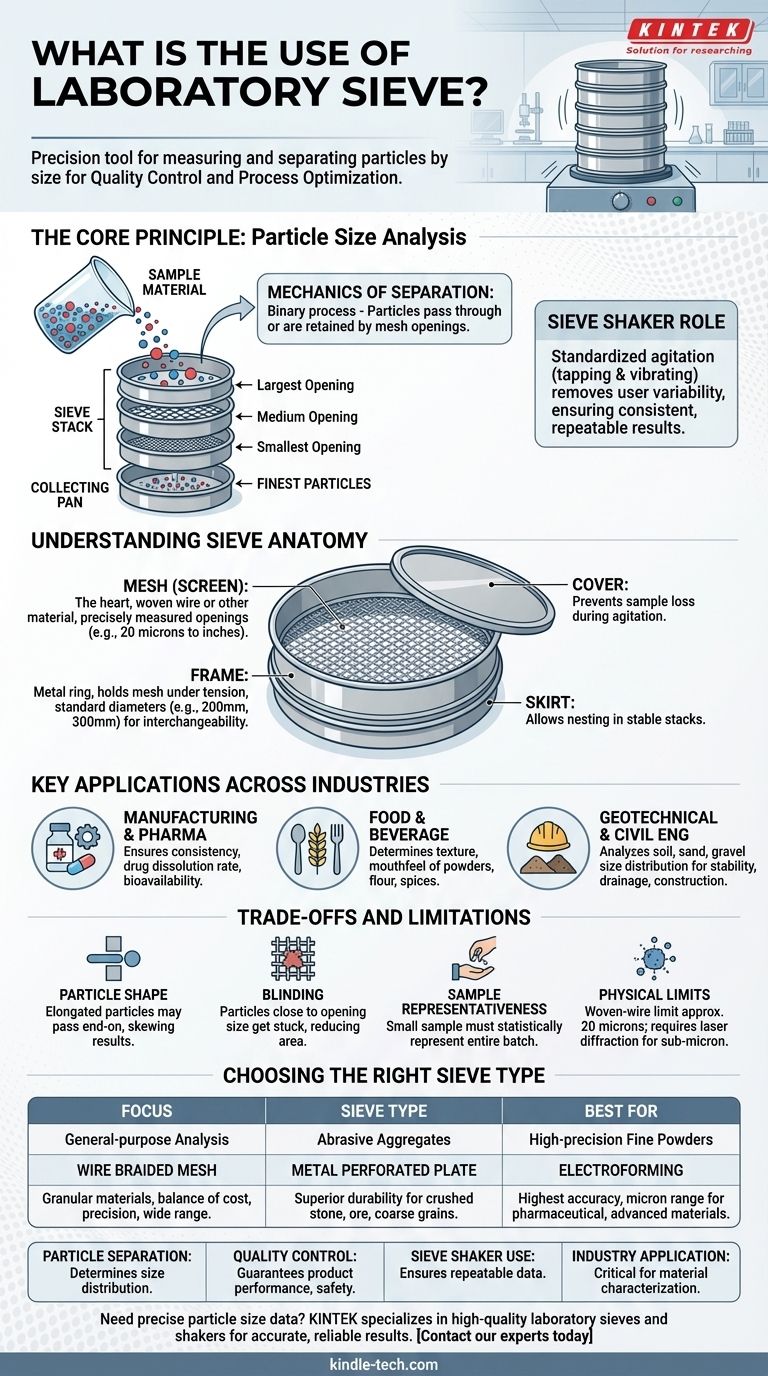
In essence, a laboratory sieve is a precision tool used to measure and separate particles by size. Its primary function is to perform particle size analysis, ensuring materials like powders, aggregates, and grains meet the specific quality and consistency standards required for research, development, and industrial production.
The true value of a laboratory sieve isn't just sorting particles; it's about providing the quantitative data needed for quality control and process optimization. By ensuring consistent particle size, you guarantee the final product's performance, safety, and reliability.

The Core Principle: How Sieves Analyze Particle Size
A laboratory sieve operates on a straightforward mechanical principle, but its application is critical for obtaining precise, repeatable results.
The Mechanics of Separation
The fundamental process involves passing a sample of material through a screen with uniform, precisely measured openings. Particles smaller than the openings pass through, while particles larger than the openings are retained on the mesh surface.
This binary separation—pass or retain—is the building block of all particle size analysis performed with sieves.
Single Sieve vs. Sieve Stacks
A single sieve can be used to quickly check if a material is above or below a certain size threshold. This is common for simple quality checks.
For a detailed analysis, multiple sieves are stacked in ascending order of opening size, from the largest at the top to the smallest at the bottom, with a solid pan at the base. This "sieve stack" allows you to separate a single sample into multiple size fractions simultaneously.
The Role of a Sieve Shaker
To ensure consistency and accuracy, the sieve stack is typically placed in a sieve shaker. This device imparts a standardized agitation—often a combination of tapping and vibrating motion—to the stack.
The mechanical shaker guarantees that every particle is given the opportunity to pass through the apertures, removing user-to-user variability and providing a repeatable, scientific result.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Test Sieve
While simple in concept, a test sieve is a precision instrument made of specific components that ensure its accuracy and durability.
The Mesh (Screen)
The mesh is the heart of the sieve and its most technical component. It is typically a woven wire mesh made of stainless steel, though other types exist.
The size of the openings is rigorously controlled and can range from several inches down to just 20 microns (0.020 mm).
The Frame
The frame is the circular metal ring that holds the mesh under tension. Frames are manufactured to standard diameters, most commonly 200mm and 300mm (or 8 and 12 inches in the U.S.), to ensure they are interchangeable and fit standard sieve shakers.
The Skirt and Cover
The skirt is the bottom edge of the frame, designed to allow sieves to nest together in a stable stack without tipping. A cover is placed on the top sieve to prevent any loss of sample material during agitation.
Key Applications Across Industries
Particle size is a critical physical property that impacts material behavior. Because of this, sieve analysis is a cornerstone of quality control in numerous fields.
Quality Control in Manufacturing
In the pharmaceutical industry, particle size can affect a drug's dissolution rate and bioavailability. In the food industry, it determines the texture and mouthfeel of products like flour and spices. Sieves provide the essential check for consistency.
Research and Development
When developing new powdered metals, polymers, or chemical compounds, R&D labs use sieves to characterize new materials and understand how particle size influences performance.
Geotechnical and Civil Engineering
Sieve analysis is used to determine the particle size distribution of soils, sands, and gravels. This data is essential for assessing soil stability, drainage, and suitability for use as a construction aggregate in concrete or asphalt.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sieve analysis is not without its limitations. Understanding these is key to interpreting results correctly.
Particle Shape vs. Sieve Opening
Sieving fundamentally measures a particle's second-smallest dimension. Elongated or flat particles may pass through an opening end-on or diagonally, even if their longest dimension is larger than the aperture. This can skew results for non-spherical materials.
The Risk of Clogging (Blinding)
Particles that are very close in size to the mesh openings can become lodged in the apertures. This phenomenon, known as blinding, reduces the available sieving area and can lead to inaccurate separation if not addressed.
Sample Representativeness
Sieve analysis uses a relatively small sample size. For the results to be meaningful, the sample taken for testing must be statistically representative of the entire batch of material. Poor sampling technique is a common source of error.
Physical Limitations
Woven-wire sieves have a practical lower limit of around 20 microns. For analyzing sub-micron particles (nanoparticles), other methods such as laser diffraction or dynamic light scattering are required.
Choosing the Right Sieve Type
The material of the mesh itself dictates the sieve's primary application.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose analysis of granular materials: Wire Braided Mesh sieves offer the best balance of cost, precision, and a wide range of available sizes.
- If your primary focus is sizing larger, more abrasive aggregates: Metal Perforated Plate sieves provide superior durability for materials like crushed stone, ore, or coarse grains.
- If your primary focus is high-precision analysis of very fine powders: Electroforming sieves deliver the highest accuracy for particles in the micron range, essential for pharmaceutical or advanced material applications.
Ultimately, mastering sieve analysis empowers you to control the fundamental properties of your material, ensuring predictable and reliable outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Separation | Separates materials by size using a precision mesh. | Determines particle size distribution for analysis. |
| Quality Control | Ensures materials meet specific size standards. | Guarantees product performance, safety, and reliability. |
| Sieve Shaker Use | Provides standardized agitation for consistent results. | Eliminates user variability and ensures repeatable data. |
| Industry Application | Used in pharmaceuticals, food, construction, and R&D. | Critical for material characterization and process optimization. |
Need precise particle size data for your materials? KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory sieves and sieve shakers designed for accuracy and durability. Whether you're in pharmaceuticals, food production, or materials science, our equipment helps you achieve reliable quality control and optimize your processes. Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy



















