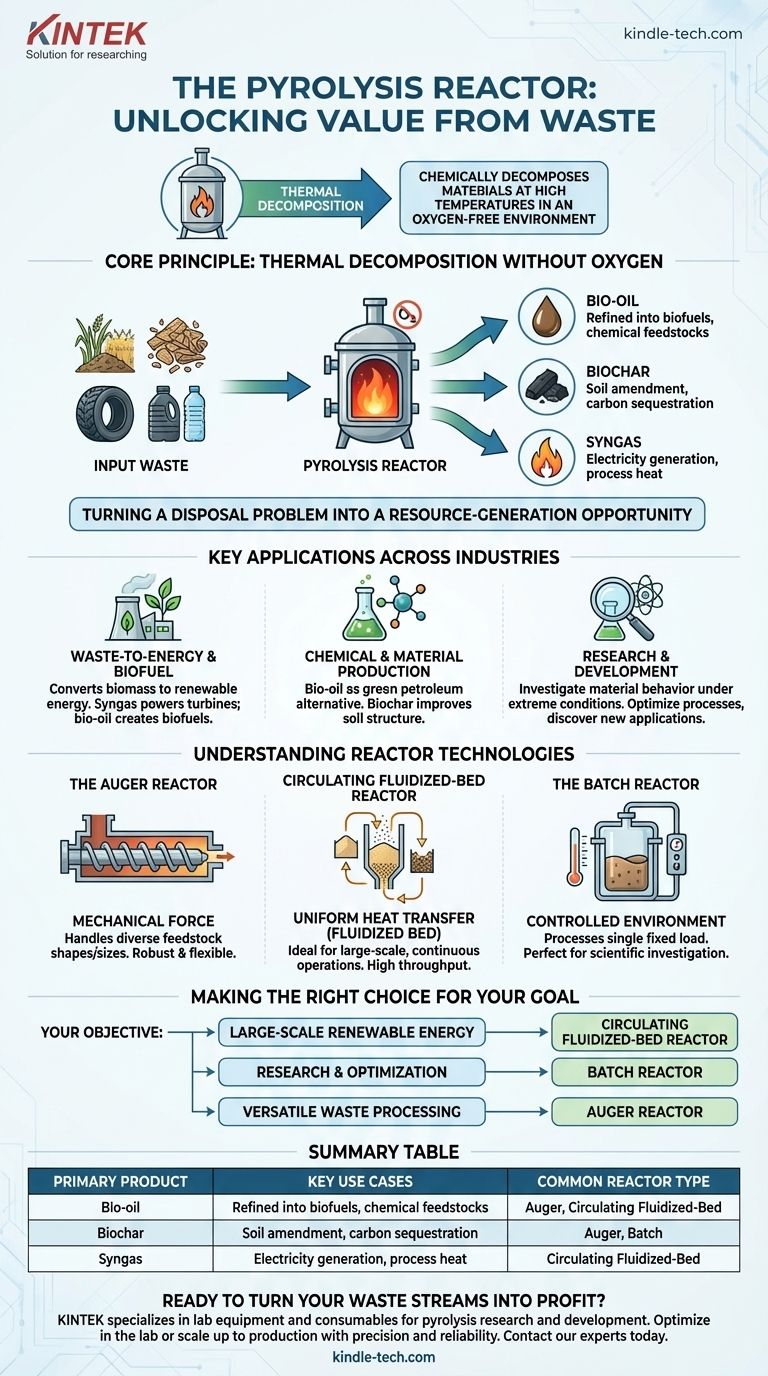
At its core, a pyrolysis reactor is a specialized furnace that chemically decomposes materials at high temperatures in an oxygen-free environment. This process, known as pyrolysis, is not about burning; it's about thermal transformation. It is used across various industries to convert low-value inputs like waste biomass, plastics, and tires into valuable products, including biofuels, chemicals, and energy.
The fundamental use of a pyrolysis reactor is to unlock the value hidden within waste materials. Instead of incineration, it breaks down organic matter to create a portfolio of valuable outputs: bio-oil, biochar, and syngas, turning a disposal problem into a resource-generation opportunity.

The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
A pyrolysis reactor's function is fundamentally different from that of an incinerator. By eliminating oxygen, it prevents combustion and instead triggers a series of chemical changes that break down complex materials into simpler, more valuable substances.
From Input Waste to Valuable Output
The process begins with a feedstock, which is typically organic material. Common inputs include agricultural waste, wood chips, used tires, or plastics.
Inside the reactor, this material is heated to extreme temperatures, causing it to decompose into three primary products:
- Bio-oil: A liquid that can be refined into transportation fuels or used as a feedstock for chemical production.
- Biochar: A stable, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal. It is highly effective as a soil amendment to improve fertility and sequester carbon.
- Syngas: A mixture of combustible gases (primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide) that can be used to generate electricity or heat.
Key Applications Across Industries
The ability to create these three distinct products makes the pyrolysis reactor a versatile tool used in waste management, energy production, and chemical manufacturing.
Waste-to-Energy and Biofuel Production
This is the most prominent application. Pyrolysis reactors are central to converting waste biomass into renewable energy, directly contributing to a reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
Circulating pyrolysis reactors, for example, are used extensively for large-scale electricity generation by using the syngas output to power turbines. The bio-oil produced can also be further processed into sustainable biofuels.
Chemical and Material Production
The outputs of pyrolysis are not just for energy. Bio-oil serves as a renewable "green" alternative to petroleum in the manufacturing of certain chemicals and materials.
Biochar is another key product with significant commercial and environmental value. Its application in agriculture improves soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability.
Research and Development
In laboratory settings, pyrolysis reactors are essential for studying how materials behave under extreme conditions.
Batch reactors, for instance, are specifically used to investigate the energy stability and reaction kinetics of pyrolytic processes. This research helps optimize industrial-scale operations and discover new applications.
Understanding the Reactor Technologies
The term "pyrolysis reactor" encompasses several designs, each optimized for different feedstocks, scales, and goals. The choice of reactor technology directly impacts efficiency and output.
The Auger Reactor
This design uses a large screw mechanism to move material through a heated chamber. It relies on mechanical force and direct contact for heat transfer.
Auger reactors are robust and can handle a variety of feedstock shapes and sizes, making them a flexible option for diverse waste streams.
The Circulating Fluidized-Bed Reactor
In this advanced system, heat is distributed uniformly by circulating hot, sand-like material alongside the feedstock. This creates a "fluidized bed" that ensures extremely efficient heat transfer.
This technology is ideal for large-scale, continuous operations where consistent output and high throughput are required, such as in dedicated power plants.
The Batch Reactor
A batch reactor processes a single, fixed load of material at a time. The chamber is sealed, heated, and then cooled before the products are removed.
While not suited for continuous production, its controlled environment makes it perfect for scientific investigation and small-scale, specialized applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal pyrolysis technology depends entirely on your end objective. Understanding your primary goal is the first step toward selecting the right system.
- If your primary focus is large-scale renewable energy: A circulating fluidized-bed reactor offers the efficiency and continuous throughput needed for consistent electricity generation.
- If your primary focus is research and process optimization: A batch reactor provides the precise control necessary to study material decomposition and reaction chemistry.
- If your primary focus is versatile waste processing: An auger reactor's ability to handle diverse feedstocks makes it a strong candidate for converting mixed waste into valuable products.
Ultimately, the pyrolysis reactor is a key enabling technology for the circular economy, transforming our perspective on waste from a liability into a valuable resource.
Summary Table:
| Primary Product | Key Use Cases | Common Reactor Type |
|---|---|---|
| Bio-oil | Refined into biofuels, chemical feedstocks | Auger, Circulating Fluidized-Bed |
| Biochar | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration | Auger, Batch |
| Syngas | Electricity generation, process heat | Circulating Fluidized-Bed |
Ready to turn your waste streams into profit? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're optimizing a process in the lab or scaling up to production, our reactors and analytical tools provide the precision and reliability you need. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your pyrolysis projects and help you unlock the value in your materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- How to design a bioreactor? A Guide to Creating the Perfect Environment for Your Cells
- How does a dual-layer design overcome ceramic limitations in SCWG reactors? Engineering High-Pressure Solutions
- What is the core function of a high-pressure static autoclave in PWR simulation? Precise Material Validation
- What advantages does a high-pressure hydrothermal reactor provide for hydroxyapatite synthesis? Boost Catalyst Performance
- Why is it necessary to use a stainless steel reactor for the alkaline hydrolysis of PV backsheets? Ensure Safety and Purity
- Why is a 100 ml quartz reactor chosen for photocatalysis? Maximize Light Transmission and Chemical Integrity
- What role does a high-pressure reactor play in the SCWO of PCBs? Ensure Total Destruction of Organic Pollutants
- What conditions must a laboratory reactor provide for alloy stress corrosion? Master the Occluded Zone with Precision



















