Their Units
The specific unit used often depends on the industry and the coating's function.
For robust, protective layers like galvanized coatings, thickness is almost always specified in microns. A typical range might be 45 to 85 μm.
For advanced thin-film applications, such as anti-reflective layers on eyeglass lenses or coatings on semiconductor chips, the dimensions are even smaller. In these cases, the nanometer (nm) is the preferred unit.
Key Measurement Relationships
Understanding the relationship between these microscopic units is crucial for interpreting technical specifications correctly. The hierarchy is simple and based on factors of one thousand.
Microns (μm)
The micron is the workhorse unit for most industrial, automotive, and architectural coatings. It provides the right balance of precision and simplicity for layers designed for durability and protection.
Nanometers (nm)
A nanometer is one-thousandth of a micron. This unit is reserved for high-technology applications where coatings can be just a few atoms thick and are designed to manipulate light or electricity.
The Conversion Rule
The conversion is straightforward: 1 micron = 1,000 nanometers. A 0.1 μm coating is the same as a 100 nm coating. Using the correct unit for the application prevents confusion and highlights the level of precision involved.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing and specifying the correct unit is the first step toward ensuring a product meets its performance requirements. Your application dictates the necessary precision.
- If your primary focus is corrosion protection or durability: Specify thickness in microns (μm), as this is the clear and established standard for protective industrial coatings.
- If your primary focus is optical performance or electronics: Specify thickness in nanometers (nm) to reflect the extreme precision required for thin-film applications.
- When reviewing technical data: Always verify the unit being used (μm or nm) to accurately understand the coating's properties and ensure it aligns with your project's needs.
Using the correct unit of measurement is the foundation for achieving precise, reliable, and effective coating performance.
Summary Table:
| Unit | Symbol | Equivalent | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Micron | μm | 1/1,000,000 meter | Galvanized steel, industrial coatings, automotive finishes |
| Nanometer | nm | 1/1,000,000,000 meter | Optical coatings, semiconductor layers, anti-reflective films |
| Conversion | — | 1 μm = 1,000 nm | — |
Need precise coating thickness measurement solutions for your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for accurate coating analysis. Our instruments help ensure your coatings meet exact specifications—whether you're working with protective industrial layers measured in microns or advanced thin-films measured in nanometers. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your coating quality control and research needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
- Shaking Incubators for Diverse Laboratory Applications
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why are Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) molds preferred for UV-cured siloxane films? Ensure Damage-Free Sample Release
- Why are PTFE beakers required for hafnium metal ICP-OES validation? Ensure Pure Sample Dissolution
- What is the function of PTFE O-rings in cellulose acid hydrolysis? Ensure Leak-Proof Reactor Sealing at 250°C
- How are PTFE gaskets utilized for POEGMA electrolyte conductivity? Ensure Precision in Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the advantages of using PTFE jars for RuTi alloy mixing? Ensure Chemical Purity and High Yield



















