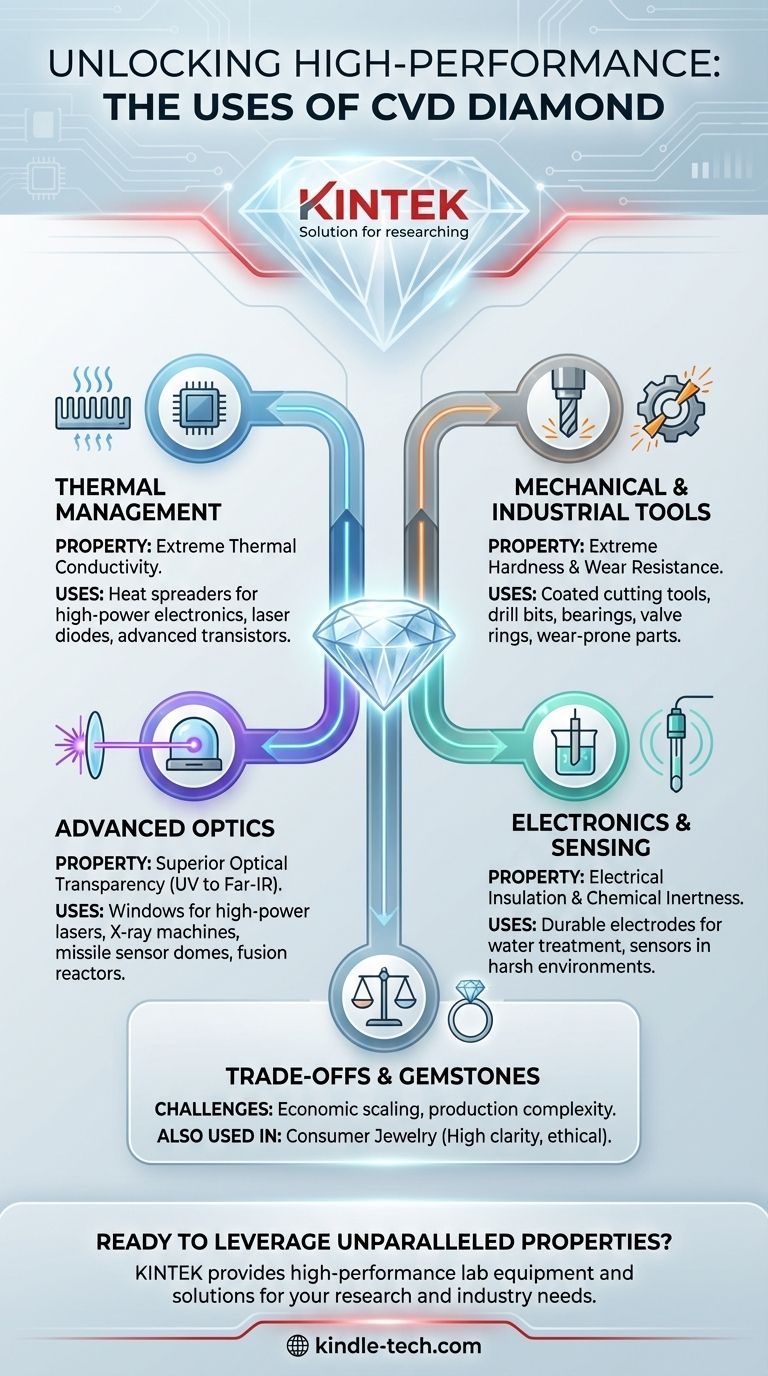
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) diamond is used as a high-performance engineering material in applications where extreme thermal, mechanical, or optical properties are required. Its uses range from industrial cutting tools and heat sinks for high-power electronics to specialized optical windows for lasers and missile systems, in addition to its more widely known application in consumer jewelry.
While often associated with gemstones, the true significance of CVD diamond is its role as a synthetic material that provides the unparalleled properties of natural diamond in an engineered, scalable form. This enables performance in thermal management, mechanical tooling, and advanced optics that is simply unattainable with other materials.
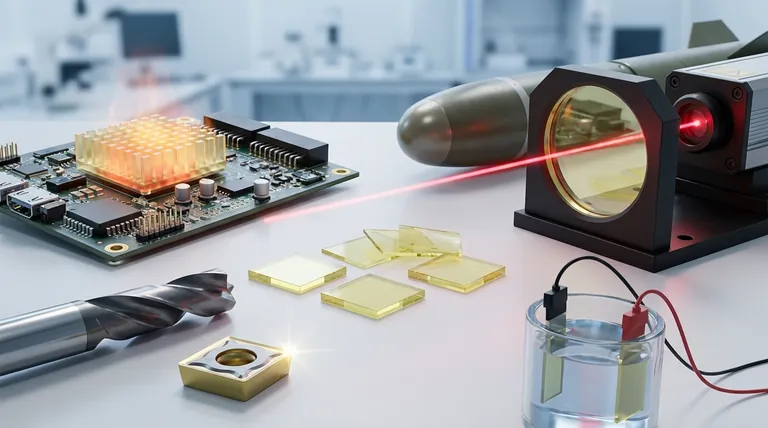
The Foundation: Why CVD Diamond is an Exceptional Material
The versatility of CVD diamond stems from a unique combination of physical properties that mirror, and in some cases can be tailored to exceed, those of the highest-quality natural diamonds. Understanding these properties is key to understanding its applications.
Unmatched Thermal Conductivity
CVD diamond is one of the best thermal conductors known to man, far surpassing copper. This makes it an invaluable material for rapidly dissipating heat.
It is used as a heat spreader or heat sink for high-power density electronics, laser diodes, and advanced transistors, preventing them from overheating and failing.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
With a hardness identical to natural diamond, CVD diamond is exceptionally resistant to abrasion and wear.
This property is leveraged by coating cutting tools, drill bits, and other wear-prone industrial parts with a thin diamond film. This dramatically extends the tool's lifespan and allows for the machining of very hard materials.
Superior Optical Transparency
CVD diamond is transparent across an exceptionally broad range of the electromagnetic spectrum, from deep ultraviolet to far-infrared and even microwaves.
This makes it the ideal material for protective windows and lenses in demanding environments, such as those for high-power lasers, X-ray machines, and the sensor domes on missiles.
Electrical and Chemical Properties
CVD diamond is an excellent electrical insulator and is chemically inert, meaning it does not react with most corrosive chemicals.
These properties are critical for applications in electrochemistry, such as creating durable electrodes for water treatment and purification systems, and for sensors operating in harsh environments.
Key Application Categories
The properties of CVD diamond directly translate into its primary uses across several high-tech fields. It is a problem-solving material chosen when performance is the top priority.
Thermal Management and Electronics
In modern electronics, managing heat is a primary limiting factor. CVD diamond provides a solution.
It is engineered into substrates for semiconductor devices and as heat spreaders in high-frequency radio and optical communication equipment, enabling them to run at higher power levels.
Mechanical and Industrial Tools
The ability to apply a super-hard coating to a less durable substrate is a major industrial application.
CVD diamond films are grown on valve rings, bearings, and non-stick surfaces. The goal is to create a component with a dramatically reduced wear rate and a low coefficient of friction.
Advanced Optics
For optical systems operating under extreme conditions, no other material can match CVD diamond's combination of durability and transparency.
It is used to create robust windows for nuclear fusion reactors (ITER), military sensor systems, and high-power industrial lasers where other optical materials would be damaged by heat or radiation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, CVD diamond is not a universal solution. Its adoption is governed by a balance of performance requirements and economic viability.
The Challenge of Economic Scaling
The primary barrier to wider adoption is often cost and manufacturing scale. The CVD process is highly technical and energy-intensive.
While ideal for non-stick cookware due to its hardness and low friction, coating large consumer items economically remains a significant challenge. Its use is typically reserved for applications where the performance benefit justifies the premium cost.
Production Complexity and Quality Control
Creating a flawless, gem-quality diamond is different from producing a large, uniform film for an optical window. Each application has specific requirements for purity, grain size, and thickness.
Achieving the precise properties needed for a specific technical application requires sophisticated control over the deposition process. Post-processing, such as High-Pressure/High-Temperature (HPHT) treatment, can be used to further refine the diamond's properties, particularly for gem applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use CVD diamond should be driven by a specific, demanding performance goal.
- If your primary focus is thermal management: Use CVD diamond as a superior heat spreader for high-power density electronics and laser optics.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability: Apply CVD diamond coatings to cutting tools and wear surfaces to dramatically extend their operational life.
- If your primary focus is advanced optical systems: Specify CVD diamond for windows and lenses that must perform under extreme conditions or across wide spectral ranges.
- If your primary focus is acquiring gemstones: Consider CVD diamond for its high clarity, ethical production, and more competitive pricing.
Ultimately, understanding CVD diamond's properties is the key to leveraging it as a powerful problem-solving material in engineering and science.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Property Utilized | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Management | Extreme Thermal Conductivity | Heat spreaders for high-power electronics, laser diodes |
| Industrial Tools | Extreme Hardness & Wear Resistance | Coated cutting tools, drill bits, wear-prone parts |
| Advanced Optics | Broad Optical Transparency | Windows for high-power lasers, X-ray machines, sensor domes |
| Electronics & Sensing | Excellent Electrical Insulation & Chemical Inertness | Electrodes for water treatment, sensors in harsh environments |
Ready to leverage CVD diamond's unparalleled properties in your lab or production line?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to meet the demanding needs of modern research and industry. Whether you're developing next-generation electronics, advanced optical systems, or durable industrial tools, our expertise can help you integrate cutting-edge materials like CVD diamond for superior results.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your thermal management, mechanical durability, and optical performance. Let's solve your toughest engineering challenges together!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the process of lab created diamonds? A Clear Guide to HPHT & CVD Methods
- What is the future of CVD diamond? Unlocking Next-Gen Electronics & Thermal Management
- What is the fluorescence of a CVD diamond? A Guide to Its Unique Glow and Purpose
- What is the future value of lab grown diamond? Understanding Its Depreciating Financial Worth
- What are the common sources of contamination during CVD diamond growth? Improve Purity and Quality Control














