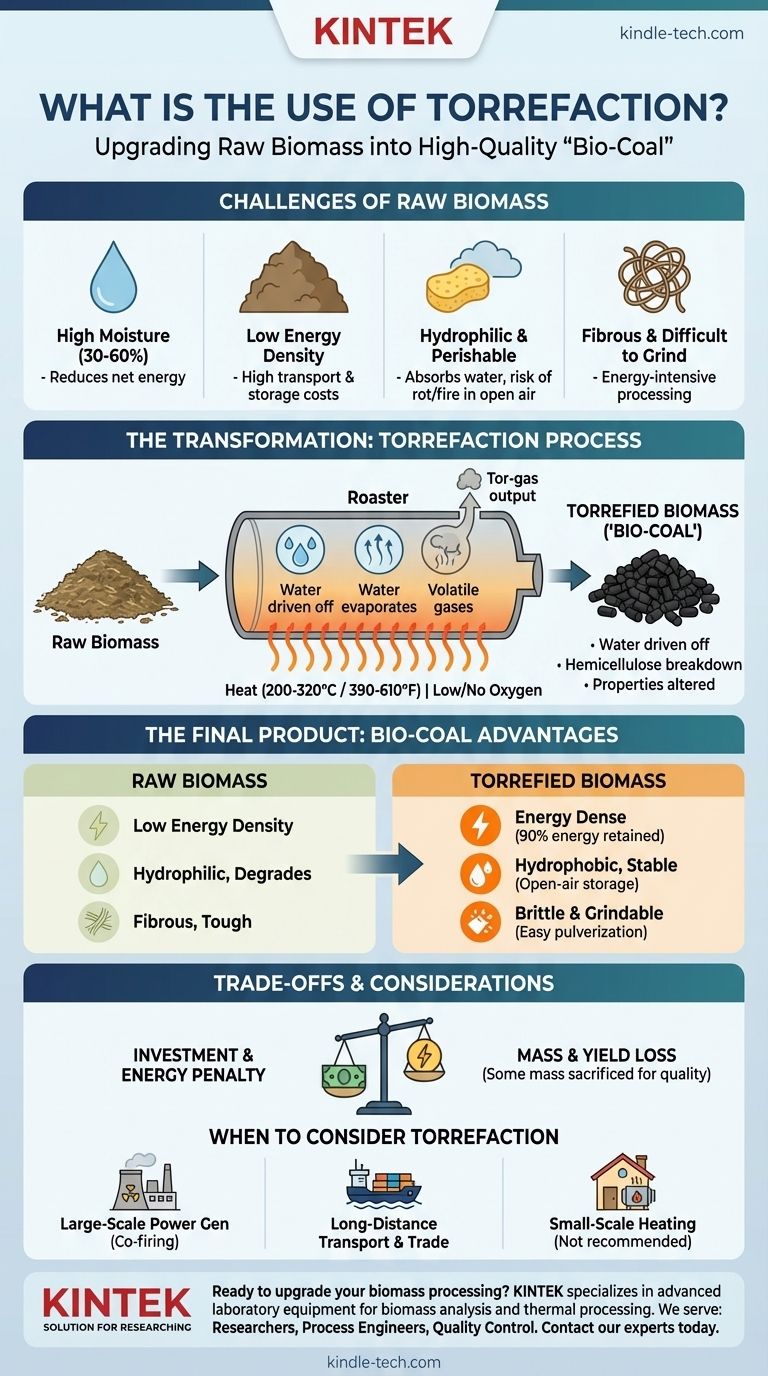
In essence, the primary use of torrefaction is to upgrade raw biomass into a high-quality, energy-dense solid biofuel that behaves much like fossil coal. This thermal enhancement process removes water and low-energy volatile compounds, transforming bulky, inconsistent materials like wood chips or agricultural waste into a stable, grindable, and water-resistant product often called "bio-coal."
Torrefaction is not about creating energy, but about solving the fundamental logistical problems of biomass. It transforms a bulky, wet, and perishable resource into a stable, energy-dense fuel commodity that can integrate seamlessly with existing industrial infrastructure.

Why Torrefaction is Necessary: The Challenges of Raw Biomass
To understand the value of torrefaction, we must first recognize the inherent drawbacks of using raw biomass as an industrial-scale fuel source.
High Moisture Content
Raw biomass can contain anywhere from 30% to 60% water. This moisture must be boiled off before the material can release its energy, significantly reducing the net energy output and overall process efficiency.
Low Energy Density
Biomass is bulky and light. This means large volumes must be transported and stored to get a meaningful amount of energy, leading to high transportation costs and extensive storage requirements.
Hydrophilic (Water-Absorbing) Nature
Raw biomass readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. This makes open-air storage impossible, as it leads to biological degradation, rot, and potential self-heating, posing a significant fire risk.
Fibrous and Tenacious Structure
The tough, stringy nature of raw biomass makes it very difficult and energy-intensive to grind into the fine powder required by industrial boilers, such as those found in coal-fired power plants.
The Transformation: How Torrefaction Improves Biomass
Torrefaction is a mild form of pyrolysis, a thermochemical treatment that directly addresses the challenges listed above.
The "Roasting" Environment
The process involves heating biomass to between 200°C and 320°C (390°F to 610°F) in an environment with very little or no oxygen. The absence of oxygen is critical; it prevents the biomass from combusting and ensures it breaks down in a controlled manner.
Key Chemical and Physical Changes
During this process, the water is driven off completely. More importantly, the hemicellulose in the plant's cell walls breaks down, releasing volatile organic compounds. This decomposition fundamentally alters the material's properties.
The Final Product: "Bio-Coal"
The resulting torrefied biomass is a superior fuel with distinct advantages:
- Energy Dense: It loses up to 30% of its mass but retains up to 90% of its original energy, drastically increasing its energy density.
- Hydrophobic: It repels water, allowing for open-air storage similar to coal, which dramatically cuts storage costs and complexity.
- Brittle and Grindable: The breakdown of fibrous structures makes the material easy to crush and pulverize with significantly less energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Torrefaction is a powerful upgrading tool, but it is not without its costs and considerations. Being objective requires acknowledging these factors.
Energy Input vs. Output
The process itself consumes energy to heat the biomass. Efficient plant designs capture and burn the released volatile gases (tor-gas) to power the process, but there is always an energy penalty. The net energy gain must justify the investment.
Capital Investment
Torrefaction facilities require significant upfront capital expenditure. This cost must be factored into the economic viability of using the resulting bio-coal as a fuel source.
Mass and Yield Loss
While energy density increases, the absolute mass of the material decreases. This means a portion of the initial biomass is "lost" as gas. This is a calculated trade-off, sacrificing some mass to gain superior handling and fuel properties.
When to Consider Torrefaction
The decision to use torrefaction hinges entirely on the specific application and logistical chain for the biomass.
- If your primary focus is large-scale power generation: Torrefaction is a critical enabling technology for co-firing biomass in existing coal plants, as the material handles and grinds like coal.
- If your primary focus is long-distance transport and trade: The dramatic increase in energy density and simplified storage makes torrefied biomass economically viable to ship across oceans.
- If your primary focus is small-scale, local heating: The added cost and complexity of torrefaction are likely unnecessary, as raw biomass can often be used directly in compatible local boilers.
Ultimately, torrefaction acts as a critical bridge, allowing inconsistent, low-grade biomass to become a reliable, high-value feedstock for the global energy market.
Summary Table:
| Property | Raw Biomass | Torrefied Biomass ('Bio-Coal') |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Low | High (up to 90% energy retained) |
| Moisture & Storage | High moisture, degrades in open air | Hydrophobic, stable for open-air storage |
| Grindability | Fibrous, difficult to grind | Brittle, easy to pulverize |
| Primary Use Case | Local, small-scale heating | Large-scale power generation, long-distance transport |
Ready to upgrade your biomass processing?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment for biomass analysis and thermal processing research. Whether you are developing torrefaction processes, analyzing bio-coal properties, or scaling up your technology, our precision tools provide the reliability and data integrity you need.
We serve:
- Researchers and R&D teams in bioenergy
- Process engineers scaling up torrefaction systems
- Quality control labs ensuring fuel specifications
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can accelerate your biofuel development and ensure your process is efficient and effective.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products



















